Overview of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934
The Securities Exchange Act of 1934 is a landmark piece of legislation that was enacted in response to the stock market crash of 1929 and the subsequent Great Depression. It was designed to regulate the securities industry and restore investor confidence in the financial markets.
One of the main objectives of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 was to establish a framework for the regulation of securities exchanges and the trading of securities. It created the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), which is the primary regulatory body responsible for enforcing the provisions of the Act.
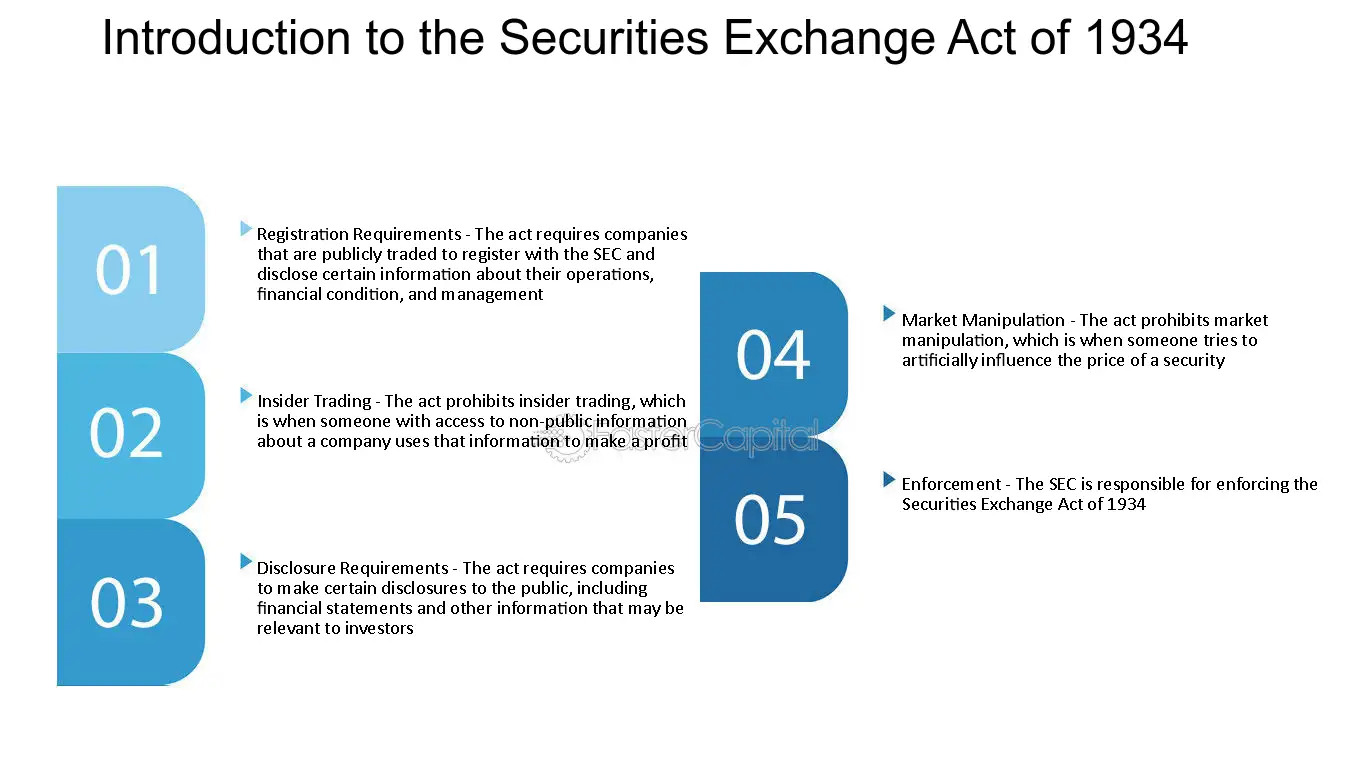
The Act requires companies to register with the SEC and disclose certain information about their business operations and financial condition. This includes regular financial reporting, disclosure of material events, and insider trading reporting. The Act also prohibits fraudulent activities in connection with the purchase or sale of securities.
