Definition of Exempt Income
Exempt income refers to the portion of an individual’s income that is not subject to taxation by the government. It is a category of income that is excluded from the calculation of taxable income, resulting in a lower tax liability for the individual.
There are various types of exempt income, and the specific rules governing what qualifies as exempt income can vary depending on the country and its tax laws. In general, exempt income can include certain types of government benefits, such as social security payments, welfare benefits, and disability benefits.
Other examples of exempt income may include certain types of investment income, such as interest earned on municipal bonds, dividends from certain types of savings accounts, and capital gains from the sale of a primary residence.
Exempt income can also include certain types of insurance proceeds, such as life insurance death benefits and certain types of disability insurance payments. Additionally, certain educational grants and scholarships may be considered exempt income.
It is important to note that while exempt income is not subject to income tax, it may still be subject to other types of taxes, such as property taxes or sales taxes. Additionally, the rules and regulations regarding exempt income can be complex, so it is advisable to consult with a tax professional or accountant to ensure compliance with the applicable laws and regulations.
Examples of Exempt Income
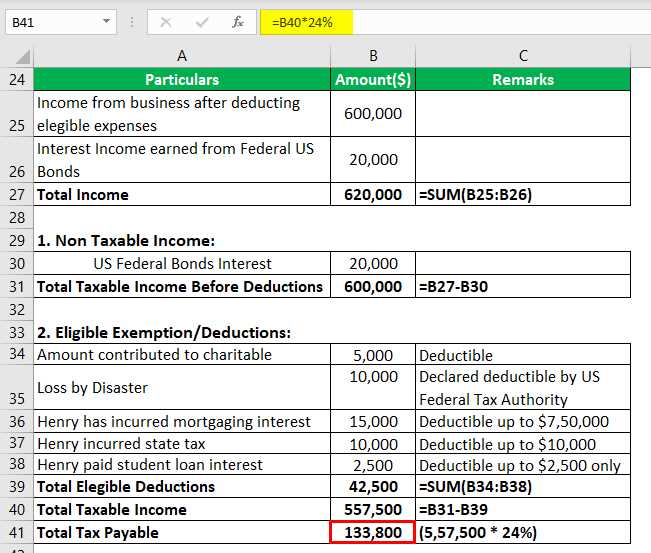
Exempt income refers to the types of income that are not subject to taxation. These income sources are excluded from the calculation of taxable income, resulting in a lower tax liability for individuals or businesses. Here are some examples of exempt income:
| Income Source | Description |
|---|---|
| Interest from Municipal Bonds | Income earned from municipal bonds issued by state or local governments is generally exempt from federal income tax. This exemption encourages investment in public infrastructure projects. |
| Qualified Roth IRA Distributions | Withdrawals from a Roth IRA account that meet certain criteria, such as being held for at least five years and being taken after the age of 59 ½, are tax-free. This provides individuals with a tax-advantaged way to save for retirement. |
| Life Insurance Proceeds | When a beneficiary receives a payout from a life insurance policy due to the death of the insured, the proceeds are generally exempt from income tax. This ensures that the funds received are not further burdened by taxation during a difficult time. |
| Gifts and Inheritances | Gifts and inheritances received by individuals are typically not considered taxable income. This allows for the transfer of wealth between generations without incurring additional tax liabilities. |
| Qualified Disability Benefits | Income received as disability benefits, such as Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) or Supplemental Security Income (SSI), is often exempt from federal income tax. This exemption recognizes the financial challenges faced by individuals with disabilities. |
It is important to note that while these examples represent common types of exempt income, there may be additional specific exemptions and rules that vary depending on the jurisdiction and individual circumstances. It is always advisable to consult with a tax professional or refer to the relevant tax laws to determine the exact treatment of different income sources.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
