A Guide for Investors
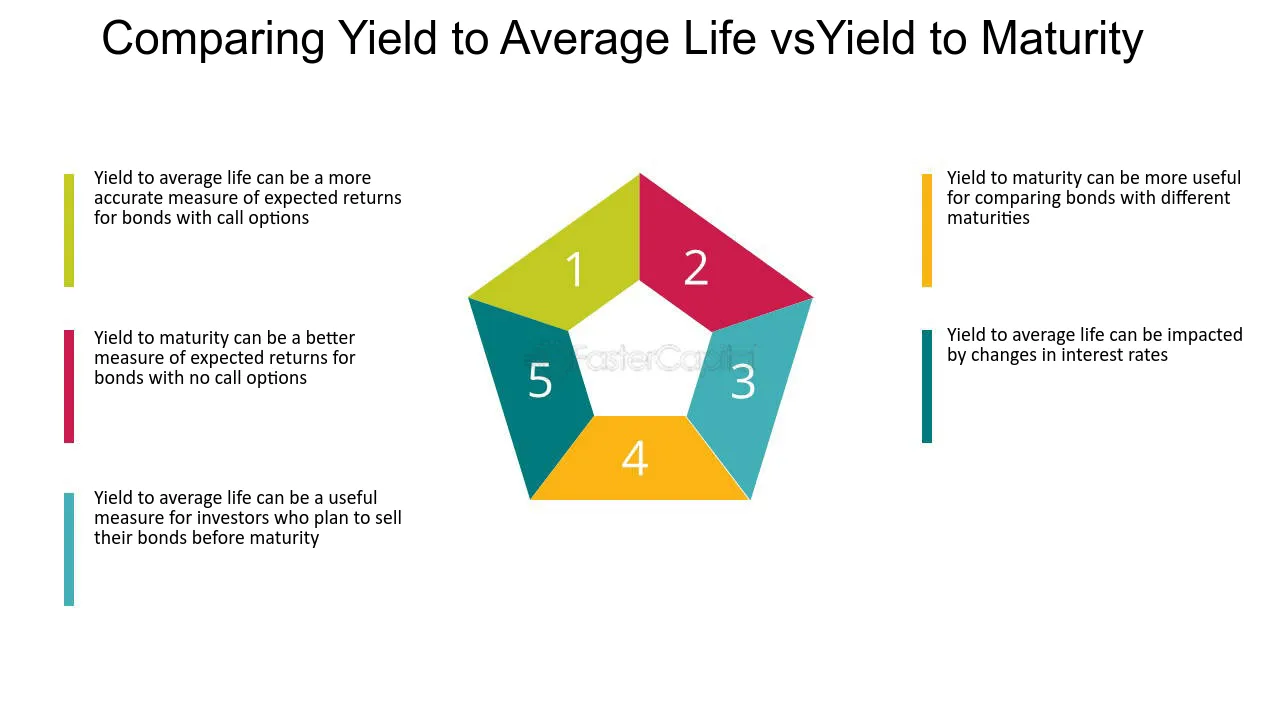
What is Yield-to-Average Life?
How Does Yield-to-Average Life Work?
To calculate yield-to-average life, the cash flows from the investment are projected over the life of the instrument. These cash flows are then discounted back to present value using a discount rate that reflects the time value of money. The average yield is then calculated based on these discounted cash flows.
Benefits of Yield-to-Average Life
Additionally, yield-to-average life can help investors assess the risk associated with a particular investment. By analyzing the timing and amount of cash flows, investors can better understand the potential for changes in interest rates or other factors that may impact the investment’s performance.
Considerations for Investors
While yield-to-average life can be a useful tool for investors, it is important to consider other factors when making investment decisions. Investors should also assess the creditworthiness of the issuer, the liquidity of the investment, and any potential tax implications.
What is Yield-to-Average Life?
When investors buy bonds or other fixed income securities, they typically receive regular interest payments and the return of their principal at maturity. However, the actual timing of these payments can vary, as some bonds may have call provisions that allow the issuer to redeem the bonds before maturity.
Yield-to-Average Life takes into account these potential variations in payment timing and calculates the yield based on the average time it takes for the investor to receive the payments. This provides a more accurate measure of the expected return on the investment.
How Does Yield-to-Average Life Work?
Yield-to-Average Life (YAL) is a measure used by investors to assess the potential return on investment for fixed income securities. It takes into account the expected cash flows and the timing of those cash flows, providing a more accurate representation of the investment’s yield.
When calculating YAL, the investor considers the average life of the security, which is the weighted average of the time it takes to receive the cash flows. This average life is calculated by multiplying the time to each cash flow by the present value of that cash flow, and then summing up these values. The resulting sum is divided by the total present value of all the cash flows.
By using YAL, investors can better understand the potential return on their investment and make more informed decisions. It allows them to compare different fixed income securities based on their expected yield, taking into account the timing of the cash flows.
Example:
Let’s say an investor is considering two fixed income securities. Security A has a yield of 4% and a maturity of 10 years, while Security B has a yield of 3% and a maturity of 5 years. At first glance, Security A may seem like the better investment due to its higher yield. However, by calculating the YAL, the investor can determine the actual potential return.
Assuming that Security A has cash flows of $100 per year for the first 5 years and $200 per year for the next 5 years, and Security B has cash flows of $150 per year for the entire 5-year period, the YAL for Security A would be calculated as follows:
| Year | Cash Flow | Present Value | Time Weighted Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1-5 | $100 | $91.74 | $458.70 |
| 6-10 | $200 | $164.70 | $823.50 |
| Total | $256.44 | $1,282.20 |
The YAL for Security A would be calculated as $1,282.20 divided by the total present value of all the cash flows, which is $256.44. This gives a YAL of approximately 5%. Comparing this to the yield of Security B, which is 3%, the investor can see that Security A may actually provide a higher potential return.
