What is Occupancy Rate?
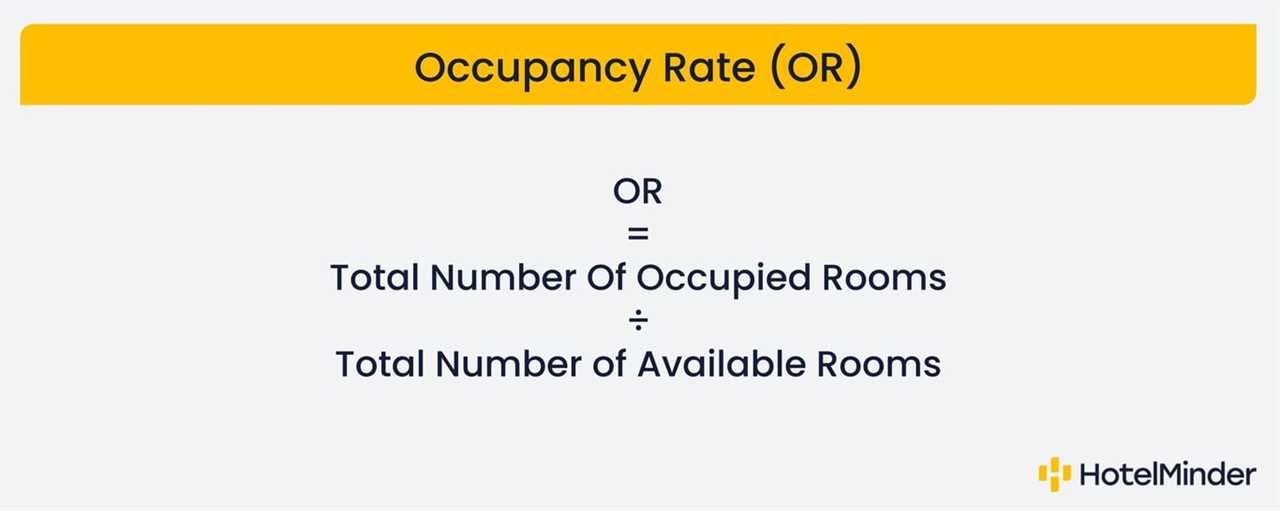
Occupancy rate is a key metric used in real estate investing to measure the percentage of occupied units in a property or market. It is a crucial indicator of the health and performance of a real estate investment. The occupancy rate is calculated by dividing the number of occupied units by the total number of units available.
Definition and Explanation
The occupancy rate provides insight into the demand for rental properties or the marketability of a property. It is commonly used by real estate investors, property managers, and analysts to assess the profitability and potential risks of an investment. A high occupancy rate indicates strong demand and a stable rental market, while a low occupancy rate may suggest a lack of demand or other issues affecting the property’s attractiveness to tenants.
The occupancy rate is typically expressed as a percentage. For example, if a property has 100 units and 90 of them are occupied, the occupancy rate would be 90%. It is important to note that the occupancy rate can vary over time due to factors such as market conditions, property management, and tenant turnover.
Importance in Real Estate Investing
The occupancy rate is a critical factor in determining the potential income and return on investment for a rental property. A high occupancy rate indicates a steady stream of rental income, while a low occupancy rate can result in financial challenges for the property owner. Real estate investors use the occupancy rate to evaluate the performance of their investments, make informed decisions about pricing and marketing strategies, and identify areas for improvement.
In addition, the occupancy rate is used to assess the overall health of a rental market. It can help investors identify trends, such as increasing demand or oversupply, and make strategic decisions about where to invest or divest their assets.
How to Analyze Occupancy Rate
When analyzing the occupancy rate, it is important to consider the specific market conditions and property type. A high occupancy rate may be desirable, but it could also indicate that rental rates are too low and potential income is being missed. Conversely, a low occupancy rate may present an opportunity for higher rental rates, but it could also indicate a lack of demand or other issues affecting the property’s attractiveness to tenants.
It is also important to compare the occupancy rate to similar properties in the market to determine how well a property is performing relative to its competition. Additionally, tracking the occupancy rate over time can help identify seasonal patterns or trends that may impact rental income and inform strategic decision-making.
| Occupancy Rate | Implications |
|---|---|
| High | Strong demand, stable rental market |
| Low | Lack of demand, potential financial challenges |
Definition and Explanation
The occupancy rate is a key metric used in the analysis of real estate investing. It measures the percentage of occupied units in a property or market at a given time. This metric is commonly used by investors, property managers, and analysts to assess the performance and potential profitability of a real estate investment.
The occupancy rate is calculated by dividing the number of occupied units by the total number of units in a property or market, and then multiplying by 100 to get a percentage. For example, if a property has 100 units and 90 of them are occupied, the occupancy rate would be 90%.
