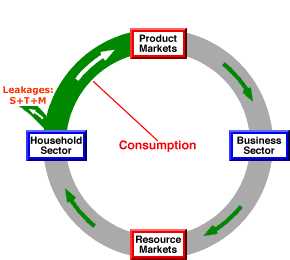
Leakage in Economics: Definition and Examples
Leakage in economics refers to the outflow or diversion of funds from a particular economic system or process. It occurs when money or resources that are intended to circulate within an economy are instead redirected elsewhere, leading to a decrease in economic activity and potential negative effects on growth and development.
Leakage can occur in various forms, including savings, taxes, and imports. When individuals or businesses save a portion of their income rather than spending it, it reduces the amount of money available for consumption and investment, resulting in a leakage from the economy. Similarly, when taxes are imposed on income or goods and services, it reduces the disposable income of individuals and the profits of businesses, leading to a leakage of funds from the economy. Additionally, when a country imports more goods and services than it exports, it results in a leakage of money to other economies.
Leakage can have both short-term and long-term effects on an economy. In the short term, it can lead to a decrease in aggregate demand, as less money is available for consumption and investment. This can result in reduced production and employment levels, leading to economic slowdown or recession. In the long term, leakage can hinder economic growth and development, as less money is available for investment in infrastructure, education, and innovation.
Types of Leakage in Economics
There are several types of leakage in economics, including:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Savings | Occurs when individuals or businesses save a portion of their income instead of spending it. |
| Taxes | Occurs when taxes are imposed on income or goods and services, reducing disposable income and business profits. |
| Imports | Occurs when a country imports more goods and services than it exports, resulting in a outflow of money. |
Causes of Leakage in Economics
Leakage in economics can be caused by various factors, including:
- High savings rates
- High tax rates
- Trade imbalances
- Government policies
- Income inequality
These factors can influence the level of leakage in an economy and impact its overall performance.
Effects of Leakage in Economics
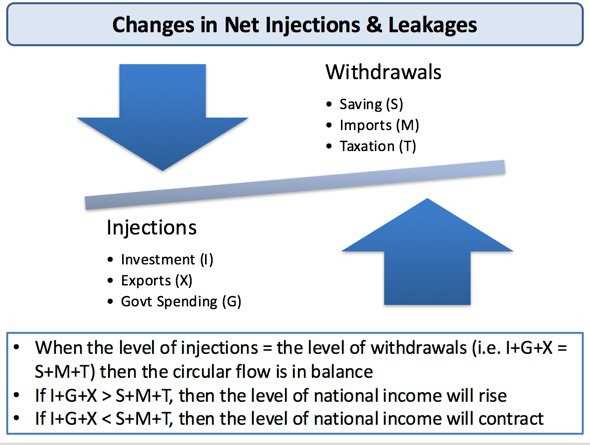
The effects of leakage in economics can be significant and wide-ranging. Some of the key effects include:
- Decreased aggregate demand
- Reduced production and employment levels
- Economic slowdown or recession
- Lower investment in infrastructure, education, and innovation
- Income inequality
These effects can hinder economic growth, development, and stability, making leakage an important concept to understand and address in economic policy-making.
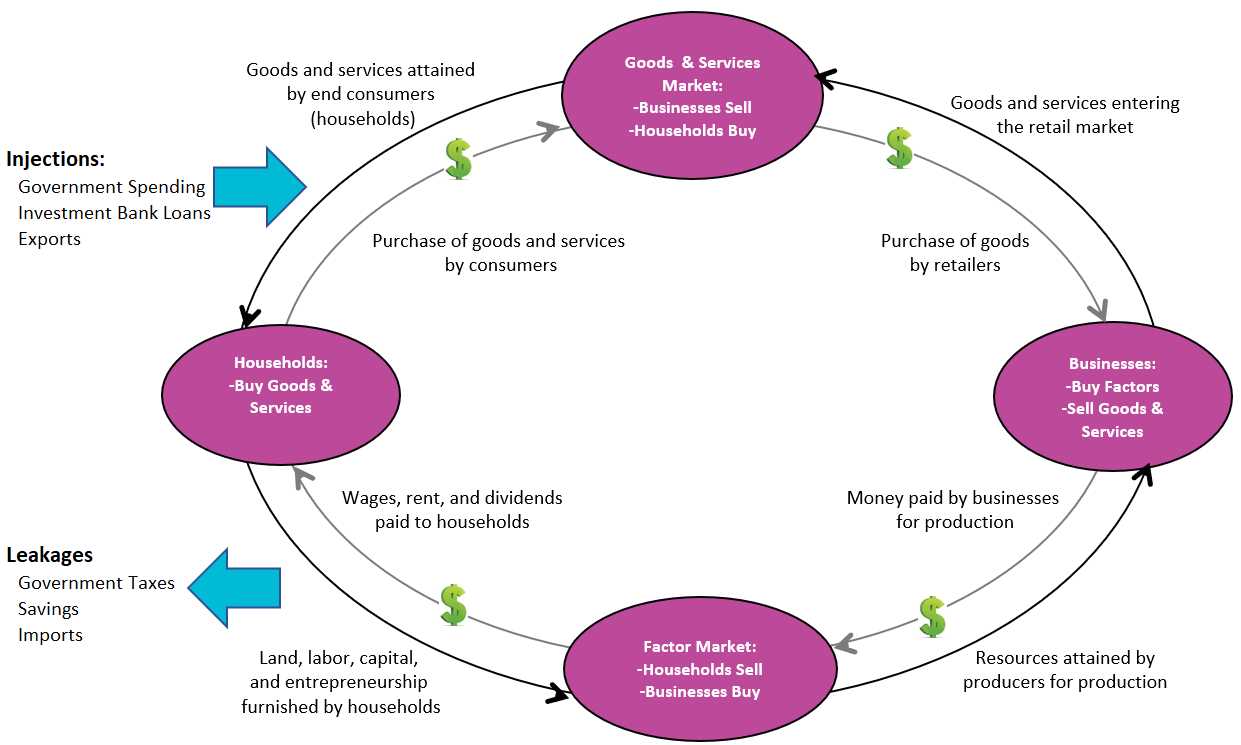
Leakage in economics refers to the outflow or diversion of funds from the intended economic system. It occurs when money that is injected into the system through various channels is not fully utilized for consumption or investment purposes within the system. Instead, it leaks out of the system through various means, such as savings, taxes, imports, or debt repayments.
