What is Smart Beta?
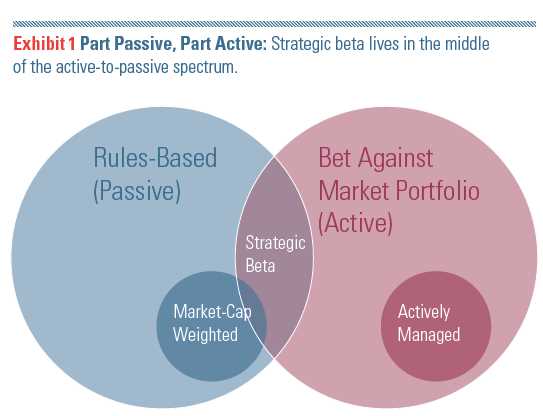
Smart Beta is a popular investment strategy that aims to provide investors with better risk-adjusted returns compared to traditional market-cap weighted indices. It combines elements of both passive and active investing, offering a middle ground between the two.
Smart Beta strategies are designed to exploit market inefficiencies and take advantage of factors that have historically been shown to drive stock returns. These factors can include value, momentum, low volatility, quality, and size.
Unlike traditional passive index funds that weight stocks based on their market capitalization, Smart Beta strategies use alternative weighting schemes. These can be based on factors such as earnings, dividends, or other fundamental metrics. The goal is to tilt the portfolio towards stocks that are expected to outperform based on these factors.
Implementing Strategies
There are various ways to implement Smart Beta strategies. One common approach is through the use of exchange-traded funds (ETFs) or mutual funds that are specifically designed to track a Smart Beta index. These funds typically have rules-based methodologies for selecting and weighting stocks based on the chosen factor or factors.
Another approach is to construct a customized portfolio that follows a Smart Beta strategy. This can involve selecting individual stocks or using a combination of stocks and other financial instruments to create a portfolio that aligns with the desired factor exposure.
Real-Life Examples
There are numerous examples of Smart Beta strategies being implemented in the market. For instance, a value-based Smart Beta strategy may involve selecting stocks with low price-to-earnings ratios or high dividend yields. A momentum-based strategy, on the other hand, may focus on stocks that have exhibited strong recent price performance.
Some popular Smart Beta ETFs include the iShares Edge MSCI USA Value Factor ETF, which focuses on stocks with attractive valuations, and the Invesco S&P 500 Low Volatility ETF, which targets low volatility stocks. These ETFs provide investors with a convenient way to access Smart Beta strategies.
Smart Beta is a popular investment strategy that combines elements of both passive and active investing. It aims to provide investors with a systematic and rules-based approach to portfolio construction, while still allowing for potential outperformance compared to traditional market-cap weighted indexes.
What is Smart Beta?
Unlike traditional index funds that weight stocks based on their market capitalization, Smart Beta strategies use alternative weighting schemes. These schemes can be based on fundamental factors such as earnings or dividends, or they can be based on quantitative factors such as volatility or price momentum.
How Does Smart Beta Work?
Smart Beta strategies typically start with a rules-based approach to selecting and weighting stocks within a portfolio. These rules can be based on academic research, historical data analysis, or a combination of both. The goal is to identify stocks that exhibit the desired factor characteristics and construct a portfolio that maximizes exposure to these factors.
Once the stocks are selected, Smart Beta strategies use alternative weighting schemes to determine the portfolio allocations. These weighting schemes can be equal-weighted, where each stock receives the same weight, or they can be based on the specific factor being targeted. For example, a value-based Smart Beta strategy may allocate more weight to stocks with lower price-to-earnings ratios.
By using alternative weighting schemes, Smart Beta strategies aim to exploit market inefficiencies and capture the desired factor premiums. This can result in a portfolio that is tilted towards certain factors, such as value or momentum, which may outperform the broader market over time.
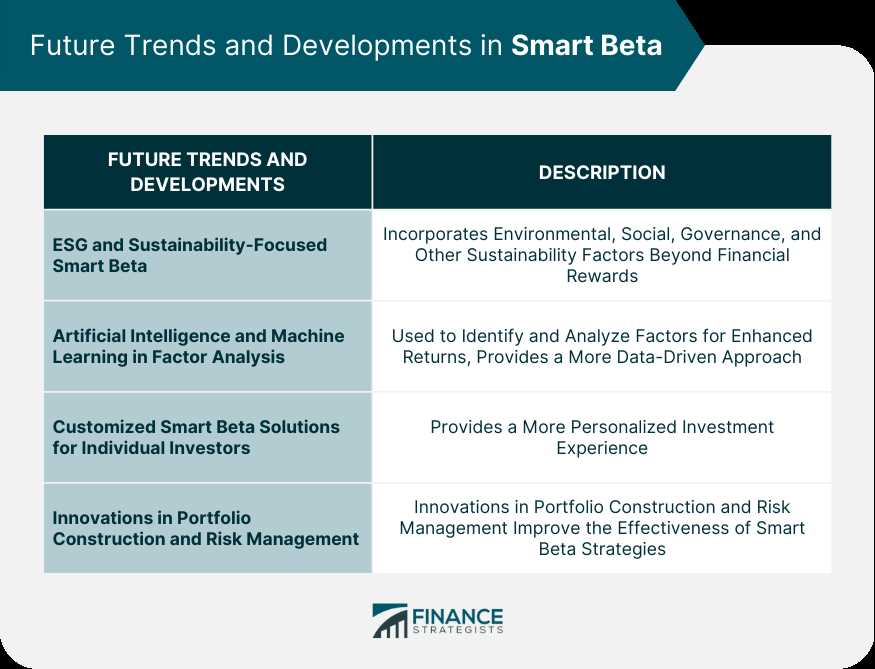
Benefits of Smart Beta
Conclusion
Smart Beta is a popular investment strategy that aims to provide investors with a systematic and rules-based approach to portfolio construction. By targeting specific factors or characteristics, Smart Beta strategies seek to enhance returns or reduce risk compared to traditional market-cap weighted indexes. While not guaranteed to outperform, Smart Beta strategies offer potential benefits such as a systematic approach, potential outperformance, and diversification benefits.
