What is Price-to-Book Ratio?
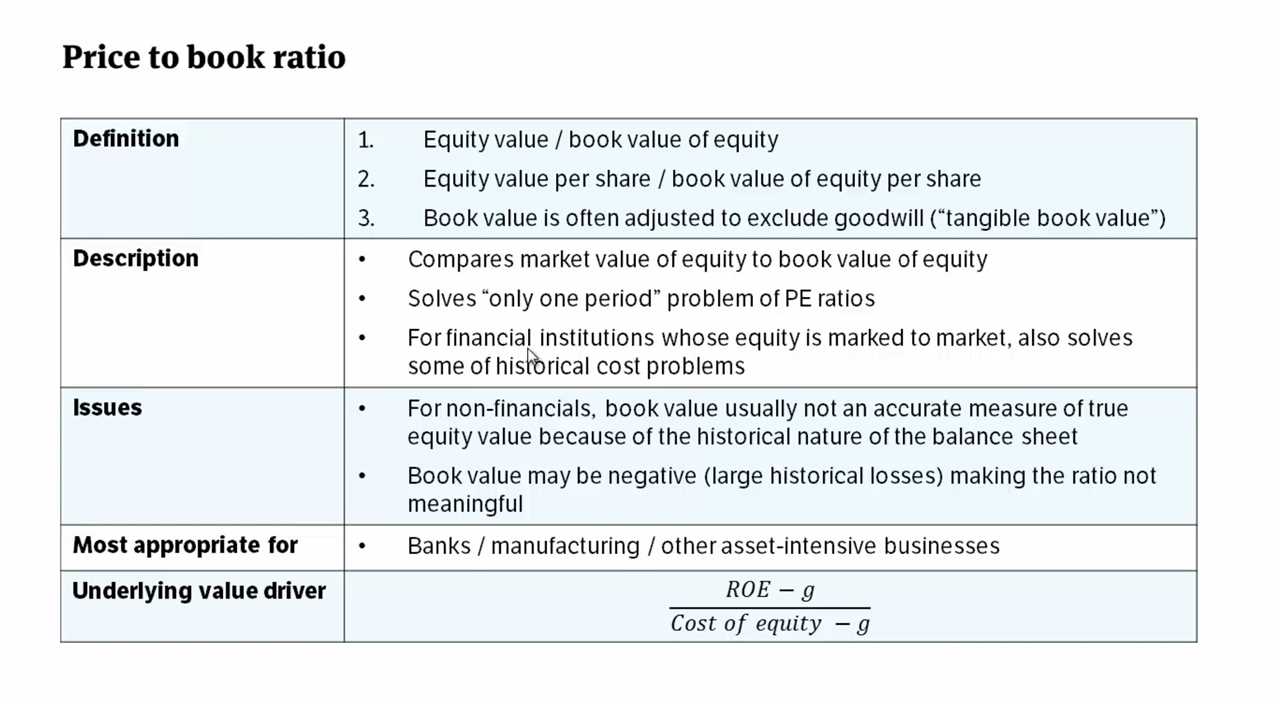
The Price-to-Book Ratio (P/B ratio) is a financial metric used to evaluate a company’s market value relative to its book value. It is a measure of how much investors are willing to pay for each dollar of a company’s net assets. The ratio is calculated by dividing the market price per share by the book value per share.
The book value of a company is the value of its assets minus its liabilities, as stated on its balance sheet. It represents the net worth of the company and is an indicator of its financial health. The market price per share is the current trading price of a company’s stock in the stock market.
Formula for Price-to-Book Ratio
The formula for calculating the Price-to-Book Ratio is:
P/B ratio = Market Price per Share / Book Value per Share
Where:
- Market Price per Share is the current trading price of a company’s stock.
- Book Value per Share is the book value of the company divided by the number of outstanding shares.
Interpreting the Price-to-Book Ratio
The Price-to-Book Ratio is used by investors to determine if a stock is overvalued or undervalued. A ratio below 1 indicates that the stock is trading at a discount to its book value, suggesting it may be undervalued. Conversely, a ratio above 1 suggests that the stock is trading at a premium to its book value, indicating it may be overvalued.
