What is Asset Liability Management?

Asset Liability Management (ALM) is a strategic approach used by financial institutions to manage the risks associated with their assets and liabilities. It involves the coordination of various factors, including interest rate risk, liquidity risk, and credit risk, to ensure that the institution’s assets and liabilities are properly aligned.
The primary goal of ALM is to optimize the balance between the institution’s assets and liabilities to minimize risk and maximize profitability. This is achieved by carefully monitoring and managing the various risks that the institution faces.
ALM involves a comprehensive analysis of the institution’s balance sheet, including its assets, liabilities, and off-balance sheet items. It takes into account the maturity, interest rate sensitivity, and credit quality of these items to determine the overall risk profile of the institution.
Effective ALM strategies involve the development and implementation of risk management policies and procedures. These strategies may include hedging techniques, such as interest rate swaps or options, to mitigate interest rate risk. They may also involve the use of liquidity management tools, such as cash flow forecasting and contingency funding plans, to manage liquidity risk.
Furthermore, ALM requires ongoing monitoring and evaluation of the institution’s risk profile. This includes regular stress testing and scenario analysis to assess the potential impact of adverse market conditions on the institution’s financial position.
The Meaning of Asset Liability Management
Asset Liability Management (ALM) is a crucial financial management strategy that helps organizations effectively manage their assets and liabilities. It involves the process of matching the maturity and cash flow characteristics of assets and liabilities to ensure the organization’s financial stability and minimize risks.
ALM plays a vital role in various industries, including banking, insurance, and investment management. It enables organizations to assess and control their exposure to interest rate, liquidity, and credit risks. By aligning assets and liabilities, organizations can optimize their financial performance and ensure they have sufficient funds to meet their obligations.
Asset Liability Management comprises two main components: assets and liabilities.
Assets: Assets refer to the financial resources owned by an organization, including cash, investments, loans, and properties. These assets generate income and are essential for the organization’s operations. Effective asset management involves analyzing the risk and return characteristics of different assets and making informed investment decisions.
Liabilities: Liabilities represent the financial obligations of an organization, such as loans, bonds, and deposits. Managing liabilities involves assessing the organization’s borrowing needs, determining the appropriate sources of funding, and monitoring the repayment terms and interest rates associated with these liabilities.
The Importance of Asset Liability Management
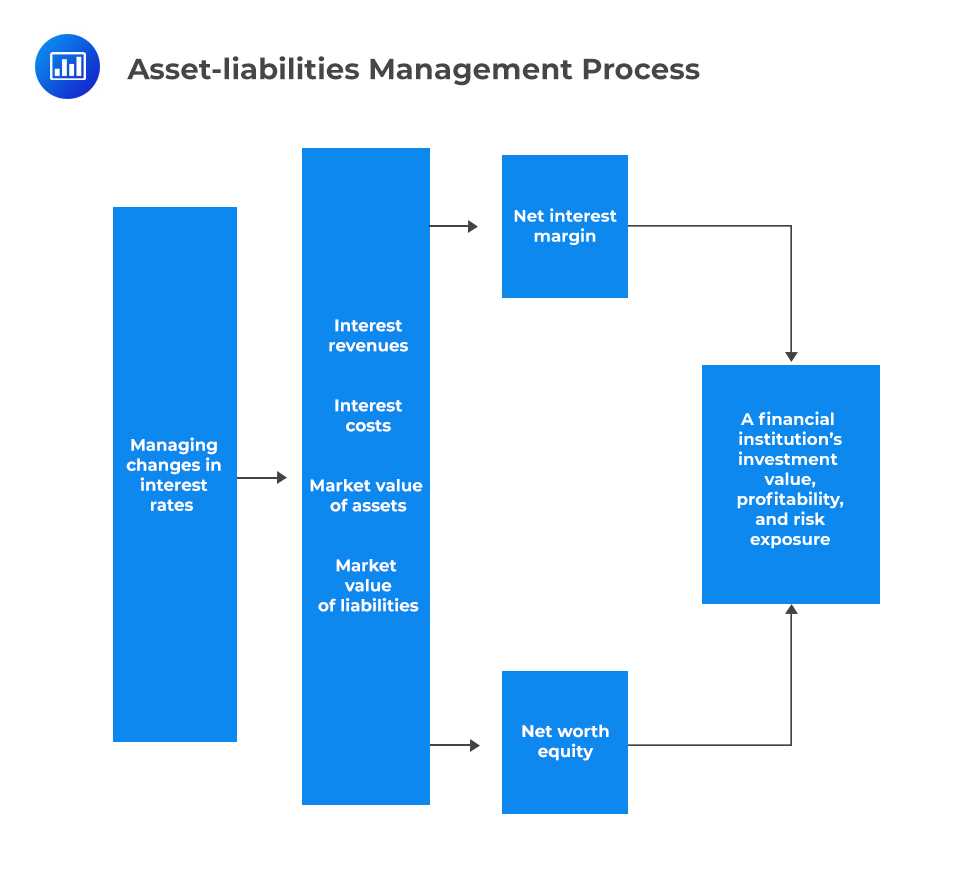
Proper asset liability management is crucial for the long-term sustainability and success of an organization. It helps organizations mitigate risks, optimize their balance sheet, and enhance their financial performance. Here are some key reasons why asset liability management is important:
- Risk Management: ALM enables organizations to identify and manage various risks, including interest rate risk, liquidity risk, and credit risk. By aligning assets and liabilities, organizations can minimize the impact of these risks on their financial stability.
