Return on Revenue: How to Calculate and Apply It
To calculate the Return on Revenue ratio, you need to divide the net income by the total revenue and multiply the result by 100 to express it as a percentage. The formula is as follows:
ROR = (Net Income / Total Revenue) * 100
For example, if a company has a net income of $1 million and total revenue of $10 million, the Return on Revenue ratio would be 10%.
The Return on Revenue ratio provides insights into how well a company is able to generate profits from its sales. A higher ratio indicates that the company is more efficient at converting its revenue into profits, while a lower ratio suggests that the company may have higher expenses or lower profit margins.
Investors and analysts use the Return on Revenue ratio to compare the profitability of different companies within the same industry or to track a company’s performance over time. It can help identify trends and potential areas for improvement.
There are several ways to apply the Return on Revenue ratio in financial analysis:
- Comparative Analysis: Compare the Return on Revenue ratios of different companies in the same industry to identify the most profitable ones.
- Trend Analysis: Track a company’s Return on Revenue ratio over multiple periods to identify any improvements or declines in profitability.
- Industry Benchmarking: Compare a company’s Return on Revenue ratio to the industry average to assess its performance relative to its peers.
- Internal Analysis: Use the Return on Revenue ratio to evaluate the effectiveness of cost management strategies and identify areas for cost reduction.
Overall, the Return on Revenue ratio is a valuable tool for assessing a company’s profitability and efficiency. By calculating and applying this ratio, investors and analysts can gain valuable insights into a company’s financial performance and make more informed investment decisions.
The return on revenue ratio is an important indicator of a company’s financial health and efficiency. It helps investors and analysts assess the company’s ability to generate profits from its operations and manage its costs effectively. A higher return on revenue ratio indicates that a company is more efficient in converting its revenue into profit, while a lower ratio suggests that the company may be facing challenges in generating profits.
Calculating Return on Revenue Ratio
The return on revenue ratio is calculated by dividing the net income by the total revenue and multiplying the result by 100 to express it as a percentage. The formula for calculating the return on revenue ratio is as follows:
Return on Revenue Ratio = (Net Income / Total Revenue) * 100
For example, if a company has a net income of $500,000 and total revenue of $2,000,000, the return on revenue ratio would be:
Return on Revenue Ratio = ($500,000 / $2,000,000) * 100 = 25%
This means that for every dollar of revenue the company earns, it generates a profit of 25 cents.
Interpreting Return on Revenue Ratio
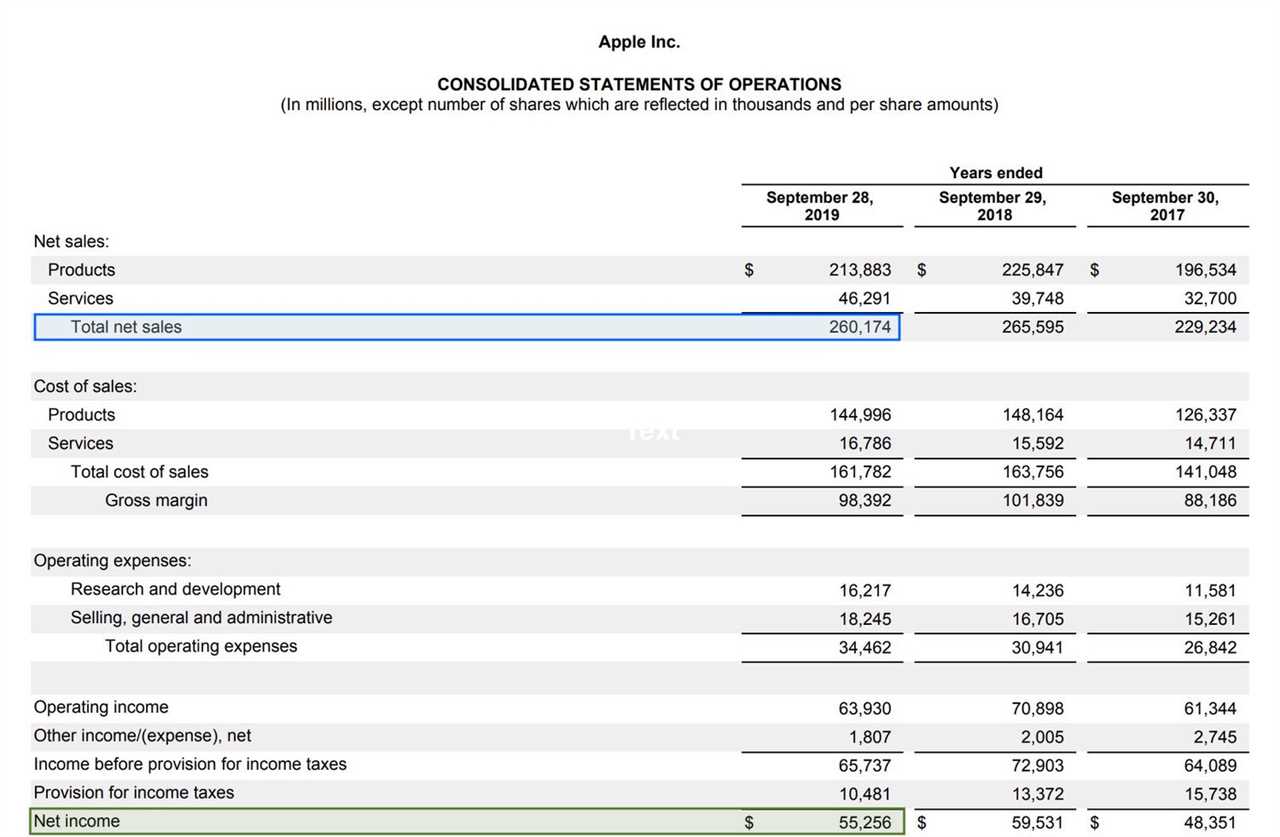
The return on revenue ratio can vary significantly between industries. Some industries, such as technology or pharmaceuticals, may have higher profit margins due to the nature of their products or services. On the other hand, industries with high competition or low-profit margins, such as retail or hospitality, may have lower return on revenue ratios.
Investors and analysts also use the return on revenue ratio to evaluate a company’s financial performance over time. By comparing the ratio from different periods, they can assess whether the company’s profitability is improving or declining.