Types of Leakage
There are several types of leakage in economics:
- Savings: When individuals or businesses save a portion of their income instead of spending it, it leads to leakage from the economic system. Savings are typically deposited in banks or invested in financial instruments, which reduces the amount of money available for consumption or investment.
- Taxes: When individuals or businesses pay taxes to the government, it constitutes a leakage from the economic system. Taxes reduce the disposable income of individuals and the profits of businesses, limiting their ability to spend or invest.
- Imports: When a country imports goods and services from other countries, it leads to leakage from the domestic economy. The money spent on imports leaves the country, reducing the amount of money available for domestic consumption or investment.
- Debt Repayments: When individuals, businesses, or governments repay their debts, it constitutes a leakage from the economic system. The money used for debt repayments could have been used for consumption or investment within the system.
These types of leakage can have both positive and negative effects on the economy. For example, savings can contribute to capital formation and investment, leading to economic growth. However, excessive savings can also lead to reduced consumption and aggregate demand, which can hinder economic growth.
Conclusion
Types of Leakage in Economics
1. Savings Leakage
Savings leakage occurs when individuals or households save a portion of their income instead of spending it on goods and services. This can happen due to various reasons, such as a desire to accumulate wealth or uncertainty about the future. While saving is important for long-term financial stability, excessive savings can lead to a decrease in consumer spending, which can have a negative impact on economic growth.
2. Tax Leakage
Tax leakage refers to the loss of tax revenue due to various factors. This can include tax evasion, where individuals or businesses intentionally avoid paying their taxes, as well as tax loopholes and exemptions that allow certain entities to reduce their tax liability. Tax leakage can have significant implications for government budgets and public services, as it reduces the funds available for essential programs and infrastructure.
3. Import Leakage
Import leakage occurs when a country imports more goods and services than it exports. This leads to a trade deficit, where the value of imports exceeds the value of exports. Import leakage can have a negative impact on a country’s balance of payments and can contribute to a loss of domestic production and employment opportunities. It also increases the dependence on foreign goods and can potentially harm domestic industries.
4. Capital Leakage
Capital leakage refers to the outflow of financial capital from an economy. This can happen through various channels, such as foreign direct investment, portfolio investment, or debt repayments to foreign entities. Capital leakage can have both positive and negative effects on an economy. On one hand, it can bring in foreign investment and stimulate economic growth. On the other hand, excessive capital outflows can lead to currency depreciation, financial instability, and reduced domestic investment.
5. Brain Drain
Brain drain is a type of leakage that occurs when highly skilled or educated individuals leave their home country to seek better opportunities abroad. This can result in a loss of human capital and expertise, which can hinder a country’s economic development. Brain drain can also lead to a decrease in innovation and productivity, as talented individuals contribute to the growth of other economies instead of their own.
Causes of Leakage in Economics
In economics, leakage refers to the flow of money or resources out of an economic system, which can have significant impacts on the overall functioning of the economy. There are several causes of leakage in economics, which can occur at various levels of the economic system.
1. Savings
One of the main causes of leakage in economics is savings. When individuals or households save their income instead of spending it, this money is not being circulated back into the economy. Instead, it is being saved or invested, which can lead to a decrease in consumer spending and overall economic activity.
2. Taxes
Taxes are another major cause of leakage in economics. When individuals or businesses pay taxes, this money is taken out of the economy and used by the government for various purposes. While taxes are necessary for funding public goods and services, they can also reduce the amount of money available for consumption and investment.
