What is Industry Life Cycle Analysis?
Industry Life Cycle Analysis is a strategic tool used to understand the various stages that an industry goes through over time. It helps businesses and investors gain insights into the current and future prospects of an industry, allowing them to make informed decisions.
Definition and Importance
One of the key benefits of Industry Life Cycle Analysis is that it allows businesses to identify opportunities and threats within an industry. By recognizing the stage an industry is in, businesses can tailor their strategies accordingly. For example, in the introduction stage, businesses may focus on product development and market penetration, while in the maturity stage, they may shift their focus to cost reduction and market consolidation.
Furthermore, Industry Life Cycle Analysis can help businesses anticipate future trends and changes within an industry. By studying the patterns and dynamics of each stage, businesses can make more accurate predictions about the future direction of an industry. This can be particularly useful for long-term planning and investment decisions.
The 4 Stages of Industry Life Cycle
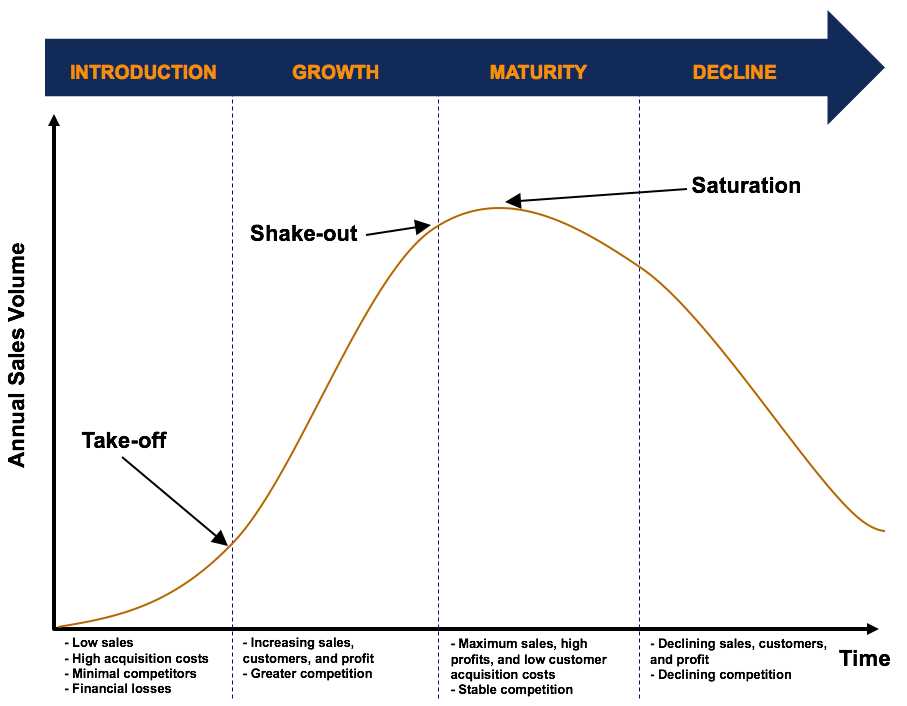
The four stages of Industry Life Cycle are:
- Decline: In the decline stage, the industry experiences a decline in demand and profitability. Companies may face challenges such as obsolescence and decreasing market share. Some companies may exit the industry, while others may look for new opportunities or diversify their offerings.
Example of Industry Life Cycle Analysis
Let’s consider the example of the smartphone industry to illustrate how Industry Life Cycle Analysis works. The smartphone industry went through the following stages:
- Introduction: In the early 2000s, smartphones were introduced to the market, but they were expensive and had limited features. Companies like Nokia and BlackBerry dominated the market during this stage.
- Growth: With advancements in technology and the introduction of touchscreens, the smartphone industry experienced rapid growth. Companies like Apple and Samsung entered the market and gained significant market share.
- Maturity: The smartphone industry reached maturity as market saturation increased and competition intensified. Companies focused on differentiating their products through features, design, and brand image.