Overall, the return on revenue ratio is a valuable tool for investors, analysts, and managers to assess a company’s profitability and efficiency. It provides insights into how effectively a company is generating profits from its revenue and helps in making informed decisions about investments and business strategies.
Calculating Return on Revenue Ratio
Formula

The formula for calculating the return on revenue ratio is:
Return on Revenue Ratio = (Net Profit / Total Revenue) * 100
Example
Let’s say Company XYZ has a net profit of $500,000 and total revenue of $2,000,000. To calculate the return on revenue ratio, we can use the formula:
Return on Revenue Ratio = ($500,000 / $2,000,000) * 100 = 25%
This means that Company XYZ has a return on revenue ratio of 25%, indicating that for every dollar of revenue generated, the company earns 25 cents in net profit.
Interpretation
The return on revenue ratio is an important metric for investors and analysts as it provides insights into a company’s profitability. A higher ratio indicates that the company is generating more profit from its revenue, which is generally seen as a positive sign. On the other hand, a lower ratio may indicate inefficiencies or low profitability.
Overall, the return on revenue ratio is a useful tool for evaluating a company’s profitability and can assist in making informed investment decisions.
Applying Return on Revenue Ratio
Interpreting the Return on Revenue Ratio
The return on revenue ratio is expressed as a percentage and indicates the amount of profit a company generates for every dollar of revenue. A higher ratio indicates that a company is more efficient at generating profits from its revenue, while a lower ratio suggests that a company may be struggling to generate profits.
It is important to compare the return on revenue ratio to industry benchmarks to assess the company’s performance relative to its competitors. If the ratio is higher than the industry average, it suggests that the company is performing well and is more profitable than its peers. On the other hand, if the ratio is lower than the industry average, it may indicate that the company needs to improve its efficiency and profitability.
Using the Return on Revenue Ratio for Decision Making
The return on revenue ratio can be used by management to make strategic decisions and evaluate the financial health of the company. Here are some ways the ratio can be applied:
| 1. Assessing Profitability |
|---|
| By analyzing the return on revenue ratio over time, management can assess whether the company’s profitability is improving or declining. If the ratio is consistently increasing, it indicates that the company is becoming more efficient at generating profits. Conversely, a declining ratio may signal that the company needs to take corrective measures to improve profitability. |
| 2. Comparing Business Units |
| The return on revenue ratio can also be used to compare the profitability of different business units within a company. By calculating the ratio for each unit, management can identify which units are generating the most profits and allocate resources accordingly. This analysis can help optimize resource allocation and drive overall profitability. |
| 3. Evaluating Investment Opportunities |
| When considering investment opportunities, the return on revenue ratio can be used to assess the potential profitability of the investment. By comparing the ratio of the potential investment to the company’s current ratio, management can determine whether the investment is likely to generate a higher return on revenue. This analysis can help prioritize investment decisions and allocate resources effectively. |

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