3. Imports
Imports can also cause leakage in economics. When a country imports goods or services from another country, money flows out of the domestic economy and into the foreign economy. This can lead to a decrease in domestic production and employment, as well as a decrease in overall economic output.
4. Debt Repayment
Debt repayment is another cause of leakage in economics. When individuals, businesses, or governments repay their debts, money is taken out of the economy and used to pay off lenders. While debt repayment is important for maintaining financial stability, it can also reduce the amount of money available for consumption and investment.
5. Leakage to the Financial Sector
Leakage can also occur within the financial sector itself. When individuals or businesses deposit money into banks or other financial institutions, this money is often used for lending or investment purposes. While this can stimulate economic activity, it can also lead to leakage if the funds are not used to finance productive investments or if they are not circulated back into the economy.
6. Foreign Aid
Foreign aid can also cause leakage in economics. When a country receives foreign aid, this money is often used for specific purposes, such as infrastructure development or humanitarian assistance. While foreign aid can be beneficial, it can also lead to leakage if the funds are not effectively utilized or if they do not contribute to long-term economic growth.
7. Leakage in International Trade
Finally, leakage can occur in international trade. When countries engage in trade, there can be imbalances in the flow of goods, services, and money between them. This can result in leakage if one country consistently imports more than it exports, leading to a decrease in domestic production and economic activity.
Effects of Leakage in Economics
Leakage in economics refers to the diversion of income or spending away from the intended target, resulting in a reduction in the effectiveness of economic policies or activities. The effects of leakage can have significant implications for the overall economy and its various sectors.
Here are some of the key effects of leakage in economics:
- Reduced economic growth: Leakage can lead to a decrease in overall economic growth as it reduces the amount of money circulating within the economy. When leakage occurs, the money that could have been spent on goods and services is diverted elsewhere, resulting in a decrease in demand and overall economic activity.
- Decreased employment opportunities: When leakage reduces economic growth, it can also lead to a decrease in employment opportunities. With reduced demand for goods and services, businesses may be forced to downsize or cut back on hiring, resulting in higher unemployment rates.
- Increased income inequality: Leakage can contribute to income inequality within a society. When income or spending is diverted away from certain groups or regions, it can exacerbate existing disparities in wealth and income distribution. This can lead to social and economic tensions within a society.
- Impaired government finances: Leakage can have a negative impact on government finances. When leakage occurs, it reduces the amount of tax revenue generated, making it more difficult for governments to fund public services and infrastructure projects. This can lead to budget deficits and increased government debt.
- Reduced investment: Leakage can also discourage investment in the economy. When leakage occurs, it reduces the amount of money available for investment, as funds are diverted elsewhere. This can hinder economic development and innovation, as businesses may struggle to secure the necessary capital for growth.
- Increased reliance on external sources: Leakage can result in a greater reliance on external sources of income or investment. When leakage occurs, it reduces domestic spending and investment, making the economy more dependent on foreign investment or loans. This can make the economy more vulnerable to external shocks and fluctuations in global markets.
Overall, the effects of leakage in economics can be detrimental to the overall health and stability of an economy. It is important for policymakers and economists to understand the causes and consequences of leakage in order to develop effective strategies to minimize its negative impacts.
Examples of Leakage in Economics
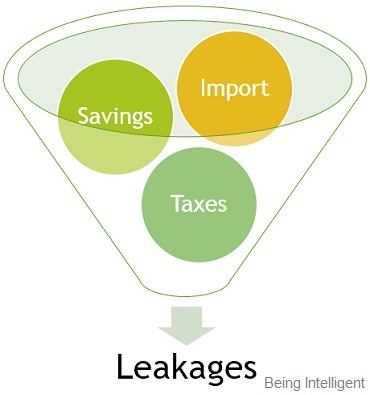
Leakage in economics refers to the outflow of money from a particular economic system, which can have various causes and effects. Let’s explore some examples of leakage in economics:
1. Savings
One common example of leakage is when individuals or households save a portion of their income instead of spending it. When people save money, it is not immediately injected back into the economy through consumption. Instead, it is stored in banks or invested in financial assets, leading to a reduction in the overall spending and demand in the economy.
2. Taxes
Taxes can also be considered a form of leakage. When individuals or businesses pay taxes, the money is transferred to the government. While the government uses these funds for various purposes such as public services and infrastructure development, it is still a leakage from the private sector. Taxes reduce the disposable income of individuals and can affect their ability to spend and contribute to economic growth.
3. Imports
Imports can be another form of leakage in economics. When a country imports goods and services from foreign countries, money flows out of the domestic economy. This can happen when consumers prefer foreign products over domestic ones or when businesses find it more cost-effective to source materials or services from abroad. Import leakage can have an impact on domestic industries, employment, and overall economic activity.
4. Debt Repayment
When individuals, businesses, or governments repay their debts, it can also be considered leakage. The money used for debt repayment is not available for consumption or investment in the economy. While debt repayment is necessary for financial stability, it can reduce the available funds for spending and investment, potentially impacting economic growth.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
