What is the Term Structure of Interest Rates?
The yield curve is typically upward sloping, which means that longer-term debt securities have higher interest rates compared to shorter-term debt securities. This is because investors generally require a higher return for tying up their money for a longer period of time. However, there are instances when the yield curve can be flat or even inverted, indicating different market conditions and expectations.
Components of the Term Structure
The term structure of interest rates is composed of several components:
- Spot Rates: These are the interest rates for debt securities with a specific maturity date. Spot rates can be used to calculate the present value of future cash flows.
- Forward Rates: These are the implied interest rates for future periods. Forward rates can be derived from spot rates and provide insight into market expectations for future interest rates.
- Yield Curve: This is a graphical representation of the term structure of interest rates. It shows the relationship between the interest rates and the time to maturity of debt securities.
Importance of the Term Structure
The term structure of interest rates is important for several reasons:
- Interest Rate Expectations: The term structure provides information about market expectations for future interest rates. This can be useful for investors and policymakers in making decisions regarding investments, borrowing, and monetary policy.
- Valuation of Securities: The term structure is used to value debt securities. By discounting future cash flows using the appropriate spot rates, investors can determine the fair value of these securities.
- Yield Curve Analysis: The shape of the yield curve can provide insights into the current and future state of the economy. For example, an inverted yield curve, where short-term interest rates are higher than long-term interest rates, is often seen as a sign of an impending economic downturn.
Factors Affecting the Term Structure of Interest Rates

The term structure of interest rates refers to the relationship between the interest rates and the time to maturity of debt instruments. It is important to understand the factors that influence the term structure of interest rates as it can have significant implications for investors and the overall economy.
1. Economic Conditions
2. Inflation Expectations
Inflation expectations also play a crucial role in determining the term structure of interest rates. If investors expect higher inflation in the future, they will demand higher interest rates to compensate for the loss of purchasing power. On the other hand, if inflation is expected to be low, interest rates will be lower as investors do not require as much compensation for inflation risk.
3. Monetary Policy
The actions of central banks, particularly changes in monetary policy, can have a significant impact on the term structure of interest rates. Central banks use various tools, such as adjusting interest rates and implementing quantitative easing, to influence the cost of borrowing and stimulate or cool down the economy. Changes in monetary policy can lead to shifts in the term structure of interest rates.
4. Market Supply and Demand
The supply and demand dynamics in the bond market also affect the term structure of interest rates. When there is high demand for bonds, prices increase, and yields decrease. Conversely, when there is low demand for bonds, prices decrease, and yields increase. Changes in market supply and demand can lead to shifts in the term structure of interest rates.
5. Credit Risk
Credit risk, or the risk of default, is another factor that affects the term structure of interest rates. Bonds with higher credit risk typically have higher interest rates to compensate investors for the increased risk. Conversely, bonds with lower credit risk tend to have lower interest rates. The perception of credit risk can lead to changes in the term structure of interest rates.
1. Predicting Future Interest Rates
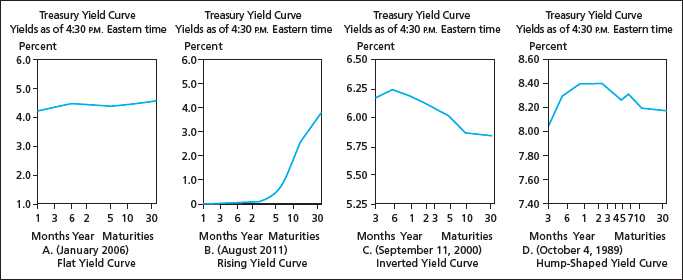
One of the key reasons why the term structure of interest rates is important is its ability to provide information about future interest rate movements. By analyzing the yield curve, which represents the term structure graphically, investors can gain insights into the market’s expectations for future interest rates.
For example, if the yield curve is upward sloping, with long-term interest rates higher than short-term rates, it suggests that market participants expect interest rates to increase in the future. Conversely, if the yield curve is downward sloping, with long-term rates lower than short-term rates, it indicates expectations of future interest rate decreases.
2. Assessing Economic Conditions
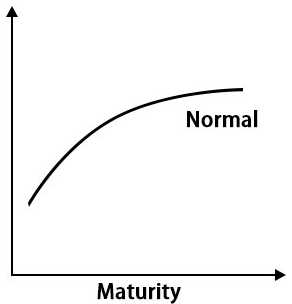
The term structure of interest rates also serves as an indicator of economic conditions. Changes in the shape of the yield curve can provide valuable information about the state of the economy and its future prospects.
For instance, a steepening yield curve, where the spread between long-term and short-term rates widens, often indicates improving economic conditions. This suggests that investors are demanding higher compensation for taking on longer-term investments, which reflects optimism about economic growth and inflation expectations.
On the other hand, a flattening yield curve, where the spread between long-term and short-term rates narrows, can signal a weakening economy. This indicates that investors are less optimistic about future growth and inflation, leading to lower long-term interest rates.
3. Assessing Risk and Pricing Bonds
The term structure of interest rates is also crucial for assessing risk and pricing bonds. Investors use the yield curve to determine the appropriate discount rate for valuing bonds with different maturities.
Typically, longer-term bonds have higher yields to compensate investors for the additional risk and uncertainty associated with longer maturities. By comparing the yields of bonds with different maturities, investors can assess the relative riskiness of these investments and make informed decisions about their portfolio allocations.
Moreover, the term structure of interest rates can help in pricing bonds. By discounting the future cash flows of a bond using the appropriate discount rate derived from the yield curve, investors can determine the fair value of the bond and make buy or sell decisions accordingly.
| Predicting future interest rates |
| Assessing economic conditions |
| Assessing risk and pricing bonds |

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