- Decline: In recent years, the smartphone industry has faced a decline in growth due to market saturation and the emergence of new technologies such as wearables and smart home devices. Companies are now exploring new opportunities and diversifying their offerings.
Case Study: The Smartphone Industry
A detailed case study on the smartphone industry can provide further insights into the specific strategies and challenges faced by companies in each stage of the Industry Life Cycle. It can also showcase the impact of technological advancements and changing consumer preferences on the industry.
The definition of industry life cycle analysis refers to the systematic examination of the various stages that an industry passes through over time. These stages include the introduction or emergence stage, growth stage, maturity stage, and decline stage. Each stage is characterized by different levels of growth, competition, innovation, and profitability.
Similarly, during the growth stage, businesses can capitalize on increasing demand and expanding market opportunities. This stage is often characterized by intense competition and the need for innovation to maintain market share. By analyzing the industry life cycle, businesses can identify emerging trends and technologies that can drive growth and stay ahead of the competition.
The maturity stage of an industry is characterized by slower growth rates and market saturation. During this stage, businesses need to focus on differentiating their products or services and finding new market segments to sustain growth. Industry life cycle analysis can help businesses identify potential areas for diversification or expansion and make strategic decisions to maintain profitability.
The 4 Stages of Industry Life Cycle
1. Introduction Stage
Example: The electric vehicle industry is currently in the introduction stage. Companies like Tesla and Rivian are pioneering the development and production of electric vehicles, facing challenges such as high production costs and limited consumer adoption.
2. Growth Stage
Example: The e-commerce industry is currently in the growth stage. Companies like Amazon and Alibaba have experienced significant revenue growth as more consumers embrace online shopping. These companies are continuously expanding their product offerings and investing in logistics and infrastructure to meet the increasing demand.
3. Maturity Stage
Example: The smartphone industry is currently in the maturity stage. Major players like Apple and Samsung face intense competition and must continuously innovate and improve their products to stay ahead. Differentiation through features, design, and user experience becomes critical in maintaining market share.
4. Decline Stage
Example of Industry Life Cycle Analysis
Industry life cycle analysis is a valuable tool that helps businesses understand the various stages that an industry goes through over time. By analyzing the industry life cycle, companies can gain insights into the current state of the industry and make informed decisions about their strategies and investments.
Stage 1: Introduction
The first stage of the industry life cycle is the introduction stage. This is when a new product or service is introduced to the market. During this stage, there is typically a high level of uncertainty and risk, as companies are trying to establish themselves and gain market share. The focus is on product development, building brand awareness, and attracting early adopters.
Stage 2: Growth
Stage 3: Maturity
In the maturity stage, the market becomes saturated, and growth slows down. The competition is fierce, and companies need to differentiate themselves to maintain their market share. Price competition becomes more prominent, and companies may need to focus on cost-cutting measures to stay profitable. Innovation becomes crucial to stay ahead of the competition.
Stage 4: Decline
Case Study: The Smartphone Industry
Introduction:
The smartphone industry emerged in the late 1990s with the introduction of the first mobile phones capable of accessing the internet and running applications. Initially, smartphones were bulky and expensive, limiting their adoption to a niche market. However, advancements in technology and increased competition led to the rapid growth and evolution of the industry.
Stage 1: Introduction and Innovation:
In the early stages, the smartphone industry was characterized by a few key players introducing innovative products to the market. Companies like Nokia, BlackBerry, and Palm were among the pioneers, offering devices with features like email access, QWERTY keyboards, and basic internet browsing. These early smartphones were primarily targeted at business professionals and tech enthusiasts.
Stage 2: Growth and Expansion:
Stage 3: Maturity and Consolidation:
Stage 4: Decline and Transformation:
The smartphone industry is currently in the decline and transformation stage. This is primarily due to market saturation, slowing innovation, and the emergence of new technologies like wearable devices and augmented reality. Smartphone sales have plateaued, and companies are now exploring new avenues for growth and diversification.
Conclusion:

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