Another important aspect of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 is the regulation of securities exchanges. The Act requires exchanges to register with the SEC and comply with certain rules and regulations. It also empowers the SEC to oversee the activities of exchanges and take enforcement actions against violations of the Act.
In addition to regulating securities exchanges and companies, the Act also provides for the regulation of brokers, dealers, and other market participants. It establishes rules for fair and orderly markets, promotes transparency and investor protection, and sets standards for the conduct of market participants.
The Securities Exchange Act of 1934 has had a significant impact on the financial industry. It has helped to create a more transparent and efficient marketplace, fostered investor confidence, and provided a framework for the regulation of securities exchanges and market participants. The Act continues to play a crucial role in safeguarding the integrity of the financial markets and protecting investors.
Key Provisions of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934
One of the key provisions of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 is the requirement for companies to register with the SEC and disclose relevant information to the public. This includes regular financial statements, annual reports, and other material information that may impact the value of the company’s securities. By mandating disclosure, the Act aims to provide investors with the necessary information to make informed investment decisions and prevent fraud and manipulation in the markets.
The Act also prohibits insider trading, which refers to the buying or selling of securities based on non-public information. Insider trading is considered unfair and undermines the integrity of the markets. The Securities Exchange Act of 1934 imposes strict penalties on individuals who engage in insider trading, including fines and imprisonment. This provision helps to level the playing field for all investors and promotes market integrity.
Another important provision of the Act is the regulation of securities exchanges and brokers. The Act requires exchanges to register with the SEC and comply with certain rules and regulations to ensure fair and orderly trading. It also establishes a framework for the licensing and regulation of brokers and dealers, who act as intermediaries between investors and the markets. This helps to maintain market stability and protect investors from fraudulent practices.
Impact of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 on the Financial Industry
The Securities Exchange Act of 1934 had a profound impact on the financial industry in the United States. This landmark legislation was enacted in response to the stock market crash of 1929 and aimed to restore investor confidence and regulate the securities markets.
By establishing the SEC, the Act brought about a new era of regulation and oversight in the financial industry. The SEC was empowered to require companies to provide detailed financial information to the public, including annual reports and quarterly filings. This increased transparency helped to level the playing field for investors and reduced the likelihood of fraudulent activities.
The Act also introduced regulations for securities exchanges, requiring them to register with the SEC and adhere to certain standards of operation. This helped to ensure that exchanges provided fair and orderly markets for trading securities.
Overall, the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 had a transformative effect on the financial industry. It brought about increased transparency, regulation, and oversight, which helped to restore investor confidence and promote fair and efficient markets. The Act continues to play a crucial role in shaping the modern securities industry and protecting the interests of investors.
Historical Significance of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934

The Securities Exchange Act of 1934 holds immense historical significance as it laid the foundation for the regulation and oversight of the securities industry in the United States. Enacted in response to the stock market crash of 1929 and the subsequent Great Depression, this landmark legislation aimed to restore investor confidence and stabilize the financial markets.
Prior to the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the securities industry was largely unregulated, leading to rampant speculation, fraud, and market manipulation. The lack of transparency and accountability resulted in the collapse of numerous financial institutions and devastating losses for investors.
The Securities Exchange Act of 1934 also established rules for the registration and regulation of securities exchanges, ensuring that they operated in a fair and transparent manner. It provided guidelines for the listing and trading of securities, promoting investor confidence and market integrity.
Furthermore, the act empowered the SEC to enforce compliance with its regulations through inspections, investigations, and enforcement actions. It granted the SEC the authority to bring civil lawsuits against violators and impose penalties for non-compliance.
The Securities Exchange Act of 1934 played a crucial role in restoring stability to the financial markets and rebuilding investor trust. It set the stage for the modern regulatory framework that governs the securities industry, protecting investors and promoting fair and efficient markets.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
