Macro Manager: Definition and Importance
Macro Manager is a term used in business to describe a manager who focuses on the overall strategic direction and performance of an organization. Unlike micro managers who are more concerned with the day-to-day details and tasks, macro managers take a broader perspective and are responsible for setting goals, making key decisions, and ensuring the organization is on track to achieve its objectives.
The importance of macro managers cannot be overstated. They play a crucial role in guiding the organization towards success by aligning the company’s vision with its operations. Macro managers are responsible for developing and implementing strategies that drive growth, increase profitability, and maintain a competitive advantage in the market.
Responsibilities of a Macro Manager
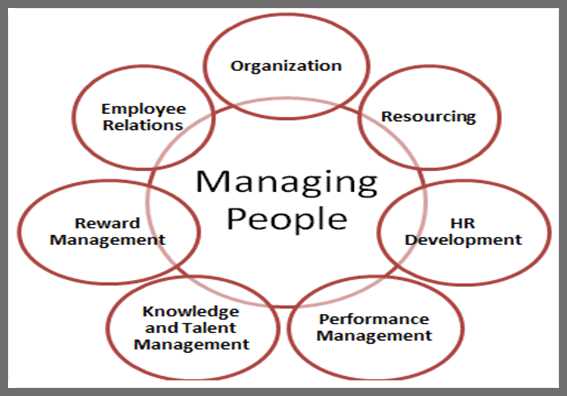
A macro manager is responsible for a wide range of tasks and responsibilities. Some of the key responsibilities include:
- Setting organizational goals and objectives
- Developing strategic plans and initiatives
- Allocating resources effectively
- Monitoring and evaluating performance
- Making key decisions and solving complex problems
- Building and maintaining relationships with stakeholders
- Ensuring compliance with regulations and industry standards
Benefits of Having a Macro Manager
Hiring a macro manager can bring numerous benefits to an organization. Some of the key benefits include:
- Clear strategic direction: A macro manager ensures that the organization has a clear vision and strategic direction, which helps align the efforts of all employees towards common goals.
- Efficient resource allocation: By analyzing the organization’s needs and priorities, a macro manager can allocate resources effectively, ensuring that they are utilized in the most efficient and productive manner.
- Enhanced performance monitoring: Macro managers establish performance metrics and regularly monitor the organization’s progress towards its goals. This allows for timely adjustments and interventions to ensure continued success.
- Strong stakeholder relationships: Building and maintaining relationships with stakeholders, such as customers, suppliers, and investors, is crucial for the success of any organization. Macro managers excel at managing these relationships and ensuring mutual satisfaction.
What is Macro Manager?
Macro Manager is a term used in business management to refer to a person or a team responsible for overseeing and coordinating the overall strategic direction and operations of an organization. They focus on the big picture and ensure that the company’s goals and objectives are aligned with its mission and vision.
Roles and Responsibilities of a Macro Manager
A Macro Manager is responsible for:
- Developing and implementing the organization’s strategic plans and initiatives
- Setting goals and objectives for different departments and teams
- Monitoring and evaluating the performance of the organization
- Identifying and managing risks and opportunities
- Allocating resources effectively
- Building and maintaining relationships with stakeholders
- Ensuring compliance with legal and regulatory requirements
- Leading and motivating employees
Skills and Qualifications of a Macro Manager
To be an effective Macro Manager, one should possess the following skills and qualifications:
- Strong leadership and management skills
- Excellent communication and interpersonal skills
- Strategic thinking and problem-solving abilities
- Analytical and decision-making skills
- Financial acumen
- Ability to work under pressure and meet deadlines
- Knowledge of industry trends and best practices
- Experience in business planning and development
Overall, a Macro Manager plays a crucial role in guiding the organization towards success by ensuring effective planning, coordination, and execution of strategies. They are responsible for creating a vision for the company and aligning all departments and teams towards achieving that vision.
The Importance of Macro Manager in Business
A macro manager plays a crucial role in the success of a business by overseeing and managing the overall operations and strategies at a high level. This individual is responsible for setting the direction and goals of the company, as well as ensuring that all departments and teams are aligned and working towards the same objectives.
Another crucial aspect of a macro manager’s role is their ability to create and implement effective strategies. They are responsible for developing a comprehensive plan that outlines the company’s goals, objectives, and the steps needed to achieve them. This involves analyzing market data, conducting research, and collaborating with other key stakeholders to ensure that the strategies are well-informed and aligned with the overall business objectives.
Furthermore, a macro manager is instrumental in ensuring that all departments and teams are working together towards a common goal. They act as a bridge between different functional areas and facilitate communication and collaboration. This helps to break down silos and promote a cohesive and unified approach to achieving the company’s objectives.
Additionally, a macro manager is responsible for monitoring and evaluating the performance of the company. They analyze key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics to assess the effectiveness of the strategies and initiatives implemented. This allows them to identify areas of improvement and make necessary adjustments to ensure that the company is on track to meet its goals.
Macro Manager: Management Process and Benefits
Macro management is a crucial aspect of business leadership and plays a significant role in the success of an organization. A macro manager is responsible for overseeing the overall operations and strategic direction of a company.
Management Process
The macro management process involves setting clear goals and objectives for the organization, developing strategies to achieve them, and ensuring that the necessary resources are allocated effectively. The macro manager works closely with department heads and team leaders to establish performance metrics and monitor progress towards goals.
Effective communication is a key component of the management process. The macro manager must clearly communicate the company’s vision, mission, and objectives to all employees, ensuring that everyone is aligned and working towards a common goal. Regular meetings and updates are essential to keep the team informed and engaged.
Additionally, the macro manager must analyze market trends, competitor activities, and industry developments to identify opportunities and potential threats. This information is used to make informed decisions and adjust strategies accordingly.
Benefits of Macro Management
Macro management offers several benefits to organizations:
1. Strategic Alignment: By setting clear goals and objectives, macro management ensures that all employees are working towards a common vision. This alignment enhances productivity and efficiency, as everyone understands their role in achieving the company’s objectives.
2. Resource Optimization: Macro management involves effectively allocating resources to different departments and projects. This optimization ensures that resources are utilized efficiently, reducing wastage and maximizing productivity.
3. Adaptability: By monitoring market trends and industry developments, macro managers can identify changes and adapt their strategies accordingly. This flexibility allows organizations to stay ahead of the competition and seize new opportunities.
4. Employee Development: Macro managers play a crucial role in employee development. By setting performance metrics and providing regular feedback, they help employees grow and improve their skills. This investment in employee development leads to a motivated and engaged workforce.
5. Risk Management: Macro managers are responsible for identifying potential risks and developing strategies to mitigate them. By analyzing market conditions and competitor activities, they can anticipate challenges and take proactive measures to minimize the impact on the organization.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