However, it is important to note that the interpretation of the Price-to-Book Ratio depends on the industry and the company’s specific circumstances. Industries with high capital expenditures, such as technology companies, may have higher P/B ratios due to the value of their intangible assets. On the other hand, industries with low capital expenditures, such as utilities, may have lower P/B ratios.
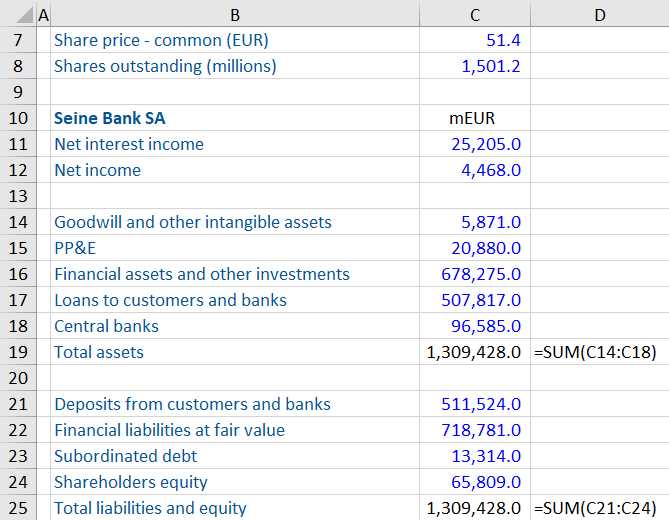
How to Calculate Price-to-Book Ratio?
The price-to-book ratio (P/B ratio) is a financial metric used to evaluate a company’s market value relative to its book value. It is calculated by dividing the market price per share by the book value per share. The P/B ratio provides investors with insights into how the market values a company’s assets compared to its market price.
Formula for Price-to-Book Ratio
The formula for calculating the price-to-book ratio is as follows:
| P/B Ratio | = | Market Price per Share | / | Book Value per Share |
The market price per share represents the current market value of a company’s stock, while the book value per share represents the net asset value of the company per share.
Example of Price-to-Book Ratio Calculation
Let’s consider an example to illustrate how to calculate the price-to-book ratio. Suppose Company XYZ has a market price per share of $50 and a book value per share of $10. The price-to-book ratio would be calculated as follows:
| P/B Ratio | = | $50 | / | $10 |
| P/B Ratio | = | 5 |
Investors use the price-to-book ratio to assess whether a company’s stock is overvalued or undervalued. A higher P/B ratio may indicate that the market has high expectations for the company’s future growth prospects. Conversely, a lower P/B ratio may suggest that the market has lower expectations for the company’s performance.
Example of Price-to-Book Ratio Calculation
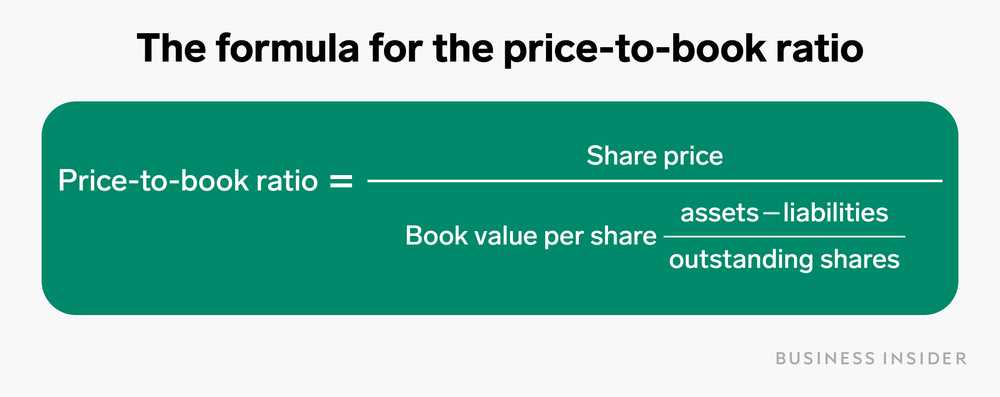
To calculate the P/B ratio, you need to divide the market price per share by the book value per share. The market price per share can be obtained from the stock market, while the book value per share can be calculated by dividing the total book value of the company by the number of outstanding shares.
