Dividend Growth Rate: Definition and Importance
Definition:
The dividend growth rate is a financial metric that measures the annual rate of increase in dividends paid out by a company to its shareholders. It is an important indicator of a company’s financial health and its ability to generate consistent and growing returns for its investors.
Importance:
The dividend growth rate is important for several reasons:
- Investor Income: Dividends are a key source of income for many investors, especially those who rely on their investments for retirement or other financial goals. A higher dividend growth rate indicates that a company is increasing its dividend payments over time, which can lead to higher income for shareholders.
- Financial Stability: A consistent and growing dividend growth rate is often seen as a sign of financial stability and strength. Companies that are able to consistently increase their dividends are typically well-managed and have a solid financial foundation.
- Investor Confidence: A company’s ability to consistently increase its dividends can also instill confidence in investors. A higher dividend growth rate may attract more investors to the stock, leading to increased demand and potentially higher stock prices.
- Long-Term Returns: Studies have shown that companies with a higher dividend growth rate tend to outperform those with lower or no dividend growth over the long term. This is because companies that are able to consistently increase their dividends often have strong cash flows and are able to reinvest in their business for future growth.
What is Dividend Growth Rate?
The dividend growth rate is a financial metric that measures the rate at which a company’s dividend payments to shareholders increase over time. It is an important indicator of a company’s financial health and its ability to generate consistent and growing returns for its shareholders.
Calculation of Dividend Growth Rate
The dividend growth rate can be calculated using the following formula:
This formula calculates the percentage increase in dividend payments over a specific period of time, usually on an annual basis. It compares the dividend payment at the end of the period to the dividend payment at the beginning of the period to determine the growth rate.
Importance of Dividend Growth Rate
The dividend growth rate is an important metric for investors, as it provides insights into a company’s financial performance and its ability to generate consistent returns. A higher dividend growth rate indicates that a company is increasing its dividend payments at a faster pace, which can be a positive sign for investors.
Investors often look for companies with a track record of consistently increasing their dividend payments over time. A higher dividend growth rate can also indicate that a company has a strong and sustainable business model, as it is able to generate increasing profits and cash flows to support higher dividend payments.
Additionally, companies that have a history of increasing their dividends tend to attract income-focused investors who rely on dividend income for their investment returns. A higher dividend growth rate can make a company more attractive to these investors, potentially leading to an increase in demand for its stock and a higher stock price.
Example of Dividend Growth Rate
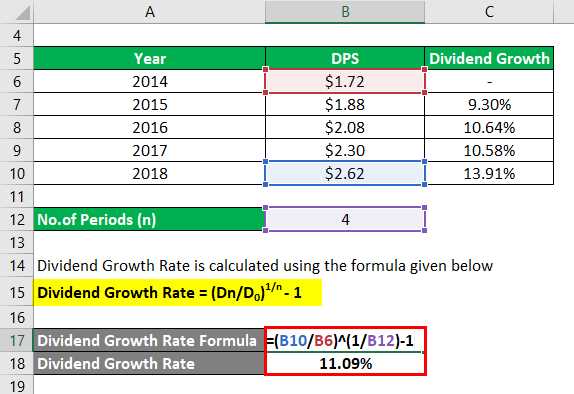
Let’s consider an example to illustrate the calculation of dividend growth rate. Company XYZ paid a dividend of $1 per share at the beginning of the year and increased it to $1.20 per share at the end of the year. Using the formula mentioned earlier, the dividend growth rate would be:
This means that Company XYZ increased its dividend payments by 20% over the course of the year. This growth rate can be compared to other companies in the same industry or the overall market to assess the company’s performance and attractiveness as an investment.
| Year | Dividend per Share |
|---|---|
| 2016 | $1.00 |
| 2017 | $1.20 |
| 2018 | $1.44 |
How to Calculate Dividend Growth Rate
Calculating the dividend growth rate is an important step in analyzing the performance of a company’s dividend payments over time. It provides investors with valuable insights into the company’s ability to increase its dividends and generate consistent returns.
To calculate the dividend growth rate, you need to follow these steps:
Step 1: Gather the necessary information
First, you need to gather the necessary information, including the company’s dividend payments for a specific period, usually a year. This information can be found in the company’s financial statements or dividend history.