- Optimal Funding: Effective asset liability management helps organizations determine the optimal mix of funding sources. It ensures that the organization has sufficient funds to meet its obligations while minimizing the cost of borrowing.
- Strategic Decision Making: ALM provides organizations with valuable insights into their financial position and cash flow dynamics. This information helps organizations make informed strategic decisions, such as expanding operations, entering new markets, or diversifying their investment portfolio.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many industries, such as banking and insurance, have strict regulatory requirements regarding capital adequacy and risk management. Proper asset liability management ensures organizations comply with these regulations and maintain a strong financial position.
Effective Strategies for Asset Liability Management
Asset liability management (ALM) is a crucial practice for any organization, especially in the field of accounting. It involves managing the assets and liabilities of a company in order to ensure financial stability and minimize risk. To effectively carry out ALM, organizations need to implement various strategies that align with their goals and objectives.
2. Cash Flow Management: Managing cash flow is vital for effective ALM. Organizations need to ensure that they have enough cash on hand to meet their financial obligations. This involves monitoring cash inflows and outflows, forecasting future cash flows, and implementing strategies to optimize cash management.
3. Diversification: Diversifying assets and liabilities is another key strategy for effective ALM. By spreading out investments and liabilities across different categories, organizations can reduce the impact of market fluctuations and minimize risk. This can be achieved by investing in a variety of asset classes, diversifying funding sources, and maintaining a balanced portfolio.
4. Interest Rate Risk Management: Interest rate risk is a significant factor in ALM, especially for organizations that have a large amount of debt or rely on interest income. Effective interest rate risk management involves monitoring interest rate movements, analyzing their impact on the organization’s financial position, and implementing strategies to mitigate the risks. This may include hedging strategies, refinancing options, or adjusting the organization’s investment portfolio.
5. Stress Testing: Stress testing is a valuable tool for assessing the resilience of an organization’s assets and liabilities under adverse conditions. By subjecting the organization’s financial position to various stress scenarios, organizations can identify vulnerabilities and develop strategies to address them. This helps organizations prepare for unexpected events and ensures their financial stability in challenging times.
6. Regular Monitoring and Review: Finally, effective ALM requires regular monitoring and review of the organization’s financial position. This involves analyzing financial statements, monitoring key performance indicators, and assessing the effectiveness of implemented strategies. By regularly reviewing the organization’s ALM practices, organizations can identify areas for improvement and make necessary adjustments to ensure long-term financial stability.
The Importance of Asset Liability Management in Accounting
Asset Liability Management (ALM) plays a crucial role in the field of accounting. It involves managing the assets and liabilities of a company to ensure its financial stability and profitability. ALM helps businesses to effectively allocate their resources and make informed decisions regarding their financial obligations.
Asset Liability Management refers to the process of monitoring and controlling the risks associated with a company’s assets and liabilities. It involves assessing the cash flows, interest rate risks, and market fluctuations to minimize potential losses and maximize returns. ALM helps businesses to maintain a balance between their assets and liabilities, ensuring that they have enough liquidity to meet their financial obligations.
The Meaning of Asset Liability Management
Effective Strategies for Asset Liability Management
There are several strategies that businesses can employ to effectively manage their assets and liabilities:
- Asset-Liability Matching: This strategy involves matching the maturities and cash flows of assets and liabilities. By aligning the timing of cash inflows and outflows, businesses can reduce the risk of liquidity shortages.
- Interest Rate Risk Management: This strategy involves analyzing the interest rate sensitivity of assets and liabilities. By hedging against interest rate fluctuations, businesses can protect themselves from potential losses.
- Diversification: This strategy involves diversifying the portfolio of assets and liabilities. By spreading the risk across different investments, businesses can minimize the impact of any single asset or liability.
- Stress Testing: This strategy involves simulating various scenarios to assess the impact on assets and liabilities. By stress testing their financial position, businesses can identify potential vulnerabilities and take proactive measures to mitigate risks.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