Formula for calculating the P/B ratio:
P/B Ratio = Market Price per Share / Book Value per Share
For example, let’s consider a company with a market price per share of $50 and a book value per share of $10. To calculate the P/B ratio, we divide $50 by $10, resulting in a P/B ratio of 5.
The interpretation of the P/B ratio depends on the industry and the company’s growth prospects. In general, a P/B ratio above 1 indicates that the market values the company higher than its book value, suggesting potential overvaluation. Conversely, a P/B ratio below 1 suggests that the market values the company lower than its book value, indicating potential undervaluation.
Importance of Price-to-Book Ratio in Financial Analysis
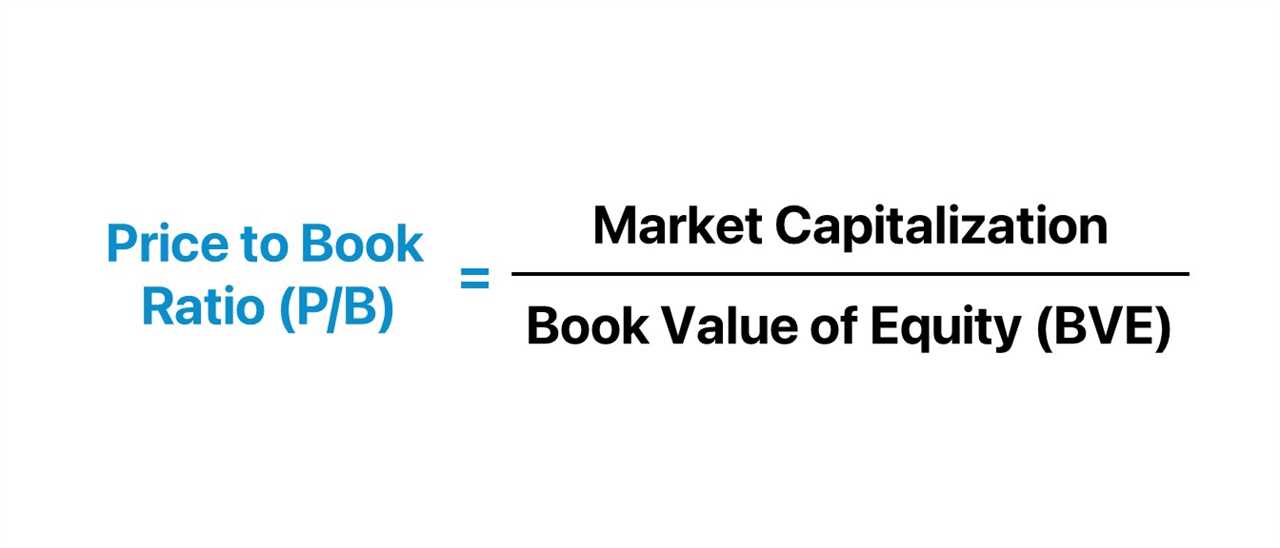
The Price-to-Book (P/B) ratio is a key financial ratio that is widely used by investors and analysts to evaluate the value and financial health of a company. It is a simple yet powerful tool that provides insights into how the market values a company relative to its book value.
The P/B ratio is calculated by dividing the market price per share by the book value per share. The market price per share represents the current market value of a company’s stock, while the book value per share represents the net asset value of the company per share.
Furthermore, the P/B ratio can also be used to compare the valuation of a company with its industry peers. By comparing the P/B ratios of different companies in the same industry, investors can gain insights into which companies are relatively undervalued or overvalued compared to their competitors.
Another important aspect of the P/B ratio is its relationship with the company’s return on equity (ROE). The ROE is a measure of the company’s profitability and efficiency in generating profits from its shareholders’ equity. The P/B ratio can be used in conjunction with the ROE to assess whether a company is generating a sufficient return on its equity.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
