Calculation Methods and Formulas
There are two common calculation methods used in amortization schedules: the straight-line method and the declining balance method.
Straight-Line Method:
Declining Balance Method:
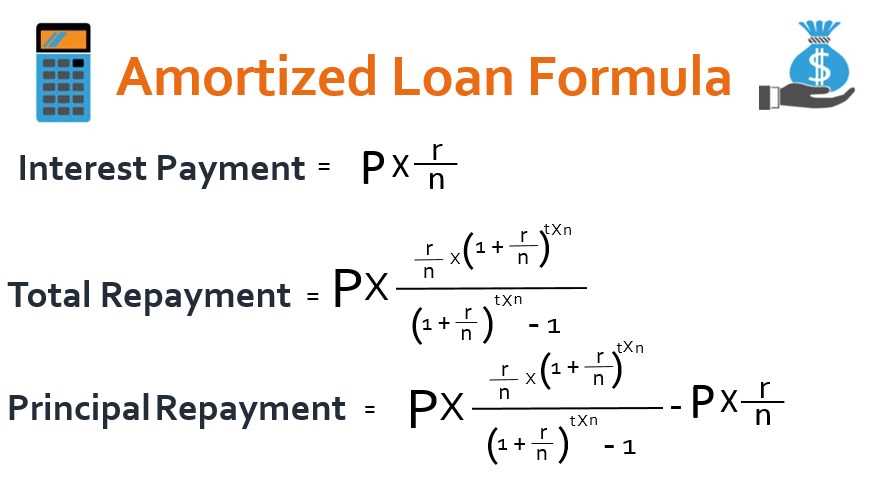
For the straight-line method, the formula is:
Payment Amount = (Loan Principal + Total Interest) / Number of Payments
For the declining balance method, the formula is more complex and involves calculating the interest expense for each period based on the remaining loan principal.
Importance in Accounting
Accurate Financial Reporting
By utilizing amortization schedules, accountants can accurately report the value of assets and liabilities over time. This is essential for financial statements, as it allows stakeholders, such as investors and creditors, to understand the true value and financial health of a company.
Amortization schedules ensure that the depreciation or reduction in value of assets is properly accounted for. This helps prevent overstatement or understatement of asset values, which can distort financial statements and mislead stakeholders.
Compliance with Accounting Standards
By following a standardized amortization schedule, businesses can ensure that their financial statements are in line with these accounting standards. This is important for maintaining transparency and credibility in financial reporting.
Strategic Decision Making
For example, a business may use an amortization schedule to determine the optimal time to replace or upgrade an asset. By analyzing the amortization schedule, they can assess the remaining value and useful life of the asset, and make decisions based on cost-effectiveness and long-term financial goals.
Benefits and Applications
One of the main benefits of using amortization schedules is that they provide a systematic approach to allocating the cost of an asset over its useful life. This helps businesses to better manage their finances and plan for future expenses.
Amortization schedules also play a key role in budgeting and forecasting. By knowing the expected amortization expenses for each period, businesses can accurately estimate their future cash flows and make informed decisions about investments and expenditures.
Furthermore, amortization schedules are essential for tax purposes. They help businesses calculate the deductible portion of an asset’s cost, which can result in significant tax savings.
Applications of Amortization Schedules
Amortization schedules find applications in various industries and sectors. Some common applications include:
- Real Estate: Amortization schedules are commonly used in mortgage loans to determine the monthly payments and interest expenses over the loan term.
- Auto Loans: Car financing companies use amortization schedules to calculate the monthly payments and interest charges for auto loans.
- Student Loans: Amortization schedules are used to determine the monthly payments and interest costs for student loans.
- Business Loans: Businesses use amortization schedules to calculate the repayment schedule and interest expenses for loans taken to finance their operations.
- Investments: Amortization schedules are also used in investment analysis to calculate the return on investment and determine the time required to recoup the initial investment.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
