What is the Overnight Rate?
The overnight rate is a key interest rate that determines the cost of borrowing money on a short-term basis. It is the rate at which banks lend funds to each other overnight in the money market. This rate is set by the central bank of a country and serves as a benchmark for other interest rates in the economy.
The overnight rate plays a crucial role in the functioning of the financial system and the overall economy. It affects borrowing costs, influences investment decisions, and has an impact on inflation and economic growth.
How is the Overnight Rate Determined?
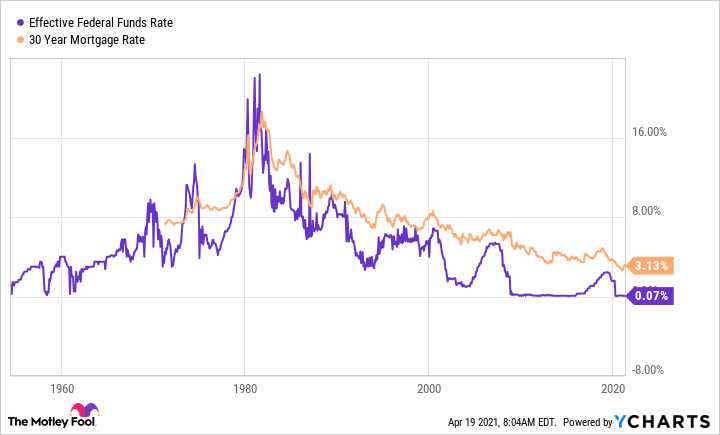
The central bank of a country is responsible for setting the overnight rate. It uses various tools and strategies to manage the rate and achieve its monetary policy objectives. The central bank may increase the overnight rate to control inflation and reduce borrowing and spending in the economy. Conversely, it may lower the rate to stimulate economic activity and encourage borrowing and investment.
The central bank’s decision to change the overnight rate is based on several factors, including the current state of the economy, inflation levels, and the overall monetary policy stance. Economic indicators such as GDP growth, employment rates, and consumer price index (CPI) are closely monitored to assess the need for adjusting the overnight rate.
Impact of the Overnight Rate
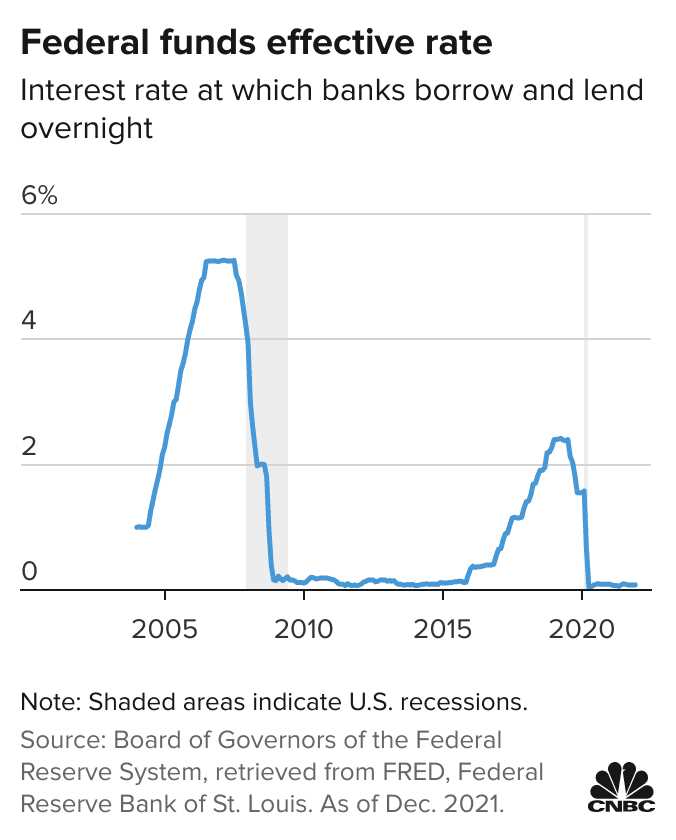
The overnight rate has a significant impact on the economy. Changes in the overnight rate can influence borrowing costs for businesses and individuals. When the overnight rate is low, borrowing becomes cheaper, encouraging businesses to invest and consumers to spend. This can stimulate economic growth and increase employment opportunities.
On the other hand, when the overnight rate is high, borrowing becomes more expensive, discouraging businesses and individuals from taking on debt. This can slow down economic activity and reduce inflationary pressures. The central bank uses the overnight rate as a tool to manage inflation and stabilize the economy.
Furthermore, the overnight rate affects other interest rates in the economy. When the overnight rate is increased, banks may raise their prime lending rates, which affects the cost of borrowing for mortgages, loans, and credit cards. Conversely, when the overnight rate is decreased, banks may lower their lending rates, making borrowing more affordable for consumers and businesses.
The Role of Central Banks in Setting the Overnight Rate
Central banks play a crucial role in setting the overnight rate as part of their monetary policy framework. They use this rate to influence the overall level of interest rates in the economy and to manage inflation and economic growth.
Central banks typically have a target for the overnight rate, which they aim to achieve through various policy tools. One of the main tools used is open market operations, where the central bank buys or sells government securities to adjust the level of reserves in the banking system. By increasing or decreasing the supply of reserves, central banks can influence the overnight rate.
