Stage 2: Growth
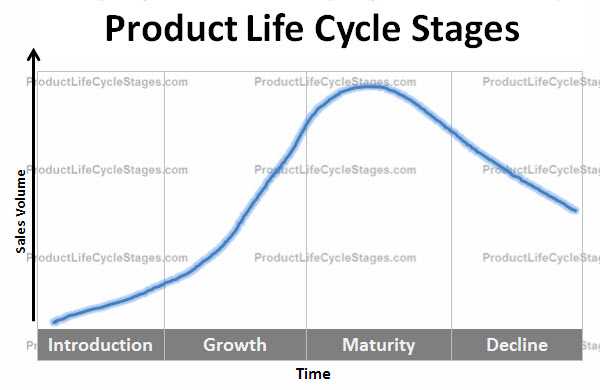
During the growth stage, the product experiences a surge in demand as more customers become aware of its benefits and features. This increased demand leads to an increase in production and distribution efforts to meet the growing market needs.
Marketing and promotional activities play a crucial role in driving the growth of the product during this stage. Companies invest in advertising, public relations, and other marketing strategies to create awareness and generate excitement among potential customers.
As sales continue to grow, competitors may also enter the market, offering similar products or alternatives. This intensifies competition and forces companies to differentiate their product and maintain a competitive edge.
During the growth stage, companies often invest in research and development to improve the product and introduce new features or variations. This helps to sustain the growth momentum and meet evolving customer demands.
Profitability is typically high during the growth stage as sales increase and economies of scale are realized. However, companies must also manage their costs effectively to ensure sustainable growth and avoid pricing themselves out of the market.
It is important for companies to capitalize on the growth stage and establish a strong market position. This can be achieved by building customer loyalty, expanding distribution channels, and continuously innovating to stay ahead of competitors.
Overall, the growth stage of the product life cycle is an exciting phase where companies experience rapid sales growth and expansion. It is a critical time for companies to establish themselves in the market and lay the foundation for long-term success.
Stage 4: Decline
The decline stage is the final phase in the product life cycle. During this stage, the product experiences a decrease in sales and profits. This decline can be attributed to various factors such as market saturation, changing consumer preferences, technological advancements, or the emergence of new and superior products.
As sales decline, companies may choose to discontinue the product or reduce its marketing efforts. They may also decide to lower the price in an attempt to attract remaining customers. However, despite these efforts, the decline stage is generally inevitable for most products.
During this stage, companies need to carefully evaluate the profitability and viability of the product. They may consider diversifying their product portfolio or investing in research and development to create new and innovative products to replace the declining one.
It is important for companies to manage the decline stage effectively to minimize losses and make a smooth transition to new products. This may involve reducing production and distribution costs, liquidating inventory, or finding alternative uses for the product.
Here is an example to illustrate the decline stage: VCRs (Video Cassette Recorders) were once a popular consumer electronic product. However, with the advent of DVD players and digital streaming services, the demand for VCRs declined rapidly. As a result, many companies stopped manufacturing VCRs and shifted their focus to newer technologies.
| Stage | Characteristics | Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Introduction | – Low sales – High costs – Negative profits |
– Heavy promotion – Limited distribution – Pricing strategies |
| Growth | – Rapid sales growth – Increasing profits – Growing market share |
– Product improvement – Market expansion – Competitive pricing |
| Maturity | – Stable sales – Saturation in the market – Intense competition |
– Product diversification – Market segmentation – Cost reduction |
| Decline | – Decreasing sales – Declining profits – Market obsolescence |
– Discontinuation – Price reduction – Portfolio diversification |
Stage 4: Decline
In the product life cycle, the decline stage is the final phase that a product goes through. At this stage, the product experiences a decrease in sales and profitability. It is important for businesses to recognize when a product is in decline in order to make informed decisions about its future.
Characteristics of the Decline Stage
During the decline stage, several characteristics become evident:
- Decrease in Sales: The demand for the product starts to decline, resulting in a decrease in sales volume. This can be due to various factors such as market saturation, changing consumer preferences, or the emergence of new technologies.
- Profitability Decline: As sales decrease, the profitability of the product also declines. This is often due to the need for price reductions in order to maintain sales volume.
- Reduced Market Share: In the decline stage, competitors may introduce newer and more innovative products, leading to a decrease in the market share of the declining product.
- Product Obsolescence: In some cases, the declining product may become obsolete as newer and more advanced products enter the market.
Strategies for Managing the Decline Stage
Businesses can employ various strategies to manage the decline stage effectively:
- Harvesting: This strategy involves reducing costs and extracting maximum cash flow from the product without making further investments. It may include cutting down on marketing expenses, streamlining operations, or focusing on specific customer segments.
- Product Diversification: Companies can explore opportunities to diversify their product offerings and enter new markets. This can help offset the decline of the existing product and maintain overall business growth.
- Product Innovation: In some cases, companies may choose to invest in product innovation to revive the declining product. This can involve adding new features, improving quality, or repositioning the product to target a different market segment.
- Exit Strategy: If the decline is irreversible and the product is no longer profitable, businesses may decide to exit the market and discontinue the product. This can free up resources to focus on more promising opportunities.
It is important for businesses to carefully evaluate the decline stage and choose the most appropriate strategy based on market conditions, customer needs, and overall business goals.
Overall, the decline stage of the product life cycle represents a challenging period for businesses. However, with effective management strategies and a proactive approach, businesses can navigate this stage and make informed decisions about the future of their products.
Examples of Product Life Cycle
Introduction Stage:
- Smartphones: When smartphones were first introduced, they were a novelty and only a few tech-savvy individuals owned them. Companies like Apple and Samsung invested heavily in research and development to create innovative features and attract early adopters.
- Electric Cars: Electric cars, such as Tesla’s Model S, are currently in the introduction stage. Although they have gained popularity in recent years, they are still not widely adopted due to factors like high prices and limited charging infrastructure.
Growth Stage:
- Streaming Services: Streaming services like Netflix and Spotify are in the growth stage. These platforms have experienced rapid growth in recent years as more consumers shift from traditional media to online streaming.
- Plant-Based Meat: Plant-based meat alternatives, such as Beyond Meat and Impossible Foods, are currently in the growth stage. With increasing consumer demand for sustainable and healthier food options, these products have gained popularity and are expanding their market presence.
Maturity Stage:
Decline Stage:
- Film Cameras: Film cameras have entered the decline stage due to the rise of digital photography. With the convenience and affordability of digital cameras and smartphones, film cameras have become obsolete for most consumers.
- Printed Encyclopedias: Printed encyclopedias, like Encyclopedia Britannica, are in the decline stage. With the availability of online resources like Wikipedia, the demand for printed encyclopedias has significantly decreased.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
