Federal Home Loan Bank (FHLB) System
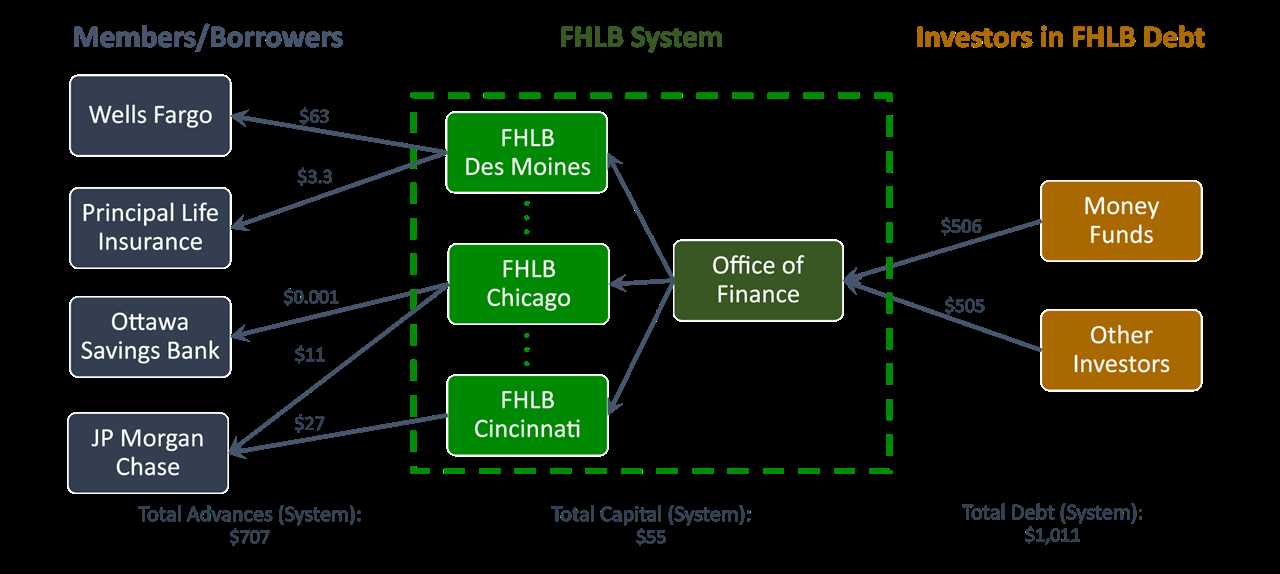
The Federal Home Loan Bank (FHLB) System is a government-sponsored entity that was established in 1932 to provide liquidity and stability to the mortgage market. It is a network of 11 regional banks that serve as a reliable source of funding for member financial institutions, such as commercial banks, credit unions, and insurance companies.
The FHLB System operates under the supervision of the Federal Housing Finance Agency (FHFA) and is regulated by the Federal Home Loan Bank Act. Its primary purpose is to promote homeownership and affordable housing by providing low-cost funding to its members, who in turn use the funds to make mortgage loans to individuals and businesses.
In addition to providing funding, the FHLB System offers a range of other services to its members. These include correspondent banking services, such as check clearing and wire transfers, as well as various financial products and tools to help members manage their interest rate and liquidity risks.
The FHLB System plays a crucial role in the mortgage industry by ensuring the availability of affordable mortgage credit. By providing a stable source of funding to its members, it helps to keep mortgage rates low and promotes the efficient functioning of the housing finance market. This, in turn, supports economic growth and stability.
| Key Features of the FHLB System |
|---|
| Government-sponsored entity |
| Network of 11 regional banks |
| Provides low-cost funding to member financial institutions |
| Issues Consolidated Obligations to raise funds |
| Offers correspondent banking services |
| Provides financial products and tools to manage risks |
| Promotes homeownership and affordable housing |
| Supports economic growth and stability |
Definition and Purpose
The Federal Home Loan Bank (FHLB) System is a government-sponsored enterprise that was established in 1932 during the Great Depression. Its purpose is to provide a stable and reliable source of funding for member financial institutions, primarily for the purpose of promoting homeownership and affordable housing.