Step 2: Determine the initial dividend
Next, determine the initial dividend for the period you are analyzing. This is typically the dividend payment at the beginning of the period.
Step 3: Determine the final dividend
Then, determine the final dividend for the period. This is usually the dividend payment at the end of the period.
Step 4: Calculate the dividend growth rate
Now, you can calculate the dividend growth rate using the following formula:
For example, if a company paid a dividend of $2 at the beginning of the year and increased it to $2.50 at the end of the year, the dividend growth rate would be:
Step 5: Interpret the dividend growth rate
Finally, interpret the dividend growth rate to assess the company’s performance. A higher dividend growth rate indicates that the company is increasing its dividends at a faster pace, which can be a positive sign for investors. On the other hand, a lower or negative growth rate may suggest that the company is facing challenges or is unable to sustain its dividend payments.
By calculating the dividend growth rate, investors can make informed decisions about investing in dividend stocks and assess the potential for future dividend income.
Importance of Dividend Growth Rate
The dividend growth rate is a key metric for investors to consider when evaluating dividend stocks. It provides valuable information about the potential future growth of a company’s dividends and can help investors make informed decisions about their investment portfolio.
1. Predictability of Income
By analyzing the dividend growth rate, investors can assess the predictability of a company’s income stream. A consistently increasing dividend growth rate indicates that the company has a stable and growing business, which can provide a reliable source of income for investors. This predictability is especially important for income-focused investors who rely on dividends for regular cash flow.
2. Long-Term Capital Appreciation
Dividend growth rate is also an indicator of a company’s long-term capital appreciation potential. A company that consistently increases its dividends is likely to have a strong and growing business, which can lead to an increase in the company’s stock price over time. This can result in capital gains for investors in addition to the regular dividend income.
3. Dividend Reinvestment
The dividend growth rate is particularly important for investors who choose to reinvest their dividends. By reinvesting dividends, investors can take advantage of the power of compounding, where the reinvested dividends generate additional income and can lead to significant wealth accumulation over time. A higher dividend growth rate means a higher rate of compounding, which can greatly enhance the total return on investment.
Overall, the dividend growth rate provides valuable insights into a company’s financial health, stability, and potential for future growth. It allows investors to assess the predictability of income, the long-term capital appreciation potential, and the benefits of dividend reinvestment. By considering the dividend growth rate, investors can make more informed decisions and build a well-rounded investment portfolio.
Example of Dividend Growth Rate
Let’s consider a hypothetical company called XYZ Inc. that has been paying dividends to its shareholders for the past five years. We will calculate the dividend growth rate for this company based on the dividend payments over the years.
Step 1: Gather the Data
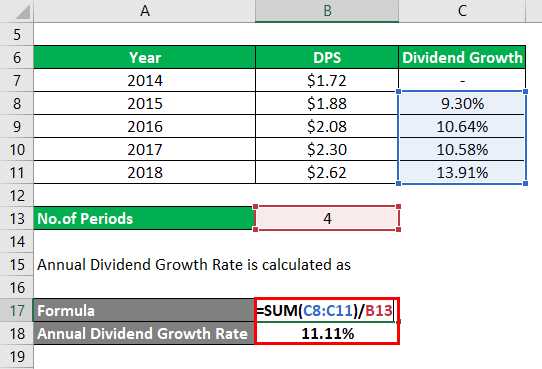
First, we need to gather the dividend payments made by XYZ Inc. for the past five years. Let’s assume the following dividend payments:
- Year 1: $1.00 per share
- Year 2: $1.20 per share
- Year 3: $1.50 per share
- Year 4: $1.80 per share
- Year 5: $2.00 per share
Step 2: Calculate the Dividend Growth Rate
To calculate the dividend growth rate, we will use the following formula:
Using the dividend payments from XYZ Inc., we can calculate the dividend growth rate as follows:
Therefore, the dividend growth rate for XYZ Inc. is 1.00, or 100%.
Step 3: Interpretation
A dividend growth rate of 1.00 indicates that XYZ Inc. has been increasing its dividend payments at a consistent rate of 100% over the past five years. This is a positive sign for investors, as it demonstrates the company’s ability to generate increasing profits and return them to shareholders in the form of dividends.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
