What are Operating Earnings?
Operating earnings provide insight into the profitability and efficiency of a company’s day-to-day operations. By focusing on the core business activities, operating earnings allow investors and analysts to assess how well a company is able to generate profits from its primary operations.
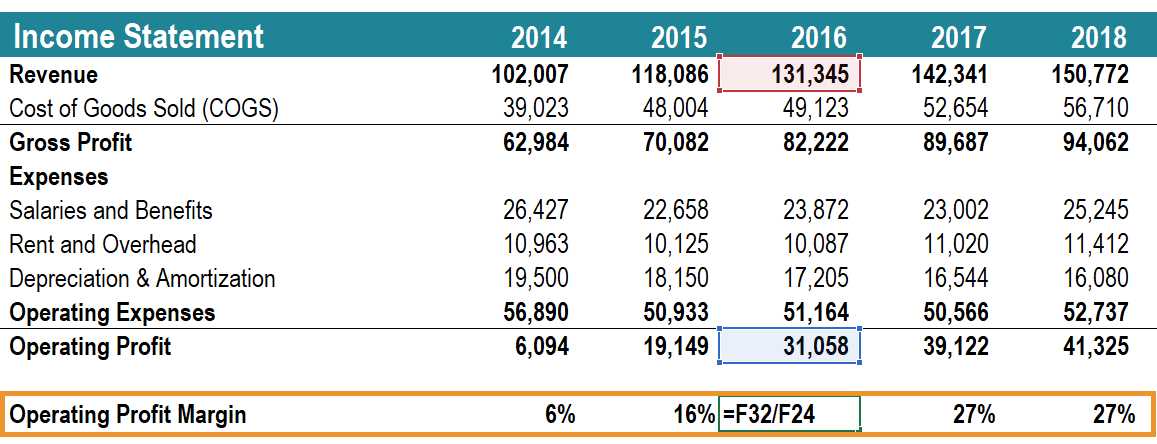
Calculation of Operating Earnings
The calculation of operating earnings starts with the company’s revenue or sales. From the revenue, all the direct costs associated with the production or delivery of goods or services are subtracted to arrive at the gross profit. These direct costs include the cost of goods sold, direct labor expenses, and direct overhead costs.
After calculating the gross profit, operating expenses such as salaries, rent, utilities, marketing expenses, and research and development costs are deducted to determine the operating income. Operating expenses are the costs incurred in running the day-to-day operations of the business.
The formula for calculating operating earnings is:
Importance of Operating Earnings
Comparing the operating earnings of a company over time or against industry peers can help identify trends and evaluate the company’s performance relative to its competitors. It can also be used to assess the effectiveness of cost management and operational efficiency.
Furthermore, operating earnings are often used in financial ratios and valuation models to determine the value of a company’s stock or to assess its financial health.
Calculating Operating Earnings

To calculate operating earnings, you need to gather the necessary financial information from a company’s income statement. The income statement provides a breakdown of the company’s revenue, COGS, and operating expenses.
Here is the formula to calculate operating earnings:
Let’s break down each component of the formula:
- Total Revenue: This is the total amount of money generated from the company’s sales of goods or services. It includes all sales revenue, such as product sales, service fees, and licensing fees.
- COGS: This is the direct cost associated with producing or delivering the company’s goods or services. It includes the cost of raw materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead.
- Operating Expenses: These are the costs incurred in running the day-to-day operations of the business. They include expenses such as salaries, rent, utilities, marketing, and administrative expenses.
By subtracting the COGS and operating expenses from the total revenue, you can determine the operating earnings of a company. This measure provides insight into the profitability of a company’s core operations, excluding any non-operating or one-time expenses.
Operating earnings are important because they help investors and analysts assess the financial health and performance of a company. It allows them to evaluate the company’s ability to generate profits from its core business activities and compare it to industry peers.
It’s worth noting that operating earnings may be adjusted for non-recurring items or extraordinary expenses to provide a clearer picture of a company’s ongoing profitability. These adjustments are typically made to exclude one-time events or non-operating activities that are not reflective of the company’s core operations.
Importance of Operating Earnings
Operating earnings play a crucial role in evaluating the financial performance of a company. They provide valuable insights into the core operations of a business and help investors, analysts, and stakeholders assess its profitability and efficiency.
1. Measure of Profitability: Operating earnings serve as a key indicator of a company’s profitability. By excluding non-operating expenses and income, such as interest, taxes, and one-time gains or losses, operating earnings provide a more accurate representation of the company’s ability to generate profits from its core operations.
2. Comparison Across Industries: Operating earnings allow for meaningful comparisons of profitability across different industries. Since they focus on the core operations of a business, they provide a standardized measure that can be used to evaluate companies in various sectors. This enables investors to assess the relative performance of companies within the same industry or sector.
3. Evaluation of Efficiency: Operating earnings also help in assessing a company’s operational efficiency. By analyzing the relationship between operating earnings and revenue, investors can determine how effectively a company is utilizing its resources to generate profits. A higher operating margin indicates better efficiency, while a lower margin may suggest inefficiencies or higher costs.
4. Forecasting Future Performance: Operating earnings provide valuable information for forecasting a company’s future performance. By analyzing trends in operating earnings over time, investors can gain insights into the company’s growth prospects, profitability, and ability to generate sustainable earnings. This information is crucial for making informed investment decisions.
5. Investor Confidence: Operating earnings are a key factor in building investor confidence. A company with consistent and growing operating earnings is likely to attract more investors and enjoy a higher valuation in the market. Investors view strong operating earnings as a sign of a well-managed company with a sustainable business model.
Illustration of Operating Earnings

Let’s take a closer look at an example to illustrate how operating earnings are calculated and what they represent. Imagine a company called XYZ Inc., which manufactures and sells electronic devices. XYZ Inc. reports the following financial information:
– Revenue from sales: $1,000,000
– Cost of goods sold: $600,000
– Selling, general, and administrative expenses: $200,000
– Depreciation and amortization expenses: $50,000
Operating earnings represent the profitability of a company’s core operations, excluding non-operating items such as interest income, interest expenses, and taxes. It provides insight into how well a company is generating profits from its primary business activities.
Investors and analysts often use operating earnings as a key metric to evaluate a company’s financial performance and compare it to its competitors. It allows them to assess the company’s ability to generate profits from its core operations and make informed investment decisions.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
