U.S. Treasury: A Comprehensive Guide to History, IRS, Treasury Bills and Bonds
The U.S. Treasury is a vital government department responsible for managing the country’s finances and implementing economic policies. This comprehensive guide provides an overview of the history of the U.S. Treasury, the role of the Internal Revenue Service (IRS), and the importance of Treasury bills and bonds in the financial market.
History of the U.S. Treasury
The U.S. Treasury has a rich history that dates back to the founding of the nation. It was established in 1789 by the first Secretary of the Treasury, Alexander Hamilton. Since then, it has played a crucial role in shaping the country’s economic policies and managing its finances.
Role of the IRS in the U.S. Treasury
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) is an integral part of the U.S. Treasury. It is responsible for collecting taxes and enforcing tax laws to ensure compliance. The IRS plays a critical role in funding the government’s operations and programs, as taxes are the primary source of revenue for the U.S. Treasury.
The IRS not only collects taxes but also provides assistance and guidance to taxpayers. It offers various resources and tools to help individuals and businesses understand their tax obligations and file their returns accurately. Additionally, the IRS investigates and takes legal action against those who engage in tax evasion or fraud.
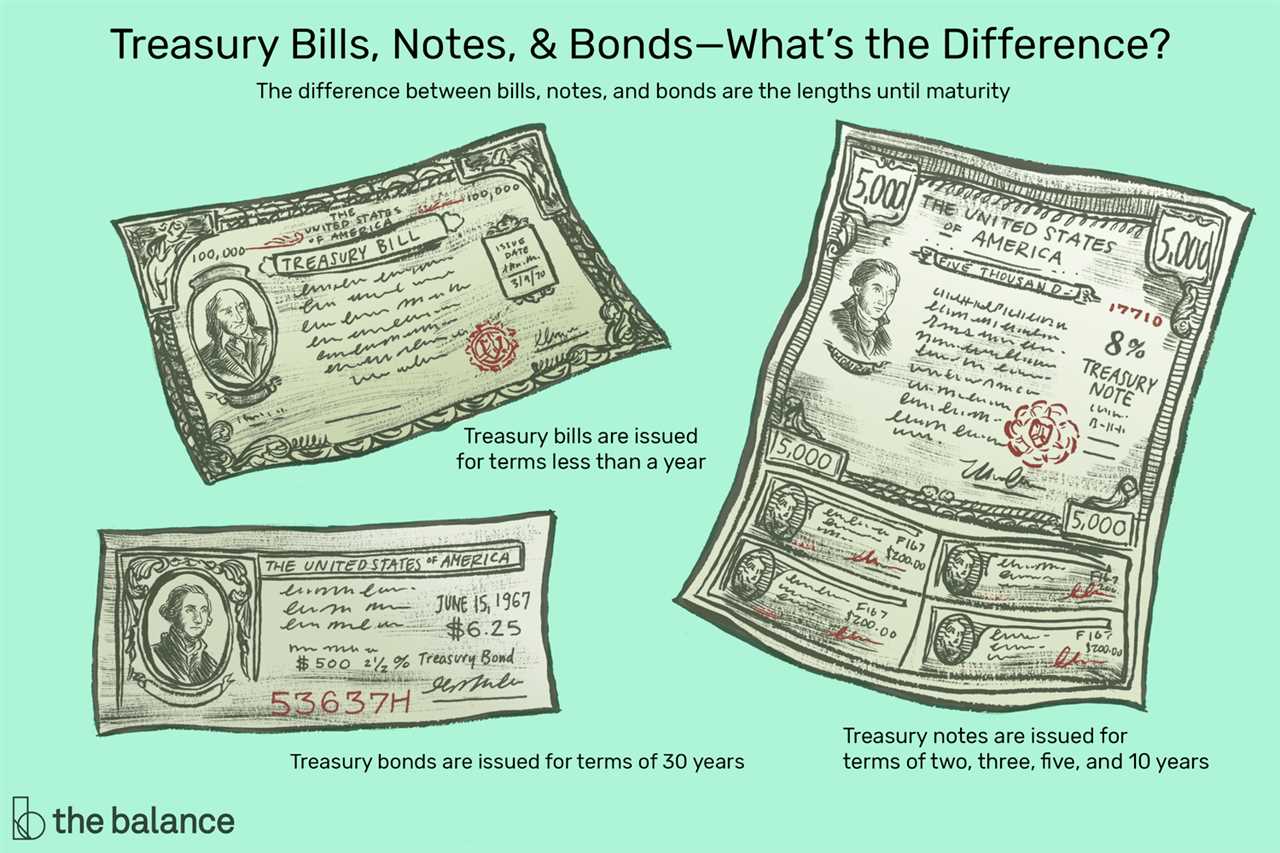
Treasury Bills and Bonds
History of the U.S. Treasury
The history of the U.S. Treasury dates back to the early days of the United States. In the early years of the republic, the government faced significant financial challenges, including the need to fund the Revolutionary War and establish a stable financial system. Alexander Hamilton, the first Secretary of the Treasury, played a crucial role in shaping the department and its policies.
Today, the U.S. Treasury continues to play a vital role in the nation’s economy. It manages the issuance of Treasury bonds and bills, which are used to finance the government’s operations and fund public projects. The department also works to combat financial crimes, such as money laundering and terrorist financing.
Role of the IRS in the U.S. Treasury
One of the primary roles of the IRS is to collect taxes from individuals, businesses, and other entities. It ensures that taxpayers comply with their tax obligations by providing guidance, conducting audits, and taking enforcement actions when necessary. The revenue collected by the IRS is essential for funding the operations of the U.S. government and supporting various public programs and services.
Functions of the IRS
The IRS performs several key functions within the U.S. Treasury:
- Tax Administration: The IRS is responsible for administering the tax laws and regulations. It provides guidance to taxpayers on how to comply with their tax obligations, processes tax returns, and issues refunds.
- Tax Collection: The IRS collects taxes from individuals, businesses, and other entities. It uses various methods, such as withholding taxes from paychecks, conducting audits, and enforcing tax liens and levies, to ensure compliance.
- Taxpayer Assistance: The IRS offers assistance to taxpayers through various channels, including phone helplines, online resources, and in-person assistance centers. It helps taxpayers understand their rights and responsibilities and provides guidance on tax-related issues.
Importance of the IRS

