Marginal Revenue Product: Definition and Importance

Definition of Marginal Revenue Product
Importance of Marginal Revenue Product
Additionally, MRP can also help businesses determine the optimal level of input to employ. If the MRP of an input is decreasing, it indicates that the business is reaching a point of diminishing returns, where the additional revenue generated by each additional unit of input is decreasing. This can help businesses avoid overutilizing resources and optimize their production processes.
Conclusion
The Marginal Revenue Product is a valuable concept in economics that helps businesses understand the value and productivity of different inputs. By analyzing the MRP, businesses can make informed decisions regarding resource allocation and optimize their production processes to maximize their revenue and profits.
What is Marginal Revenue Product?
Marginal Revenue Product (MRP) is a concept in economics that measures the additional revenue generated by an additional unit of a specific input, such as labor or capital. It is used to determine the value of each unit of input in the production process and helps businesses make decisions regarding resource allocation and hiring.
MRP is calculated by multiplying the marginal product of the input by the marginal revenue generated by the output. The marginal product is the additional output produced by adding one more unit of the input, while the marginal revenue is the additional revenue generated by selling one more unit of output.
Importance of Marginal Revenue Product
Marginal Revenue Product is an important concept in economics as it helps businesses determine the optimal level of input usage. By comparing the MRP of different inputs, businesses can identify which inputs are most valuable and allocate resources accordingly. This information is crucial for businesses to maximize their profits and minimize costs.
Additionally, MRP is used in determining wages and salaries for employees. The MRP of labor is used to determine the value of an employee’s contribution to the production process. Higher MRP indicates a higher value of the employee’s work, which can justify higher wages or salaries.
Calculating Marginal Revenue Product
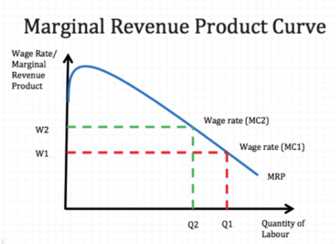
To calculate the Marginal Revenue Product, you need to follow these steps:
- Determine the change in output resulting from adding one more unit of the input. This is the marginal product.
- Determine the change in revenue resulting from selling one more unit of output. This is the marginal revenue.
- Multiply the marginal product by the marginal revenue to get the Marginal Revenue Product.
Once you have calculated the MRP, you can compare it to the cost of the input to determine if it is profitable to hire additional units of that input.
How is Marginal Revenue Product Calculated?
The calculation of marginal revenue product (MRP) is an important concept in economics that helps businesses determine the value of an additional unit of input, such as labor or capital, to their production process. It is a measure of the additional revenue generated by employing an additional unit of input.
Formula for Calculating Marginal Revenue Product
The formula for calculating marginal revenue product is:
MRP = Marginal Product of Labor (MPL) x Marginal Revenue (MR)
Where:
- Marginal Product of Labor (MPL) is the change in output resulting from employing one additional unit of labor.
- Marginal Revenue (MR) is the change in total revenue resulting from selling one additional unit of output.
By multiplying the marginal product of labor by the marginal revenue, businesses can determine the additional revenue generated by employing one more unit of labor.
Example Calculation
Let’s say a company produces widgets and employs 10 workers. The marginal product of labor is 5 widgets per worker, and the marginal revenue for each widget is $10. To calculate the marginal revenue product, we use the formula:
MRP = 5 widgets per worker x $10 per widget = $50 per worker
This means that by employing one additional worker, the company can generate an additional $50 in revenue.
Businesses can use the concept of marginal revenue product to make informed decisions about the optimal level of input to employ in their production process. By comparing the marginal revenue product to the cost of employing additional units of input, businesses can determine whether it is profitable to hire more workers or invest in additional capital.
The Importance of Marginal Revenue Product
One of the key benefits of MRP is its ability to measure the additional revenue generated by each additional unit of a resource, such as an employee. By calculating the MRP, businesses can determine the optimal number of resources to employ, ensuring maximum productivity and profitability. This information is especially valuable in industries where labor costs constitute a significant portion of total expenses.
Moreover, MRP helps businesses evaluate the value of different resources and make informed decisions about their allocation. By comparing the MRP of different resources, such as employees with different skill sets or machinery with different capabilities, businesses can determine which resources are the most productive and allocate them accordingly. This enables businesses to optimize their production processes and maximize their output.
MRP is also closely related to the concept of marginal cost. By comparing the MRP with the marginal cost of employing an additional unit of a resource, businesses can determine whether it is economically beneficial to hire more resources. If the MRP exceeds the marginal cost, it indicates that hiring additional resources will result in increased revenue and profitability.
Furthermore, MRP can provide valuable insights into the demand for a particular resource. If the MRP of a resource is high, it suggests that the resource is in high demand and its scarcity may drive up its value. This information can help businesses negotiate wages and attract and retain talented employees.
Predicting Marginal Revenue Product
There are several factors that can help predict MRP. One of the key factors is the demand for the final product or service. If the demand for a product is high, the MRP is likely to be higher as well. This is because businesses can sell more units of the product and generate more revenue by employing additional resources.
Another factor to consider is the productivity of the resource. If a resource is highly productive and can contribute significantly to the production process, its MRP is likely to be higher. On the other hand, if a resource is less productive or can be easily substituted, its MRP may be lower.
The availability of substitutes is also an important factor in predicting MRP. If there are readily available substitutes for a resource, the MRP may be lower as businesses have more options to choose from. However, if a resource is scarce or there are limited substitutes, its MRP is likely to be higher.
Market conditions and competition can also impact the prediction of MRP. If a market is highly competitive, businesses may need to offer higher wages or prices to attract and retain skilled resources. This can increase the MRP of the resource. Conversely, in a less competitive market, the MRP may be lower.
Predicting MRP requires a thorough analysis of these factors and their interplay. Economic models and statistical techniques can be used to estimate MRP based on historical data and market trends. By accurately predicting MRP, businesses can make informed decisions about resource allocation, pricing strategies, and overall production efficiency.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
