Mortgage Interest Deduction: Everything You Need to Know
The mortgage interest deduction is a tax benefit that allows homeowners to deduct the interest they pay on their mortgage loans from their taxable income. This deduction is one of the most significant tax breaks available to homeowners and can result in substantial savings.
So how does the mortgage interest deduction work? When you take out a mortgage loan to purchase or refinance a home, you are required to make monthly payments that include both principal and interest. The interest portion of your mortgage payment is tax-deductible, meaning you can subtract it from your taxable income. This reduces the amount of income you are taxed on, resulting in lower tax liability.
To qualify for the mortgage interest deduction, you must meet certain criteria. First, the loan must be secured by your primary residence or a second home. Investment properties do not qualify for this deduction. Second, the loan must be used to buy, build, or improve the home. You cannot deduct the interest on a loan used for other purposes, such as paying off credit card debt or financing a vacation.
The benefits of the mortgage interest deduction are twofold. First, it reduces your taxable income, which can result in a lower tax bill. Second, it makes homeownership more affordable by reducing the overall cost of owning a home. This can make a significant difference in the monthly mortgage payment and can help make homeownership more accessible to a wider range of individuals and families.
What is the Mortgage Interest Deduction?
The mortgage interest deduction is a tax benefit provided to homeowners in many countries, including the United States. It allows homeowners to deduct the interest they pay on their mortgage from their taxable income, reducing the amount of taxes they owe.
When individuals or families purchase a home, they often take out a mortgage loan to finance the purchase. The mortgage loan comes with an interest rate, which is the cost of borrowing the money. The mortgage interest deduction allows homeowners to deduct this interest expense from their taxable income, providing them with potential tax savings.
How Does the Mortgage Interest Deduction Work?
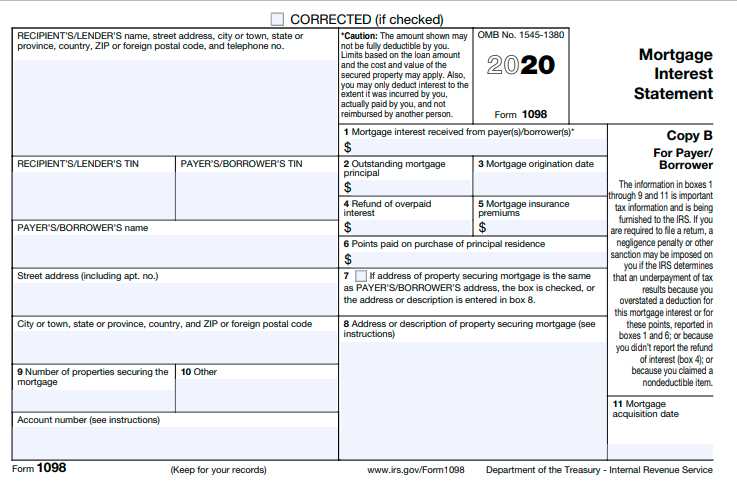
To take advantage of the mortgage interest deduction, homeowners must itemize their deductions on their tax return. This means they must list and provide documentation for all their eligible expenses, including mortgage interest, rather than taking the standard deduction.
The amount of mortgage interest that can be deducted depends on several factors. In the United States, for example, the mortgage interest deduction is limited to interest paid on mortgage debt up to $750,000 for married couples filing jointly, or $375,000 for individuals. Additionally, the mortgage must be secured by a qualified residence, such as a primary home or a second home.
Who Qualifies for the Mortgage Interest Deduction?
In general, homeowners who have a mortgage on their primary or secondary residence may qualify for the mortgage interest deduction. However, there are certain criteria that must be met to be eligible.
Firstly, the mortgage must be secured by a qualified residence, which includes a primary home and a second home. This means that vacation homes or investment properties may also qualify for the deduction.
Secondly, the homeowner must itemize their deductions on their tax return. This requires keeping track of all eligible expenses, including mortgage interest, and providing documentation to support the deductions claimed.
Overall, the mortgage interest deduction can provide significant tax savings for homeowners. It is important to consult with a tax professional or financial advisor to fully understand the eligibility requirements and potential benefits of this deduction.
How Does the Mortgage Interest Deduction Work?
