Mixed Economic System: Characteristics, Examples, Pros and Cons
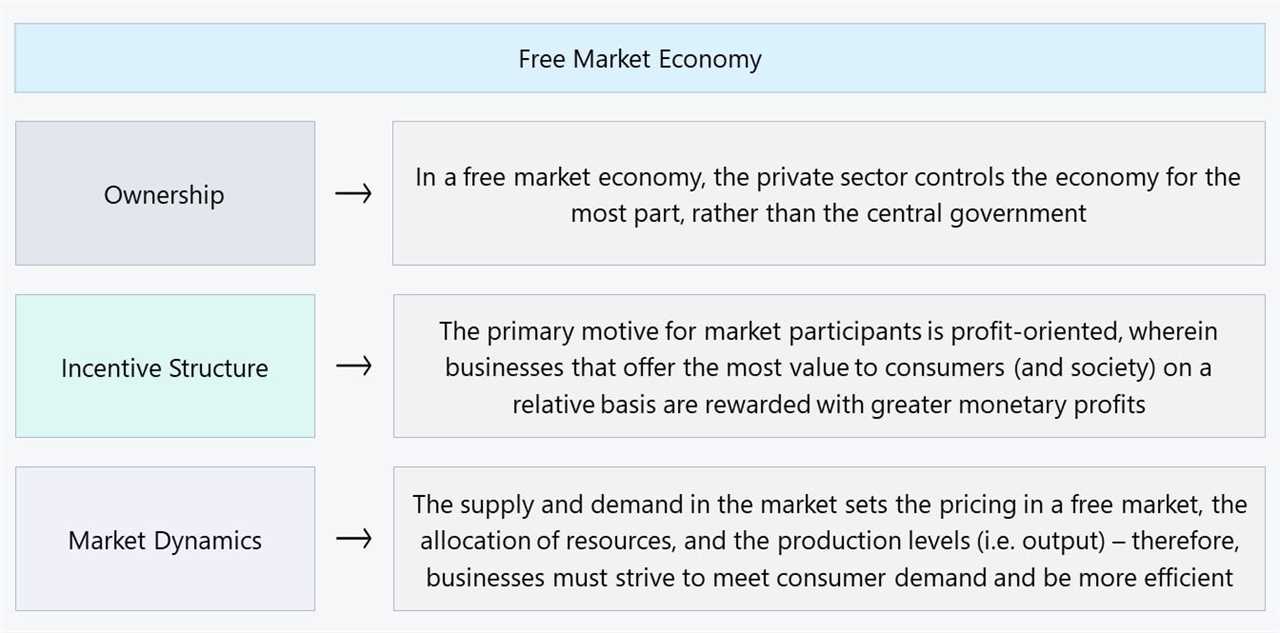
A mixed economic system is a combination of a free market economy and a planned economy. It incorporates elements of both capitalism and socialism, allowing for private ownership and entrepreneurship while also providing government intervention and regulation. This unique blend of economic systems aims to balance individual freedom and economic efficiency with social welfare and equality.
One of the key characteristics of a mixed economic system is the presence of both private and public sectors. The private sector consists of privately owned businesses and individuals who engage in economic activities for profit. The public sector, on the other hand, includes government-owned enterprises and services that are provided for the benefit of society as a whole.
In a mixed economic system, the government plays a crucial role in regulating and overseeing economic activities. It sets rules and regulations to ensure fair competition, protect consumers, and prevent monopolies. The government also provides public goods and services such as education, healthcare, and infrastructure, which may not be adequately provided by the private sector alone.
Examples of mixed economic systems can be found in many countries around the world. The United States, for instance, has a mixed economy where private businesses operate freely, but the government also provides social welfare programs and intervenes in certain industries. Similarly, countries like Canada, Germany, and Sweden have mixed economies that combine market forces with government intervention to varying degrees.
However, a mixed economic system also has its drawbacks. One of the main criticisms is that it can lead to inefficiencies and bureaucracy due to government intervention. Additionally, the balance between private and public sectors can be difficult to achieve, and there is often debate over the appropriate level of government involvement in the economy.
Definition and Overview
In a mixed economic system, the government typically regulates certain industries and provides public goods and services such as education, healthcare, and infrastructure. At the same time, the private sector is allowed to operate freely and compete in the market, determining prices and producing goods and services based on consumer demand.