Implementing Strategies
Implementing smart beta strategies involves a systematic approach to selecting and weighting securities within a portfolio. There are several different strategies that can be used, each with its own unique characteristics and goals.
One common strategy is the equal-weighted approach, where each security in the portfolio is given an equal weighting. This strategy aims to provide a more balanced exposure to all securities, regardless of their market capitalization or other factors.
Another strategy is the minimum volatility approach, which aims to construct a portfolio with the lowest possible volatility. This strategy typically involves selecting securities that have historically exhibited lower levels of price fluctuations.
Factor-based strategies are also popular in smart beta investing. These strategies involve selecting securities based on specific factors, such as value, momentum, or quality. For example, a value-based strategy may involve selecting securities that have low price-to-earnings ratios or high dividend yields.
Implementing smart beta strategies can be done through various investment vehicles, such as exchange-traded funds (ETFs) or mutual funds. These funds are designed to track specific smart beta indices and provide investors with exposure to the chosen strategy.
Real-Life Examples
1. Low Volatility Strategy:
One popular smart beta strategy is the low volatility strategy. This strategy aims to invest in stocks with lower volatility than the overall market. The idea behind this strategy is that stocks with lower volatility tend to outperform the market over the long term. This is because investors are often willing to pay a premium for stocks with lower risk.
For example, the iShares Edge MSCI Min Vol USA ETF (USMV) is an exchange-traded fund that tracks the performance of U.S. stocks with lower volatility. This ETF has consistently outperformed the S&P 500 index over the past few years.
2. Dividend Growth Strategy:
Another popular smart beta strategy is the dividend growth strategy. This strategy aims to invest in stocks that have a history of increasing their dividends over time. The idea behind this strategy is that companies that consistently increase their dividends tend to have strong financials and stable cash flows.
For example, the Vanguard Dividend Appreciation ETF (VIG) is an exchange-traded fund that tracks the performance of U.S. stocks with a history of increasing their dividends. This ETF has consistently provided investors with a steady stream of income and has outperformed the S&P 500 index over the long term.
3. Equal Weight Strategy:
The equal weight strategy is another smart beta strategy that aims to invest in all the stocks in a given index in equal proportions. This strategy differs from traditional market-cap weighted strategies, where the weight of each stock is determined by its market capitalization.
For example, the Invesco S&P 500 Equal Weight ETF (RSP) is an exchange-traded fund that tracks the performance of all the stocks in the S&P 500 index in equal proportions. This ETF has historically outperformed the S&P 500 index, as it gives equal weight to both large and small-cap stocks.
These are just a few examples of smart beta strategies that have been successful in the market. It is important to note that while these strategies have performed well in the past, there is no guarantee that they will continue to do so in the future. Investors should carefully consider their investment goals and risk tolerance before implementing any smart beta strategy.
Technical Analysis Basic Education
Technical analysis is a method of evaluating securities by analyzing statistical trends gathered from trading activity, such as price movement and volume. It is based on the belief that historical price patterns can be used to predict future price movements.
Key Concepts
- Trend Analysis: Technical analysts study price charts to identify trends, such as uptrends, downtrends, and sideways trends. They use various tools and indicators to determine the strength and duration of a trend.
- Support and Resistance: Support levels are price levels where buying pressure is expected to outweigh selling pressure, causing prices to bounce back up. Resistance levels, on the other hand, are price levels where selling pressure is expected to outweigh buying pressure, causing prices to reverse downward.
- Chart Patterns: Technical analysts look for recurring patterns on price charts, such as head and shoulders, double tops, and triangles. These patterns can provide clues about future price movements.
- Indicators: Technical analysts use various indicators, such as moving averages, oscillators, and volume indicators, to generate buy or sell signals. These indicators are based on mathematical calculations applied to price and volume data.
Advantages and Limitations
Application in Smart Beta
Technical analysis can be applied in the context of smart beta strategies. Smart beta refers to a set of investment strategies that aim to outperform traditional market-cap weighted indexes by using alternative weighting schemes based on factors such as volatility, value, momentum, and quality.
Technical analysis can be used to identify trends and patterns in the underlying securities of a smart beta strategy. By analyzing price charts and applying technical indicators, investors can make informed decisions about when to buy or sell the securities in the portfolio.
For example, if a smart beta strategy is based on momentum, technical analysis can be used to identify stocks that are exhibiting strong upward price trends. Conversely, if a smart beta strategy is based on value, technical analysis can be used to identify undervalued stocks that may be poised for a price increase.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
