The Basics of Credit Bureaus: What They Are, What They Do, and the Major Players
Credit bureaus play a crucial role in the financial system by collecting and maintaining information about individuals’ credit history. This information is used by lenders, such as banks and credit card companies, to assess the creditworthiness of potential borrowers.
So, what exactly are credit bureaus? Credit bureaus are companies that gather and store credit information on individuals. They collect data from various sources, including lenders, utility companies, and public records. This data includes details about individuals’ borrowing and repayment history, such as credit card payments, loans, and bankruptcies.
The major players in the credit bureau industry include Equifax, Experian, and TransUnion. These companies are responsible for collecting and maintaining credit information for millions of individuals. They use sophisticated algorithms and statistical models to analyze this data and generate credit reports.
Credit bureaus also play a role in helping individuals monitor their own credit. They provide individuals with access to their credit reports, allowing them to review the information and ensure its accuracy. If there are any errors or discrepancies, individuals can dispute them with the credit bureau to have them corrected.
What are Credit Bureaus?
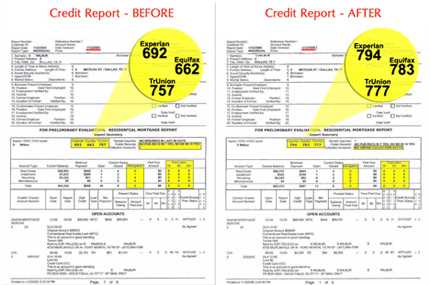
These credit reports contain information such as personal identification details, credit history, payment history, and public records like bankruptcies and tax liens. Credit bureaus use this information to calculate credit scores, which are numerical representations of an individual’s creditworthiness.
What Do Credit Bureaus Do?
Credit bureaus have several key functions:
- Collecting and maintaining credit information: Credit bureaus gather data from various sources and compile it into credit reports. They update these reports regularly to ensure accuracy.
- Calculating credit scores: Credit bureaus use the information in credit reports to calculate credit scores. These scores help lenders assess the risk of lending to an individual or business.
- Providing credit reports to lenders: Credit bureaus provide credit reports to lenders when they request information about a potential borrower. Lenders use these reports to make informed decisions about extending credit.
- Assisting with identity verification: Credit bureaus help verify the identity of individuals applying for credit. They use personal information and credit history to confirm the identity of the applicant.
- Handling disputes: If individuals find errors or inaccuracies in their credit reports, they can file a dispute with the credit bureau. The bureau is responsible for investigating the dispute and correcting any errors if necessary.
Overall, credit bureaus act as intermediaries between lenders and borrowers, providing crucial information that helps lenders make informed decisions about extending credit.
Major Players in the Credit Bureau Industry
There are three major credit bureaus in the United States:
- Equifax: Equifax is one of the largest credit bureaus in the world. It collects and maintains credit information on millions of individuals and businesses.
- Experian: Experian is another prominent credit bureau that provides credit information and services to individuals and businesses.
- TransUnion: TransUnion is a leading global credit bureau that offers credit information and risk management solutions.
These three credit bureaus dominate the industry and are widely used by lenders and financial institutions to assess creditworthiness.
Role of Credit Bureaus in the Financial System

Credit bureaus play a crucial role in the financial system by collecting and maintaining credit information on individuals and businesses. This information is then used by lenders, creditors, and other financial institutions to assess the creditworthiness of borrowers and make informed decisions about lending.
One of the main functions of credit bureaus is to gather data from various sources, such as banks, credit card companies, and other lenders. This data includes information about an individual’s payment history, outstanding debts, and credit limits. By compiling this information into comprehensive credit reports, credit bureaus provide a snapshot of an individual’s financial health and creditworthiness.
When a borrower applies for a loan or credit, the lender can request a credit report from one or more credit bureaus. This report helps the lender evaluate the borrower’s creditworthiness and determine the level of risk associated with lending to them. Based on the information in the credit report, the lender can make an informed decision about whether to approve the loan, set an appropriate interest rate, or establish a credit limit.
Furthermore, credit bureaus also play a vital role in detecting and preventing fraud. By monitoring credit activity and identifying suspicious patterns, credit bureaus can alert lenders and consumers to potential fraudulent activity. This helps protect both lenders and borrowers from financial losses and damage to their credit reputation.
In addition to their role in the lending process, credit bureaus also provide credit monitoring services to individuals. These services allow individuals to regularly check their credit reports for accuracy and detect any unauthorized activity. By staying informed about their credit status, individuals can take proactive steps to improve their credit score and maintain a healthy financial profile.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
