What is Tax Relief and How Does It Work?
Tax relief refers to any measure taken by the government to reduce the tax burden on individuals or businesses. It is designed to provide financial assistance and support to taxpayers who may be facing economic hardship or other challenges.
There are several ways in which tax relief can be implemented. One common method is through tax deductions, which allow taxpayers to subtract certain expenses or contributions from their taxable income. For example, individuals may be able to deduct expenses related to education, healthcare, or charitable donations.
Another form of tax relief is tax credits, which directly reduce the amount of tax owed. Tax credits are often targeted at specific groups or activities, such as homeownership, renewable energy investments, or child care expenses. These credits can significantly lower a taxpayer’s overall tax liability.
In addition to deductions and credits, governments may also offer tax relief through tax exemptions or exclusions. These provisions allow certain types of income or transactions to be excluded from taxation altogether. For example, some countries provide tax exemptions for income earned from investments in specific industries or regions.
It is important to note that tax relief measures can vary widely between countries and jurisdictions. Each government has its own set of rules and regulations regarding tax relief, and eligibility criteria may differ depending on the specific circumstances of the taxpayer.
Benefits of Tax Relief
Tax relief can provide several benefits to individuals and businesses. Firstly, it can help stimulate economic growth by putting more money into the hands of taxpayers. This increased disposable income can be used for consumption, investment, or savings, all of which can contribute to economic activity.
Secondly, tax relief can help alleviate financial burdens on vulnerable populations. By targeting specific groups or activities, tax relief measures can provide targeted assistance to those who need it most. For example, tax credits for low-income families can help reduce poverty and improve social welfare.
Lastly, tax relief can incentivize certain behaviors or activities that are deemed beneficial to society. For example, tax credits for energy-efficient home improvements can encourage individuals to adopt more sustainable practices. Similarly, tax incentives for small businesses can promote entrepreneurship and job creation.
Conclusion
Different Types of Tax Relief
1. Tax deductions: Tax deductions are expenses that can be subtracted from your taxable income, reducing the amount of tax you owe. Common tax deductions include mortgage interest, medical expenses, and charitable contributions.
2. Tax credits: Tax credits are direct reductions in the amount of tax you owe. Unlike deductions, which reduce your taxable income, tax credits directly reduce the amount of tax you owe. Examples of tax credits include the child tax credit, earned income tax credit, and education tax credits.
3. Tax exemptions: Tax exemptions allow you to exclude certain income or expenses from your taxable income. For example, individuals may be eligible for a personal exemption, while businesses may be eligible for exemptions on certain types of income.
4. Tax deferrals: Tax deferrals allow you to postpone paying taxes on certain income or gains until a later date. This can provide temporary relief by allowing you to defer the tax liability to a future year when you may be in a lower tax bracket or have more financial resources available.
5. Tax abatement: Tax abatement is a reduction or elimination of taxes owed. This type of tax relief is often granted to individuals or businesses in certain situations, such as economic development projects or disaster recovery efforts.
6. Tax incentives: Tax incentives are designed to encourage specific behaviors or investments by providing tax benefits. These incentives can include tax credits, deductions, or exemptions for activities such as investing in renewable energy, hiring veterans, or starting a business in an economically disadvantaged area.
7. Tax amnesty: Tax amnesty programs allow individuals or businesses to come forward and pay outstanding taxes without penalties or interest. These programs are typically offered for a limited time and can provide relief for those who may have fallen behind on their tax obligations.
Real-Life Examples of Tax Relief
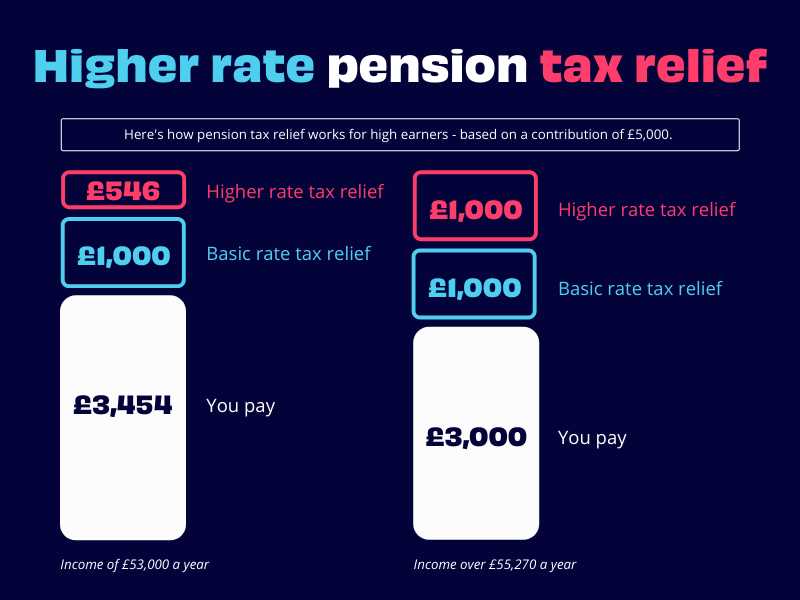
1. Tax Credits for Education
One common form of tax relief is the tax credits available for education expenses. For example, the American Opportunity Tax Credit allows eligible students to claim a credit for qualified education expenses, such as tuition and fees. This tax credit can significantly reduce the amount of tax owed and even provide a refund if the credit exceeds the tax liability.
2. Small Business Deductions
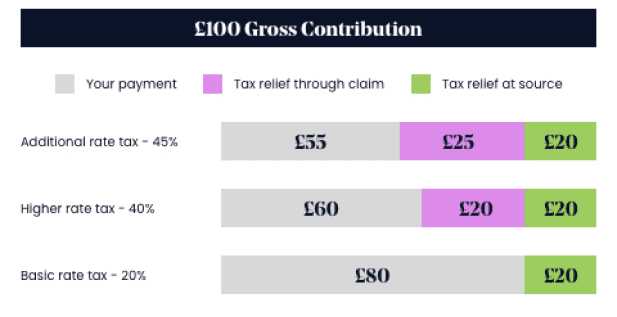
Small businesses often benefit from various tax deductions that can help reduce their tax burden. For instance, the Section 179 deduction allows businesses to deduct the full cost of qualifying equipment and software purchased or financed during the tax year. This deduction can provide substantial tax relief by lowering the taxable income of the business.
Additionally, small businesses may also qualify for the Qualified Business Income deduction, which allows eligible businesses to deduct up to 20% of their qualified business income. This deduction can result in significant tax savings for small business owners.
3. Tax Relief for Disaster Victims
In the event of a natural disaster, tax relief measures are often implemented to assist affected individuals and businesses. For example, after a hurricane or wildfire, the government may provide tax relief by allowing affected taxpayers to claim casualty loss deductions for property damage not covered by insurance. This can help alleviate the financial burden caused by the disaster.
4. Tax Exemptions for Nonprofit Organizations
Nonprofit organizations are often eligible for tax exemptions, which can provide significant tax relief. These organizations are exempt from paying federal income tax and, in some cases, state and local taxes as well. This tax relief allows nonprofits to allocate more funds towards their charitable activities and further their mission.
Overall, these real-life examples demonstrate the importance and impact of tax relief measures. Whether it’s through tax credits, deductions, or exemptions, tax relief can provide much-needed financial assistance to individuals, businesses, and communities.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