When the central bank wants to lower interest rates and stimulate economic activity, it can inject liquidity into the banking system by buying government securities. This increases the supply of reserves and puts downward pressure on the overnight rate. Conversely, when the central bank wants to tighten monetary policy and control inflation, it can sell government securities, reducing the supply of reserves and pushing up the overnight rate.
The central bank’s ability to set the overnight rate gives it significant control over short-term interest rates, which in turn affects borrowing costs for businesses and consumers. By adjusting the overnight rate, central banks can influence the cost of borrowing for mortgages, car loans, and other forms of credit. This, in turn, can impact consumer spending, investment, and overall economic activity.
In addition to managing interest rates, central banks also use the overnight rate as a tool to manage inflation. By increasing the overnight rate, central banks can reduce the money supply and slow down economic growth, which can help prevent inflation from rising too quickly. Conversely, if the central bank wants to stimulate inflation, it can lower the overnight rate to encourage borrowing and spending.
How the Overnight Rate Affects Borrowing Costs
When the overnight rate is low, it encourages banks to borrow money from the central bank at a lower cost. This, in turn, allows banks to offer lower interest rates on loans to consumers and businesses. Lower borrowing costs stimulate borrowing and investment, which can help stimulate economic growth.
Conversely, when the overnight rate is high, it becomes more expensive for banks to borrow money from the central bank. As a result, banks may increase the interest rates they charge on loans to compensate for the higher borrowing costs. Higher borrowing costs can discourage borrowing and investment, which can potentially slow down economic growth.
Changes in the overnight rate can have a ripple effect throughout the economy. For example, when borrowing costs are low, consumers may be more likely to take out loans to finance purchases such as homes or cars. This can lead to increased spending, which can stimulate economic activity. On the other hand, when borrowing costs are high, consumers may be less inclined to borrow and spend, which can have a dampening effect on the economy.
The overnight rate also affects the interest rates on savings accounts and other investments. When the overnight rate is low, banks may offer lower interest rates on savings accounts, which can discourage saving. Conversely, when the overnight rate is high, banks may offer higher interest rates on savings accounts, which can incentivize saving.
In summary, the overnight rate plays a crucial role in determining borrowing costs for financial institutions, which in turn affects the interest rates offered to consumers and businesses. By influencing borrowing costs, the overnight rate can have a significant impact on borrowing, spending, and saving, and ultimately, on the overall health of the economy.
The Impact of the Overnight Rate on the Economy
The overnight rate is a key tool used by central banks to control the money supply and influence economic activity. When the central bank raises or lowers the overnight rate, it has a ripple effect throughout the economy.
One of the main ways the overnight rate impacts the economy is through its effect on borrowing costs. When the overnight rate is lowered, it becomes cheaper for banks to borrow money from the central bank. This, in turn, allows banks to offer lower interest rates on loans to businesses and consumers. Lower interest rates encourage borrowing and spending, which stimulates economic activity.
Conversely, when the overnight rate is raised, it becomes more expensive for banks to borrow money. As a result, banks may increase the interest rates they charge on loans to compensate for the higher borrowing costs. Higher interest rates can discourage borrowing and spending, which can slow down economic growth.
Another way the overnight rate impacts the economy is through its effect on inflation. When the central bank lowers the overnight rate, it increases the money supply and stimulates economic activity. This can lead to an increase in demand for goods and services, which can push up prices. On the other hand, when the central bank raises the overnight rate, it reduces the money supply and can help to control inflation.
Overall, the overnight rate plays a crucial role in shaping the overall economic conditions. By adjusting the overnight rate, central banks can influence borrowing costs, spending, and inflation levels. This allows them to maintain price stability and promote sustainable economic growth.
The Relationship Between the Overnight Rate and Inflation
Inflation is a key economic indicator that measures the rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services is rising and, consequently, the purchasing power of currency is falling. It is influenced by various factors, including the overnight rate set by central banks.
Inflation is a natural occurrence in any economy. It can be caused by a variety of factors, such as increased demand for goods and services, rising production costs, or changes in government policies. When inflation is low and stable, it is generally considered beneficial for the economy as it encourages spending and investment.
However, when inflation becomes too high or unpredictable, it can have negative consequences. High inflation erodes the purchasing power of money, making goods and services more expensive. This can lead to a decrease in consumer spending, lower business profits, and economic instability.
The Role of the Overnight Rate
One of the main tools used by central banks to control inflation is monetary policy, which includes adjusting the overnight rate. When the central bank wants to stimulate economic growth and increase inflation, it may lower the overnight rate. Conversely, when it wants to curb inflation, it may raise the overnight rate.
Impact on Borrowing Costs
The overnight rate has a direct impact on borrowing costs for individuals, businesses, and governments. When the overnight rate is low, it becomes cheaper to borrow money, which encourages spending and investment. This can lead to increased economic activity and potentially higher inflation.
On the other hand, when the overnight rate is high, borrowing becomes more expensive, which can discourage spending and investment. This can help to cool down an overheating economy and reduce inflationary pressures.
Overall Impact on the Economy
The relationship between the overnight rate and inflation is complex and multifaceted. Changes in the overnight rate can have both immediate and long-term effects on the economy.
In the short term, a change in the overnight rate can impact borrowing costs, consumer spending, and business investment. These factors can influence the overall level of economic activity and potentially affect inflation.
In the long term, the overnight rate can also influence inflation expectations. If households and businesses anticipate that inflation will remain low and stable, they may adjust their behavior accordingly, which can help to anchor inflation at the desired level.
Conclusion

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
