Equity Compensation Definition

Equity compensation refers to a form of compensation that is given to employees in the form of ownership in the company. It is a way for companies to incentivize and reward their employees by giving them a stake in the company’s success.
How It Works
Equity compensation works by granting employees shares or stock options in the company. These shares or options can be granted as part of an initial compensation package or as a performance-based incentive. The value of the equity compensation is tied to the performance of the company’s stock.
When employees are granted equity compensation, they become partial owners of the company and have the potential to benefit from any increase in the company’s stock price. This gives employees a vested interest in the company’s success and aligns their incentives with the goals of the company.
Types of Equity
There are several types of equity compensation that companies can offer to their employees. These include:
- Restricted Stock Units (RSUs): These are units of company stock that are granted to employees, but are subject to certain restrictions, such as a vesting period.
- Employee Stock Purchase Plans (ESPPs): These plans allow employees to purchase company stock at a discounted price. ESPPs often have specific enrollment periods and contribution limits.
- Performance Shares: These are shares of company stock that are granted to employees based on the achievement of specific performance goals or targets.
Each type of equity compensation has its own unique features and benefits, and companies may choose to offer one or more of these options to their employees.
Overall, equity compensation is a valuable tool for companies to attract, retain, and motivate talented employees. It allows employees to share in the success of the company and can provide a significant financial incentive for their hard work and dedication.
Equity compensation is a form of employee compensation that provides employees with ownership in the company they work for. It is often used as a way to incentivize and reward employees for their contributions to the company’s success.
What is Equity Compensation?
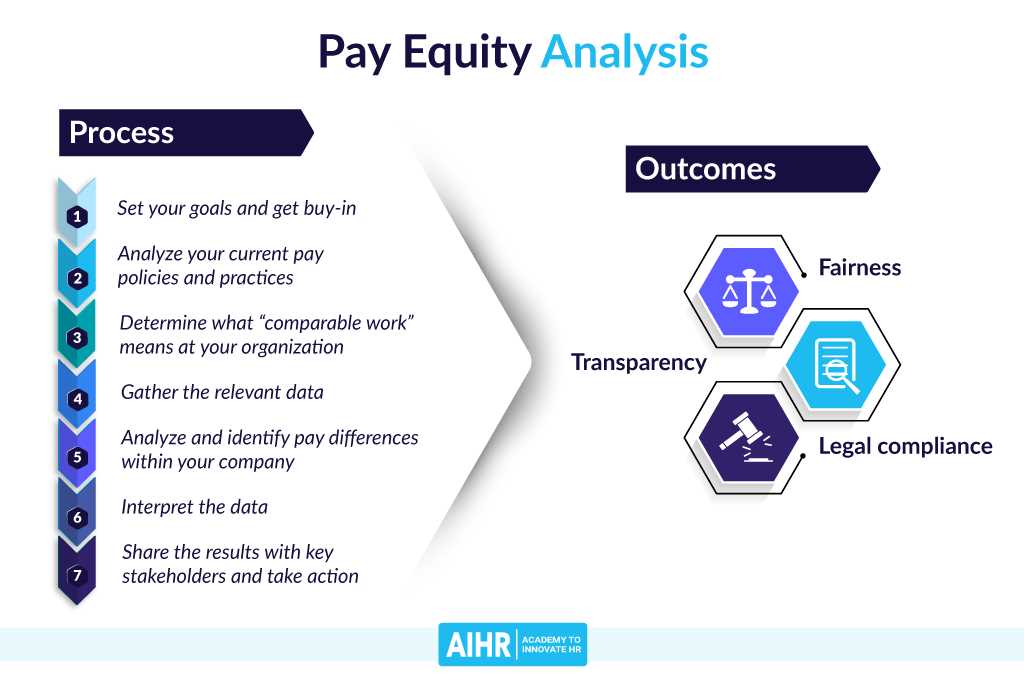
Equity compensation refers to the practice of granting employees shares of stock or other forms of ownership in a company. This can be done through various means, such as stock options, restricted stock units (RSUs), or employee stock purchase plans (ESPPs).
When employees receive equity compensation, they become shareholders in the company and have the potential to benefit financially from the company’s growth and success. This can be a powerful motivator for employees to work hard and contribute to the company’s overall performance.
How Does Equity Compensation Work?
Alternatively, employees may receive RSUs, which are units of stock that vest over time. Once the RSUs vest, the employee becomes the owner of the underlying shares of stock and can choose to sell them or hold onto them for potential future gains.
Types of Equity Compensation
There are several types of equity compensation that companies can offer to their employees. Some common types include:
- Stock Options: These give employees the right to purchase shares of stock at a specific price within a certain timeframe.
- Restricted Stock Units (RSUs): These are units of stock that vest over time and convert into shares of stock once they have vested.
- Employee Stock Purchase Plans (ESPPs): These allow employees to purchase shares of stock at a discounted price.
- Stock Appreciation Rights (SARs): These give employees the right to receive the appreciation in the value of a certain number of shares of stock.
Each type of equity compensation has its own unique features and benefits, and companies may choose to offer one or more types depending on their specific goals and objectives.
How Equity Compensation Works
Equity compensation is a form of remuneration that is offered to employees in the form of company stock or other equity instruments. It is a way for companies to incentivize and reward their employees by giving them a stake in the company’s success.
