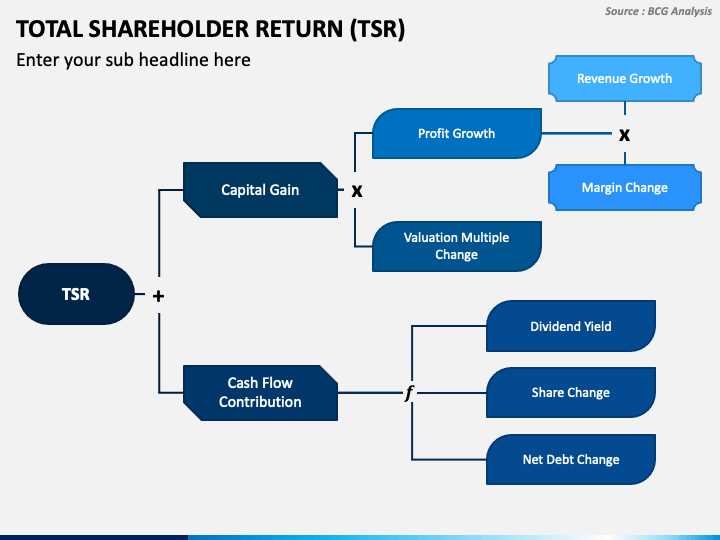
Total Shareholder Return: Definition and Formula
Total Shareholder Return (TSR) is a financial metric that measures the total return an investor receives from owning a particular stock or investment over a given period of time. It takes into account both capital appreciation (or depreciation) and any dividends or distributions received during that period.
The formula for calculating TSR is:
Where:
- Ending Share Price is the price of the stock at the end of the period.
- Beginning Share Price is the price of the stock at the beginning of the period.
- Dividends are any cash payments or distributions received from the investment during the period.
The result of the TSR calculation is expressed as a percentage, representing the total return on the investment.
Total Shareholder Return is an important metric for investors as it provides a comprehensive measure of the overall performance of an investment. It takes into account both capital gains and income generated from dividends, giving investors a clear picture of the total return they have received.
By comparing the TSR of different investments, investors can evaluate the relative performance of different stocks or investments and make informed decisions about where to allocate their capital.
Calculating TSR can be done manually using the formula mentioned above, but there are also various online tools and financial software that can automate the calculation process and provide additional analysis and insights.
What is Total Shareholder Return?
Total Shareholder Return (TSR) is a financial metric that measures the total return received by shareholders of a company over a specific period of time. It takes into account both capital appreciation (increase in stock price) and dividends received by shareholders.
TSR is an important indicator of the overall performance of a company from the perspective of its shareholders. It provides a comprehensive view of the returns generated by an investment in the company’s stock, considering both price changes and dividend payments.
Components of Total Shareholder Return
The components of TSR include:
- Capital Appreciation: This refers to the increase in the price of a company’s stock over a specific period of time. It represents the gain or loss in the value of the investment.
- Dividends: Dividends are the payments made by a company to its shareholders out of its profits. They are usually distributed on a regular basis, such as quarterly or annually. Dividends provide an additional source of income for shareholders.
By considering both capital appreciation and dividends, TSR provides a more comprehensive measure of the total return received by shareholders. It reflects not only the changes in the stock price but also the income generated from dividend payments.
Importance of Total Shareholder Return
TSR is an important metric for investors and shareholders as it helps them evaluate the performance of their investments. It provides a holistic view of the returns generated by a company’s stock, taking into account both price changes and dividend payments.
By analyzing TSR, investors can assess the effectiveness of their investment strategy and compare the performance of different companies. It allows them to make informed decisions about buying, holding, or selling stocks.
Furthermore, TSR is often used as a benchmark to evaluate the performance of company executives and management teams. It serves as a measure of their ability to generate value for shareholders.
Calculating Total Shareholder Return
The formula for calculating TSR is:
To calculate TSR, you need the beginning stock price, the ending stock price, and the total dividends received during the specific period. By plugging these values into the formula, you can determine the total return generated by the investment.
There are various tools and software available that can help investors calculate TSR efficiently. These tools automate the process and provide accurate results, saving time and effort.