Why is the occupancy rate important?
The occupancy rate is an important indicator of the demand for rental properties in a specific market. A high occupancy rate suggests that there is a strong demand for housing, which can lead to higher rental income and potential capital appreciation for investors. On the other hand, a low occupancy rate may indicate a weak market with limited demand, which can result in lower rental income and potential financial losses.
Furthermore, the occupancy rate can also provide insights into the overall health and stability of a property or market. A consistently high occupancy rate indicates that the property is well-managed and attractive to tenants, while a fluctuating or declining occupancy rate may signal issues such as poor management, competition from other properties, or changes in market conditions.
Investors and property managers use the occupancy rate to make informed decisions about their real estate investments. It helps them determine rental rates, evaluate the potential for rental income growth, and assess the risk associated with a particular property or market. Additionally, lenders and financial institutions often consider the occupancy rate when evaluating loan applications for real estate investments.
How to analyze the occupancy rate
When analyzing the occupancy rate, it is important to consider the specific market and property characteristics. A high occupancy rate may be desirable, but it is also important to assess the quality of tenants and the potential for rental income growth. A property with a high occupancy rate but low-quality tenants may result in higher turnover and maintenance costs.
Comparing the occupancy rate to historical data and market averages can provide valuable insights into the performance and potential of a property. If the occupancy rate is consistently higher than the market average, it may indicate a strong demand and potential for rental income growth. Conversely, if the occupancy rate is consistently lower than the market average, it may indicate a weak market or issues with the property.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| – Helps assess demand and potential profitability | – Does not account for rental rates and expenses |
| – Provides insights into property management | – Can be influenced by temporary factors |
| – Considered by lenders for loan applications | – Does not measure tenant quality |
Importance in Real Estate Investing
Here are some reasons why the occupancy rate is important in real estate investing:
- Profitability: The occupancy rate is directly linked to the rental income generated by a property. A high occupancy rate indicates a steady stream of rental income, resulting in increased cash flow and profitability for the investor. On the other hand, a low occupancy rate can lead to financial challenges and lower returns.
- Risk Assessment: The occupancy rate helps investors assess the risk associated with a property. A high occupancy rate indicates strong demand and market stability, reducing the risk of potential vacancies. Conversely, a low occupancy rate may suggest a weak market or property-specific issues, increasing the risk of prolonged vacancies and financial loss.
- Market Demand: By analyzing the occupancy rate, investors can gain insights into the demand for rental properties in a specific market. A high occupancy rate suggests a strong demand for housing, indicating a potentially profitable investment opportunity. Conversely, a low occupancy rate may indicate an oversaturated market or lack of demand, signaling a less favorable investment climate.
- Property Management: The occupancy rate is a key performance indicator for property management. It helps property owners and managers evaluate their marketing strategies, tenant retention efforts, and overall operational efficiency. By monitoring and analyzing the occupancy rate, investors can identify areas for improvement and implement strategies to maximize occupancy and rental income.
- Comparative Analysis: The occupancy rate allows investors to compare different properties and make informed investment decisions. By comparing the occupancy rates of similar properties in the same market, investors can identify properties with higher potential returns and lower risks. This comparative analysis helps investors allocate their resources effectively and choose properties that align with their investment goals.
How to Analyze Occupancy Rate
1. Gather Data
2. Calculate the Occupancy Rate
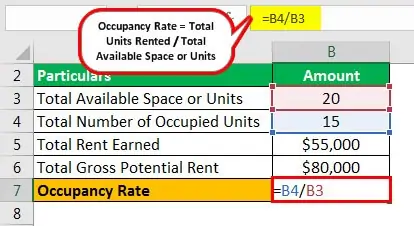
Once the data is collected, the next step is to calculate the occupancy rate. This can be done by dividing the number of occupied units by the total number of units in the property and multiplying by 100. The result will be a percentage that represents the occupancy rate.
3. Compare to Market Average
After calculating the occupancy rate, it is important to compare it to the average occupancy rate in the local market. This will provide insights into how the property is performing in relation to its competitors. If the property’s occupancy rate is significantly lower than the market average, it may indicate issues that need to be addressed.
4. Analyze Trends

Another important aspect of analyzing the occupancy rate is to identify any trends. This can be done by comparing the current occupancy rate to the historical occupancy rates of the property. If there is a consistent decline or increase in occupancy over time, it can indicate a pattern that should be taken into consideration when making investment decisions.
5. Consider Factors Affecting Occupancy
By following these steps, investors can effectively analyze the occupancy rate and make informed decisions regarding their real estate investments. It is important to regularly monitor the occupancy rate to ensure the property remains profitable and to identify any potential issues or opportunities for improvement.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