This combination of government intervention and market forces creates a balance between individual freedom and social welfare. It allows for economic growth and innovation while also ensuring that basic needs are met and income inequality is reduced.
Key Characteristics of a Mixed Economic System
There are several key characteristics that define a mixed economic system:
- Coexistence of public and private sectors: In a mixed economic system, both the government and private individuals or businesses are involved in economic activities.
- Government regulation: The government regulates certain industries to ensure fair competition, protect consumers, and promote social welfare.
- Market-based allocation of resources: The market forces of supply and demand determine the allocation of resources and the production of goods and services.
- Public goods and services: The government provides public goods and services that are necessary for the well-being of society, such as education, healthcare, and infrastructure.
- Income redistribution: The government may implement policies to reduce income inequality and provide social safety nets for those in need.
Examples of Mixed Economic Systems
There are several countries that have mixed economic systems, including the United States, Canada, Germany, and Sweden. These countries combine elements of both market economies and planned economies to varying degrees.
In the United States, for example, the government provides public goods and services, regulates certain industries, and implements social welfare programs, while also allowing for free market competition and private enterprise.
Similarly, in Sweden, the government plays a significant role in providing public services and redistributing income, but the country also has a strong private sector and a market-based economy.
Pros of a Mixed Economic System
A mixed economic system offers several advantages:
- Economic efficiency: The market-based allocation of resources allows for efficient production and distribution of goods and services.
- Social welfare: The government’s involvement ensures that basic needs are met and income inequality is reduced, promoting social welfare.
- Innovation and competition: The private sector’s freedom to compete fosters innovation and drives economic growth.
- Flexibility: A mixed economic system allows for flexibility in responding to changing economic conditions and societal needs.
Cons of a Mixed Economic System
However, there are also some drawbacks to a mixed economic system:
- Government intervention: Excessive government regulation can stifle economic growth and limit individual freedom.
- Inefficiency: The combination of government and market forces can sometimes lead to inefficiencies and resource misallocation.
- Political influence: The involvement of the government in the economy can lead to political influence and favoritism.
- Complexity: Managing a mixed economic system can be complex and challenging, requiring careful coordination between the public and private sectors.
Characteristics of a Mixed Economic System
A mixed economic system is characterized by a combination of both market and planned economies. It incorporates elements of both capitalism and socialism, allowing for private ownership and profit-driven markets, as well as government intervention and regulation.
Here are some key characteristics of a mixed economic system:
- Private and Public Ownership: In a mixed economy, there is a mix of private and public ownership. While individuals and businesses can own and operate their own enterprises, the government also owns and operates certain industries and services, such as healthcare, education, and transportation.
- Market and Planned Allocation of Resources: The allocation of resources in a mixed economy is done through both market forces and government planning. While market forces determine the allocation of resources in most sectors, the government may intervene to correct market failures, promote social welfare, or achieve specific economic goals.
- Profit Motive and Social Welfare: In a mixed economic system, there is a balance between the profit motive of private enterprises and the social welfare goals of the government. While businesses aim to maximize profits, the government may implement regulations and policies to ensure fair competition, protect consumers, and provide social services.
- Income Redistribution: A mixed economy often includes mechanisms for income redistribution. The government may collect taxes from individuals and businesses and use the revenue to provide social welfare programs, such as healthcare, education, and unemployment benefits, to ensure a more equitable distribution of wealth.
- Government Intervention: The government plays an active role in a mixed economic system, regulating markets, providing public goods and services, and implementing economic policies. It may set minimum wage laws, enforce environmental regulations, subsidize certain industries, or implement monetary and fiscal policies to stabilize the economy.
Overall, a mixed economic system combines the advantages of both market and planned economies. It allows for individual freedom and entrepreneurship, while also providing a safety net and addressing social and economic inequalities. However, it can also face challenges in striking the right balance between private and public interests, and in effectively managing government intervention and regulation.
Examples of Mixed Economic Systems
A mixed economic system combines elements of both a market economy and a planned economy. It allows for private ownership and control of resources, as well as government intervention and regulation. Here are some examples of countries with mixed economic systems:
- United States: The United States has a mixed economy with a strong emphasis on free markets. The government plays a role in regulating industries, providing public goods and services, and implementing social welfare programs.