The FHLB System consists of 11 regional banks located throughout the United States. These banks serve as wholesale lenders to their member institutions, which include commercial banks, credit unions, savings institutions, and insurance companies. The FHLB System operates as a cooperative, with its member institutions owning and controlling the system.
Membership and Benefits
To become a member of the FHLB System, financial institutions must meet certain eligibility requirements, including being regulated by a federal or state agency and having a primary mission of providing housing finance. Once admitted, members gain access to a variety of benefits.
One of the main benefits of FHLB membership is access to low-cost funding through the issuance of consolidated obligations, which are debt securities backed by the combined resources of the FHLB System. These funds can be used by member institutions to provide affordable mortgage loans to individuals and families, thereby promoting homeownership and economic stability.
In addition to funding, FHLB members also have access to a range of other services and products. These include correspondent banking services, which allow members to efficiently process payments and manage liquidity, as well as community investment programs that support affordable housing initiatives and economic development in local communities.
Regulation and Oversight
The FHLB System is subject to regulation and oversight by several federal agencies, including the Federal Housing Finance Agency (FHFA) and the Office of Finance. These agencies ensure that the FHLB System operates in a safe and sound manner and fulfills its mission of promoting housing finance and affordable homeownership.
The FHFA, in particular, plays a key role in overseeing the FHLB System. It sets capital requirements, conducts regular examinations, and approves major business activities. The Office of Finance, on the other hand, is responsible for the issuance and servicing of consolidated obligations on behalf of the FHLB System.
Overall, the FHLB System plays a crucial role in the mortgage industry by providing member institutions with access to affordable funding and other resources. This, in turn, helps to ensure the availability of affordable mortgage loans for individuals and families, thereby supporting homeownership and economic growth.
History of the Federal Home Loan Bank (FHLB) System
The Federal Home Loan Bank (FHLB) System has a rich history that dates back to the early 20th century. It was established in 1932 as a response to the Great Depression, with the goal of providing a stable source of funding for mortgage lenders.
During the Great Depression, many banks and financial institutions faced significant challenges, and the housing market was in turmoil. The FHLB System was created to address these issues and stimulate the housing market by providing low-cost loans to member banks and other financial institutions.
Over the years, the FHLB System has evolved and expanded its role in the mortgage industry. In 1989, the Financial Institutions Reform, Recovery, and Enforcement Act (FIRREA) restructured the FHLB System and introduced significant changes to its operations.
Under FIRREA, the FHLB System was required to provide more support to affordable housing initiatives and community development projects. This led to the creation of the Affordable Housing Program (AHP), which provides grants and subsidies to member institutions for the development of affordable housing.
In addition to supporting affordable housing, the FHLB System also plays a crucial role in providing liquidity to the mortgage market. It does this by offering low-cost loans and other financial services to its member institutions, which in turn use these funds to provide mortgages to homebuyers.
Today, the FHLB System consists of 11 regional banks, serving all 50 states and U.S. territories. These banks continue to provide vital funding and support to the mortgage industry, helping to ensure the availability of affordable housing and promoting economic growth.
Role in the Mortgage Industry
The Federal Home Loan Bank (FHLB) System plays a crucial role in the mortgage industry by providing liquidity and stability to member financial institutions. It serves as a reliable source of funding for mortgage lending, ensuring that banks and other lenders have access to the necessary funds to originate and service mortgage loans.
One of the primary ways in which the FHLB System supports the mortgage industry is through its Mortgage Partnership Finance (MPF) program. This program allows participating financial institutions to sell eligible mortgage loans to the FHLB System, which then provides funding for these loans. By purchasing these loans, the FHLB System helps to increase the liquidity of the mortgage market, allowing lenders to make more loans and expand homeownership opportunities.
Furthermore, the FHLB System plays a role in mitigating risk in the mortgage industry. It serves as a source of stability for member institutions by providing them with access to emergency liquidity in times of financial stress. This helps to ensure the continued operation of these institutions and maintain the stability of the overall mortgage market.
Conclusion

The Federal Home Loan Bank System plays a vital role in the mortgage industry by providing funding, support, and stability to member financial institutions. Through its programs and services, it helps to increase the availability of mortgage loans, promote affordable housing, and mitigate risk. The FHLB System’s contributions are essential for maintaining a healthy and robust mortgage market, which is crucial for the overall economy and the well-being of individuals and communities.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