The role of the IRS in the U.S. Treasury is crucial for maintaining the financial stability of the government and ensuring the fair and equitable collection of taxes. Without the IRS, it would be challenging to enforce tax laws and collect the necessary revenue to fund government operations.
The IRS also plays a vital role in promoting voluntary compliance with tax laws. By providing guidance, educational resources, and assistance to taxpayers, the IRS helps individuals and businesses understand their tax obligations and encourages them to comply willingly.
| Key Points |
|---|
| The IRS is the principal revenue collection agency of the U.S. government. |
| It administers and enforces the tax laws enacted by Congress. |
| The IRS collects taxes from individuals, businesses, and other entities. |
| It provides guidance, conducts audits, and takes enforcement actions to ensure tax compliance. |
| The IRS offers assistance to taxpayers through various channels. |
| It plays a crucial role in maintaining the financial stability of the government. |
T-bills are issued with maturities of 4, 13, 26, or 52 weeks. They are sold at a discount to their face value, which means that investors purchase them for less than their eventual redemption value. For example, if a $1,000 T-bill is sold at a discount of $950, the investor will receive $1,000 when the bill matures.
Investing in T-bills is a way for the government to raise funds to finance its operations. When investors purchase T-bills, they are essentially lending money to the government. In return, the government pays them interest, which is the difference between the purchase price and the redemption value.
T-bills are considered to be highly liquid investments because they can be bought and sold on the secondary market. This means that investors can sell their T-bills before they mature if they need to access their funds. The secondary market for T-bills is very active, and prices are determined by supply and demand.
One of the advantages of investing in T-bills is their low risk. Since they are backed by the U.S. government, the likelihood of default is extremely low. This makes them an attractive option for conservative investors who prioritize capital preservation.
Another advantage of T-bills is their simplicity. Unlike other types of investments, such as stocks or bonds, T-bills do not pay regular interest payments. Instead, investors earn interest by purchasing the bills at a discount and receiving the full face value at maturity.
Investing in Treasury Bonds

Investing in Treasury Bonds is a popular choice for many investors due to their low risk and reliable returns. Treasury Bonds are debt securities issued by the U.S. Department of the Treasury to finance the government’s borrowing needs. They are considered one of the safest investments available in the market.
What are Treasury Bonds?
Treasury Bonds are long-term debt instruments with a maturity period of 10 years or more. They are issued in denominations of $1,000 and pay interest every six months until maturity. The interest rate on Treasury Bonds is fixed at the time of issuance and remains the same throughout the life of the bond.
Investors who purchase Treasury Bonds become creditors of the U.S. government and are entitled to receive the face value of the bond at maturity, along with the interest payments. The interest income from Treasury Bonds is exempt from state and local taxes, making them even more attractive to investors.
How to Invest in Treasury Bonds
There are several ways to invest in Treasury Bonds:
- Directly from the U.S. Department of the Treasury: Investors can purchase Treasury Bonds directly from the U.S. Department of the Treasury through their website, TreasuryDirect.gov. This allows investors to buy Treasury Bonds at auction and hold them in an online account.
- Through a broker: Investors can also buy Treasury Bonds through a broker or financial institution. Brokers can provide guidance and assistance in purchasing Treasury Bonds and managing the investment.
- Through a Treasury Bond mutual fund: Another option is to invest in a Treasury Bond mutual fund. These funds pool money from multiple investors to invest in a diversified portfolio of Treasury Bonds. This option provides greater liquidity and flexibility compared to holding individual Treasury Bonds.
Benefits of Investing in Treasury Bonds
Investing in Treasury Bonds offers several benefits:
- Low risk: Treasury Bonds are backed by the full faith and credit of the U.S. government, making them one of the safest investments available. The risk of default is extremely low.
- Steady income: Treasury Bonds pay interest every six months, providing investors with a steady income stream.
- Tax advantages: The interest income from Treasury Bonds is exempt from state and local taxes, making them a tax-efficient investment.
- Diversification: Treasury Bonds can be used to diversify an investment portfolio and reduce overall risk.
Risks of Investing in Treasury Bonds
While Treasury Bonds are generally considered low risk, there are a few risks to be aware of:
- Interest rate risk: If interest rates rise, the value of existing Treasury Bonds may decline. This is because investors can earn higher returns from newly issued bonds with higher interest rates.
- Inflation risk: Inflation erodes the purchasing power of future interest payments and the face value of Treasury Bonds. If inflation rises significantly, the real return on Treasury Bonds may be lower than expected.
Conclusion

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