- United Kingdom: The United Kingdom also has a mixed economy, with a combination of private enterprise and government intervention. The government provides public services such as healthcare and education, and regulates industries to ensure fair competition.
- Germany: Germany has a social market economy, which combines elements of capitalism and socialism. The government plays a significant role in providing social welfare programs, regulating industries, and promoting economic stability.
- Sweden: Sweden has a mixed economy with a strong welfare state. The government provides extensive social welfare programs, including healthcare, education, and unemployment benefits, while also promoting free trade and private enterprise.
- China: China has a mixed economy with a unique blend of socialism and capitalism. While the government maintains control over key sectors of the economy, such as banking and energy, it has also embraced market-oriented reforms and encouraged private enterprise.
These examples demonstrate the diverse ways in which countries can implement a mixed economic system. Each country strikes a balance between market forces and government intervention based on its own political, social, and economic priorities.
Pros of a Mixed Economic System
A mixed economic system combines elements of both a market economy and a planned economy. This type of system offers several advantages that contribute to its popularity in many countries around the world. Here are some of the key pros of a mixed economic system:
1. Economic Efficiency
One of the main advantages of a mixed economic system is its ability to achieve economic efficiency. By allowing market forces to determine the allocation of resources in certain sectors, the system promotes competition and innovation, leading to increased productivity and efficiency. At the same time, the government can step in and regulate certain industries or provide public goods and services that are not efficiently provided by the market.
2. Social Welfare
A mixed economic system also aims to provide social welfare by addressing income inequality and ensuring a certain level of social safety net. The government can implement policies such as progressive taxation and income redistribution to help reduce the gap between the rich and the poor. Additionally, it can provide public services like healthcare, education, and social security to ensure a basic standard of living for all citizens.
3. Stability and Flexibility
Another advantage of a mixed economic system is its ability to provide stability and flexibility. By combining elements of both market and planned economies, the system can adapt to changing economic conditions and mitigate the negative effects of economic downturns. The government can intervene during times of crisis to stabilize the economy and prevent excessive fluctuations, while still allowing market forces to operate in other sectors.
4. Innovation and Entrepreneurship
A mixed economic system encourages innovation and entrepreneurship by providing a supportive environment for businesses. While market forces drive competition and innovation, the government can also provide incentives and support for research and development, as well as protect intellectual property rights. This combination allows for a dynamic and innovative economy that can foster technological advancements and economic growth.
5. Balance of Power

In a mixed economic system, power is distributed between the government and the private sector, which helps prevent the concentration of power in either entity. This balance of power ensures that no single entity has complete control over the economy, reducing the risk of abuse and promoting a more democratic and equitable society.
| Pros of a Mixed Economic System |
|---|
| Economic Efficiency |
| Social Welfare |
| Stability and Flexibility |
| Innovation and Entrepreneurship |
| Balance of Power |
Cons of a Mixed Economic System
A mixed economic system, which combines elements of both a market economy and a planned economy, has its own set of disadvantages. While it offers certain benefits, there are also drawbacks that need to be considered.
- Lack of efficiency: One of the main criticisms of a mixed economic system is that it can be less efficient than a purely market-based system. The presence of government intervention and regulation can lead to inefficiencies and bureaucracy, which can hinder economic growth and productivity.
- Income inequality: Another drawback of a mixed economic system is the potential for income inequality. While the government may implement policies to redistribute wealth and provide social safety nets, there can still be significant disparities in income and wealth. This can lead to social unrest and dissatisfaction among the population.
- Political influence: In a mixed economic system, there is a risk of political influence in economic decision-making. Government intervention can be influenced by political considerations rather than economic efficiency, leading to suboptimal outcomes. This can result in favoritism towards certain industries or businesses, which can distort competition and hinder economic development.
- Dependency on government: A mixed economic system often relies on government intervention to correct market failures and provide public goods. However, this can create a dependency on the government, as individuals and businesses may become reliant on government support and subsidies. This can limit innovation and entrepreneurship, as individuals may be less motivated to take risks and pursue new opportunities.
- Complexity: The combination of market forces and government intervention in a mixed economic system can create a complex and often confusing environment for businesses and individuals. The presence of multiple regulations and policies can make it difficult to navigate and understand the economic landscape, which can hinder economic growth and investment.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