Why is Total Shareholder Return Important?
Total Shareholder Return (TSR) is an important metric for investors and businesses alike. It provides a comprehensive measure of the overall return generated by an investment, taking into account both capital appreciation and dividends received. Here are some key reasons why TSR is important:
- Evaluation of Investment Performance: TSR allows investors to assess the performance of their investments over a specific period of time. By comparing the TSR of different investments, investors can determine which ones have generated the highest returns and make informed decisions about their portfolio allocation.
- Comparison with Market and Peers: TSR provides a benchmark for comparing the performance of a company or investment with the broader market and its industry peers. This helps investors and businesses evaluate how well they are performing relative to their competitors and the overall market conditions.
- Long-Term Perspective: TSR takes into account both capital gains and dividends, providing a long-term perspective on investment returns. This is particularly important for investors who are focused on generating income from their investments, as dividends contribute to the overall TSR.
- Risk Assessment: TSR can also be used as a measure of risk-adjusted returns. By comparing the TSR of different investments with their respective risk levels, investors can evaluate the risk-return trade-off and make informed decisions about their investment strategy.
How to Calculate Total Shareholder Return?
Calculating the Total Shareholder Return (TSR) is an important metric for investors to assess the performance of their investments. TSR takes into account both the capital appreciation of the stock and any dividends received by the shareholders. It provides a comprehensive measure of the overall return generated by an investment over a specific period of time.
To calculate TSR, you need to know the initial stock price, the final stock price, and any dividends paid during the period. The formula for calculating TSR is as follows:
Here is a step-by-step guide on how to calculate TSR:
- Obtain the initial stock price: This is the price of the stock at the beginning of the period you are analyzing.
- Obtain the final stock price: This is the price of the stock at the end of the period you are analyzing.
- Calculate the capital appreciation: Subtract the initial stock price from the final stock price.
- Obtain the dividends paid: This is the total amount of dividends paid to shareholders during the period.
- Add the dividends paid to the capital appreciation: This gives you the total return.
- Divide the total return by the initial stock price: This gives you the TSR.
For example, let’s say you purchased a stock for $100 at the beginning of the year. At the end of the year, the stock price is $120, and you received $5 in dividends during the year. To calculate the TSR, you would use the following formula:
Calculating the Total Shareholder Return is a valuable tool for investors to evaluate the performance of their investments. It provides a comprehensive measure of the overall return, taking into account both capital appreciation and dividends received. By using the formula and following the step-by-step guide, investors can easily calculate the TSR and make informed investment decisions.
Tools for Calculating Total Shareholder Return
Calculating Total Shareholder Return (TSR) is an important metric for investors and financial analysts to evaluate the performance of a company’s stock over a specific period of time. TSR takes into account both capital appreciation (or depreciation) and dividends received by shareholders.
1. Stock Price Data
The first tool needed to calculate TSR is accurate and up-to-date stock price data. This can be obtained from financial websites, stock exchanges, or specialized financial data providers. The stock price data should include the starting price and ending price for the desired time period.
2. Dividend Data
In addition to stock price data, dividend data is necessary to calculate TSR. Dividends are cash payments made by a company to its shareholders as a distribution of profits. Dividend data can be found in financial statements, company reports, or financial news websites.
3. Time Period
The time period for calculating TSR should be specified. It can be a single day, a month, a quarter, a year, or any other desired time frame. The starting and ending dates for the time period should be clearly defined.
4. TSR Formula
The TSR formula is straightforward and can be calculated using the following formula:
5. Percentage Calculation
To convert the TSR into a percentage, multiply the result by 100. This will provide the percentage return on investment over the specified time period.
6. Spreadsheet Software
Using spreadsheet software, such as Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets, can greatly simplify the calculation of TSR. By entering the stock price data and dividend data into separate columns, the TSR formula can be applied to calculate the TSR for each time period. The software can also be used to create charts and graphs to visualize the TSR performance over time.
By utilizing these tools, investors and financial analysts can accurately calculate Total Shareholder Return and gain valuable insights into the performance of a company’s stock. TSR is a useful metric for comparing different stocks, evaluating investment opportunities, and making informed investment decisions.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