Equity compensation typically comes in the form of stock options, restricted stock units (RSUs), or employee stock purchase plans (ESPPs). Stock options give the employee the right to buy a certain number of shares at a specified price within a specified time period. RSUs are grants of company stock that vest over a certain period of time. ESPPs allow employees to purchase company stock at a discounted price through payroll deductions.
Once an employee receives equity compensation, they may choose to exercise their options or hold onto their shares. If the employee exercises their options, they can either sell the shares immediately or hold onto them in the hopes that the stock price will increase in the future. If the employee holds onto their shares, they become a shareholder of the company and may be entitled to voting rights and dividends.
However, equity compensation also comes with risks. The value of the stock can fluctuate, and employees may end up with shares that are worth less than the exercise price. Additionally, there may be tax implications for employees when they exercise their options or sell their shares.
Exploring the Mechanics of Equity Compensation
Equity compensation is a form of employee compensation that provides ownership in a company. It is commonly used by companies to attract and retain talented employees, as it offers the potential for financial gain and aligns the interests of employees with those of the company.
How Does Equity Compensation Work?
Equity compensation typically involves granting employees stock options, restricted stock units (RSUs), or stock appreciation rights (SARs). These forms of equity give employees the right to buy or receive shares of company stock at a predetermined price or upon meeting certain conditions.
RSUs, on the other hand, are grants of company stock that vest over time. Once the RSUs vest, employees receive the shares of stock outright. The value of the RSUs is typically based on the fair market value of the company’s stock at the time of vesting.
SARs are similar to stock options, but instead of granting the right to purchase stock, they provide employees with the opportunity to receive the increase in stock value in cash or additional stock.
Benefits and Considerations of Equity Compensation

Equity compensation can be highly beneficial for employees, as it allows them to share in the success of the company and potentially earn significant financial rewards. It also incentivizes employees to work towards the long-term growth and profitability of the company.
However, there are also considerations to keep in mind. The value of equity compensation is tied to the performance of the company’s stock, which can be volatile. Additionally, there may be restrictions on when and how employees can sell or transfer their equity, which can limit their ability to access the value of their compensation.
It is important for employees to carefully review the terms and conditions of their equity compensation plans and consider the risks and potential rewards before making decisions regarding their equity holdings.
Types of Equity
Equity compensation is a popular method for companies to reward their employees with ownership in the company. There are various types of equity that can be granted to employees, each with its own unique characteristics and benefits.
1. Stock Options
There are two types of stock options: incentive stock options (ISOs) and non-qualified stock options (NSOs). ISOs have certain tax advantages, but they also come with more restrictions. NSOs, on the other hand, are more flexible but are subject to regular income tax upon exercise.
2. Restricted Stock Units (RSUs)
RSUs are another common form of equity compensation. With RSUs, employees are granted a certain number of shares of company stock, but they do not actually receive the shares until a specified vesting period has passed. Once the RSUs vest, employees can sell the shares or hold onto them, depending on their preference.
One advantage of RSUs is that they have a fixed value, regardless of the company’s stock price. This provides employees with a guaranteed payout, even if the stock price decreases. However, RSUs are subject to ordinary income tax upon vesting.
3. Restricted Stock
Restricted stock is similar to RSUs, but instead of receiving units, employees are granted actual shares of company stock. These shares are typically subject to certain restrictions, such as a vesting period or performance-based criteria.
One benefit of restricted stock is that employees have voting rights and receive dividends on the shares, even before they fully vest. However, restricted stock is also subject to ordinary income tax upon vesting.
4. Employee Stock Purchase Plans (ESPPs)
ESPPs allow employees to purchase company stock at a discounted price, usually through payroll deductions. These plans often have specific enrollment periods and may have a maximum limit on the amount of stock that can be purchased.
One advantage of ESPPs is that they provide employees with an opportunity to buy company stock at a lower price, potentially allowing them to benefit from any future increase in the stock price. However, the discount received through an ESPP is subject to ordinary income tax.
Overall, the types of equity compensation mentioned above offer employees the opportunity to share in the success of the company and potentially benefit from its growth. However, it is important for employees to understand the specific terms and tax implications associated with each type of equity compensation.
Exploring Different Forms of Equity Compensation
Equity compensation is a form of compensation that is given to employees in the form of ownership in the company. There are several different forms of equity compensation that companies can offer to their employees.
Another form of equity compensation is restricted stock units (RSUs). RSUs are units of company stock that are granted to employees, but they are not immediately vested. Instead, employees must wait for a certain period of time before they can receive the stock. Once the RSUs vest, employees can either sell the stock or hold onto it.
Employee stock purchase plans (ESPPs) are another form of equity compensation. ESPPs allow employees to purchase company stock at a discounted price. This can be a great way for employees to invest in the company and potentially benefit from any increase in the stock price.
Performance shares are another form of equity compensation that is based on the company’s performance. These shares are granted to employees based on certain performance goals or metrics. If the company meets or exceeds these goals, employees can receive additional shares of stock.
Finally, there are employee stock ownership plans (ESOPs), which are a type of retirement plan. ESOPs allow employees to become owners of the company through the purchase of company stock. This can provide employees with a sense of ownership and can also be a tax-efficient way to save for retirement.
Overall, there are many different forms of equity compensation that companies can offer to their employees. Each form has its own advantages and disadvantages, and it is important for employees to understand the details of each before making any decisions.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