Benefits of Yield-to-Average Life
| 1. Enhanced Yield Calculation | YAL takes into account the average life of a bond, which allows for a more accurate calculation of yield. This is particularly useful for bonds with call options or prepayment risks, as it provides a better estimate of the actual return an investor can expect. |
| 2. Risk Assessment | |
| 3. Portfolio Management | YAL can be a useful tool for portfolio managers in optimizing their bond portfolios. By considering the average life of bonds, managers can strategically allocate their investments to balance risk and return, ensuring a more efficient portfolio. |
| 4. Comparability | YAL allows for easier comparison between different bonds, as it provides a standardized measure of yield that takes into account the average life. This makes it easier for investors to evaluate and compare different investment options. |
| 5. Long-Term Investment Perspective | YAL encourages investors to take a long-term perspective when evaluating bond investments. By considering the average life, investors can better assess the potential returns over the life of the bond, rather than focusing solely on short-term yield. |
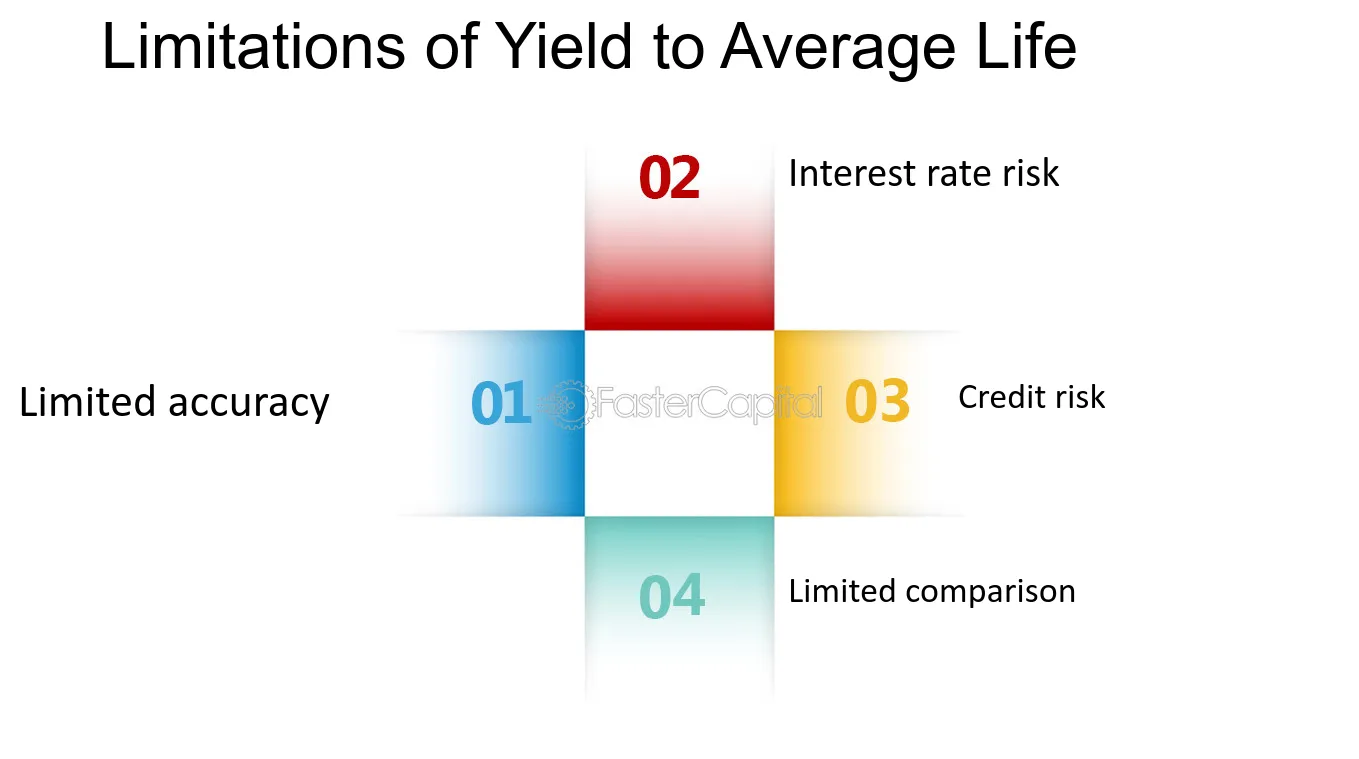
Considerations for Investors
Risk
Investors should carefully assess the level of risk associated with yield-to-average life investments. While these investments can offer attractive yields, they may also carry a higher level of risk compared to other fixed income options. It is important to evaluate the creditworthiness of the issuer and the overall market conditions before making any investment decisions.
Time Horizon
Market Conditions
The prevailing market conditions can have a significant impact on the performance of yield-to-average life investments. Investors should stay informed about the current economic environment, interest rate trends, and market volatility. This information can help investors make more informed decisions and manage their investment risks effectively.
Overall, yield-to-average life can be a valuable investment strategy for investors seeking higher yields in the fixed income market. However, it is important to carefully consider the risks, time horizon, and market conditions before making any investment decisions. By conducting thorough research and seeking professional advice, investors can make informed choices that align with their financial goals and risk tolerance.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
