Overview of Dividend Recapitalization
Dividend recapitalization is a financial strategy that involves a company borrowing money to pay a special dividend to its shareholders. This strategy allows the company to distribute excess cash to shareholders while also increasing its debt levels.
During a dividend recapitalization, the company typically issues new debt, such as bonds or loans, to raise the necessary funds for the special dividend. The amount of the dividend is usually determined based on a percentage of the company’s equity value.
Dividend recapitalization is often used by companies that have a strong cash flow but limited growth opportunities. By returning cash to shareholders through a special dividend, the company can enhance shareholder value and attract new investors.
Benefits of Dividend Recapitalization
There are several benefits associated with dividend recapitalization:
- Enhanced shareholder value: By distributing excess cash to shareholders, dividend recapitalization can increase the company’s stock price and overall shareholder value.
- Attracting new investors: A special dividend can make the company more attractive to potential investors, as it demonstrates the company’s ability to generate cash and return it to shareholders.
- Reduced tax liability: In some cases, the special dividend received by shareholders may be taxed at a lower rate compared to regular dividends, resulting in potential tax savings.
- Flexibility in capital structure: Dividend recapitalization allows the company to adjust its capital structure by increasing its debt levels, which can provide greater financial flexibility.
Overall, dividend recapitalization can be an effective strategy for companies looking to optimize their capital structure, enhance shareholder value, and attract new investors.
Benefits of Dividend Recapitalization
Dividend recapitalization offers several key benefits for companies and investors alike. Here are some of the advantages:
1. Increased liquidity: Dividend recapitalization allows companies to generate immediate cash flow by borrowing against their assets. This can be especially beneficial for companies that have a significant amount of equity tied up in their business.
2. Enhanced financial flexibility: By leveraging their assets, companies can use the funds obtained through dividend recapitalization to pursue growth opportunities, such as acquisitions or expansion into new markets. This can help companies stay competitive and adapt to changing market conditions.
3. Tax advantages: Dividend recapitalization can provide tax advantages for both companies and investors. For companies, the interest payments on the borrowed funds may be tax-deductible, reducing their overall tax liability. For investors, dividend payments may be taxed at a lower rate than capital gains.
4. Shareholder value creation: Dividend recapitalization can be a strategic move to enhance shareholder value. By returning cash to shareholders through dividends, companies can attract and retain investors, potentially increasing the value of their stock.
5. Risk management: Dividend recapitalization can help companies manage their risk by reducing their reliance on external financing sources. By using their own assets to generate cash flow, companies can become more self-sufficient and less vulnerable to changes in the lending market.
6. Improved capital structure: Dividend recapitalization can optimize a company’s capital structure by balancing debt and equity. By increasing the proportion of debt, companies can take advantage of the tax benefits and lower cost of debt financing, while still maintaining an appropriate level of equity to support their operations.
Overall, dividend recapitalization can be a valuable tool for companies looking to unlock the value of their assets, enhance their financial flexibility, and create shareholder value.
Example of Dividend Recapitalization
Dividend recapitalization is a financial strategy that involves a company taking on additional debt to pay a special dividend to its shareholders. Let’s take a closer look at an example to better understand how dividend recapitalization works.
Company XYZ
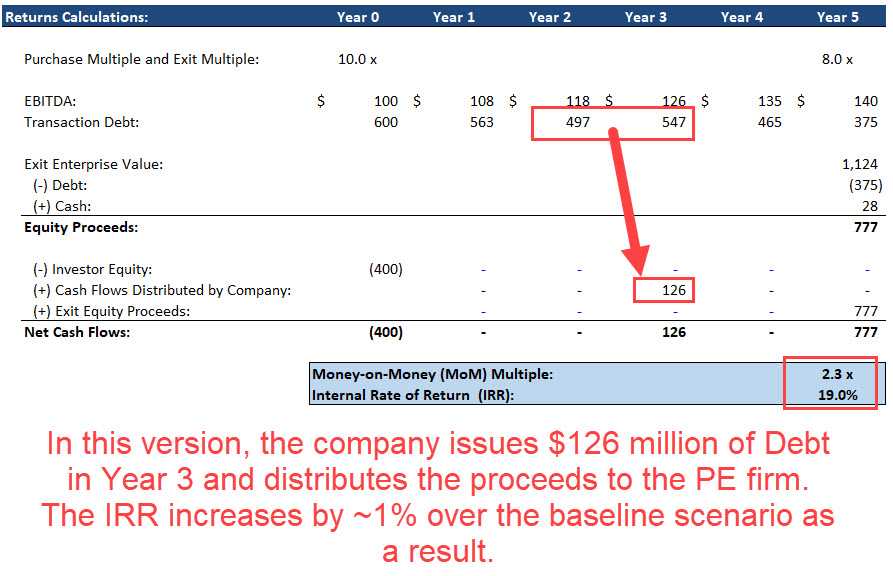
Imagine a fictional company called XYZ, which has been experiencing steady growth and generating significant profits. The company’s management team believes that the business has reached a point where it can take on additional debt to reward its shareholders.
XYZ’s board of directors decides to implement a dividend recapitalization strategy. They approach a bank and secure a loan of $100 million at a favorable interest rate. With this loan, XYZ plans to pay a special dividend of $50 million to its shareholders.
By distributing this special dividend, XYZ provides an immediate return on investment to its shareholders. This can be particularly attractive to investors who are seeking income from their investments.
Benefits of Dividend Recapitalization for XYZ
There are several benefits that XYZ can gain from implementing a dividend recapitalization strategy:
- Enhanced shareholder value: By distributing a special dividend, XYZ increases the value of its shares and rewards its shareholders for their investment.
- Improved capital structure: By taking on additional debt, XYZ can optimize its capital structure and potentially reduce its cost of capital.
- Flexibility for future growth: The additional funds obtained through the loan can be used to finance future growth initiatives, such as acquisitions or research and development.
Considerations for Dividend Recapitalization
1. Financial Stability
Before proceeding with a dividend recapitalization, it is crucial to assess the financial stability of the company. This includes evaluating the company’s cash flow, debt levels, and overall financial health. If the company is already struggling financially, a dividend recapitalization may not be the best option.
2. Growth Opportunities
3. Debt Capacity
Before implementing a dividend recapitalization, it is crucial to determine the company’s debt capacity. This involves evaluating the company’s ability to take on additional debt without jeopardizing its financial stability. It is important to consider the company’s existing debt obligations and its ability to service the new debt.
4. Shareholder Approval
Dividend recapitalization typically involves distributing a significant portion of the company’s cash to shareholders. Therefore, it is important to obtain shareholder approval before proceeding with a dividend recapitalization. This can involve presenting the benefits and risks of the transaction to shareholders and obtaining their consent through a vote.
5. Tax Implications

Dividend recapitalization can have tax implications for both the company and its shareholders. It is important to consult with tax professionals to understand the potential tax consequences of the transaction. This can help ensure that the company and its shareholders are in compliance with tax laws and regulations.
Overall, a dividend recapitalization can be a useful strategy for companies looking to distribute cash to shareholders while leveraging their existing assets. However, it is important to carefully consider these factors and seek professional advice before proceeding with a dividend recapitalization.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