The mortgage interest deduction is a tax benefit that allows homeowners to deduct the interest they pay on their mortgage from their taxable income. This deduction is one of the most significant tax breaks available to homeowners and can result in significant savings.
When you take out a mortgage to purchase a home, you will likely have to pay interest on the loan. The mortgage interest deduction allows you to deduct this interest from your taxable income, reducing the amount of income tax you owe.
To qualify for the mortgage interest deduction, you must itemize your deductions on your tax return. This means that instead of taking the standard deduction, you will need to list out all of your deductible expenses, including mortgage interest, and subtract them from your income.
Additionally, the mortgage interest deduction is only available for mortgages used to purchase, build, or improve a primary or secondary residence. It does not apply to mortgages used for investment properties or vacation homes.
It’s also worth mentioning that the mortgage interest deduction is an itemized deduction, which means that you can only take advantage of it if your total itemized deductions exceed the standard deduction. If your itemized deductions are less than the standard deduction, it may be more beneficial for you to take the standard deduction instead.
Who Qualifies for the Mortgage Interest Deduction?
The mortgage interest deduction is available to homeowners who meet certain criteria. To qualify for this deduction, you must meet the following requirements:
- You must be a homeowner who has taken out a mortgage loan to purchase, build, or improve your primary residence or a second home.
- Your mortgage loan must be secured by the property that you own.
- You must itemize your deductions on your tax return using Schedule A.
- You must have paid mortgage interest during the tax year.
- The mortgage interest you paid must be on a loan that is less than or equal to $750,000 if you are married filing jointly or $375,000 if you are single or married filing separately.
It is important to note that the mortgage interest deduction is not available to those who choose to take the standard deduction instead of itemizing their deductions. Additionally, if you are subject to the alternative minimum tax (AMT), you may not be able to claim the full deduction.
It is recommended that you consult with a tax professional or use tax preparation software to determine if you qualify for the mortgage interest deduction and to ensure that you are claiming the correct amount.
Benefits of the Mortgage Interest Deduction
The mortgage interest deduction is a tax benefit that allows homeowners to deduct the interest they pay on their mortgage from their taxable income. This deduction can result in significant savings for homeowners and is one of the most popular tax deductions available.
1. Lower Tax Liability
One of the main benefits of the mortgage interest deduction is that it can lower your overall tax liability. By deducting the interest you pay on your mortgage, you reduce your taxable income, which in turn reduces the amount of taxes you owe. This can result in substantial savings, especially for homeowners with high mortgage interest payments.
2. Increased Affordability
The mortgage interest deduction can make homeownership more affordable for many people. By reducing the amount of taxes you owe, you have more disposable income to put towards your mortgage payments. This can help make homeownership more accessible and allow individuals and families to afford a home that they may not have been able to otherwise.
3. Encourages Homeownership
The mortgage interest deduction is also seen as a way to encourage homeownership. By providing a tax incentive for homeowners, the government aims to promote the benefits of owning a home and stimulate the housing market. This deduction can make owning a home more financially attractive compared to renting, as it offers potential tax savings.
4. Stimulates the Economy
The mortgage interest deduction can also have a positive impact on the economy as a whole. By making homeownership more affordable and encouraging people to buy homes, it can stimulate the housing market and create demand for related industries, such as construction, real estate, and home improvement. This can lead to job creation and economic growth.
5. Supports Home Equity
Another benefit of the mortgage interest deduction is that it can help homeowners build equity in their homes. By reducing the amount of taxes owed, homeowners have more money available to invest in their homes or pay down their mortgage. This can help increase the value of their property over time and build wealth.
Limitations and Restrictions of the Mortgage Interest Deduction
The mortgage interest deduction is a valuable tax benefit for homeowners, but it does come with certain limitations and restrictions that you should be aware of. These limitations can affect how much of your mortgage interest you can deduct and who qualifies for the deduction.
1. Mortgage Debt Limit
One of the main limitations of the mortgage interest deduction is the mortgage debt limit. Currently, you can only deduct the interest on mortgage debt up to $750,000 if you are married filing jointly or $375,000 if you are single or married filing separately. Any mortgage debt above these limits is not eligible for the deduction.
2. Home Equity Debt Limit
Prior to 2018, homeowners could also deduct the interest on home equity debt up to $100,000. However, the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017 eliminated this deduction for most taxpayers. Starting in 2018, you can only deduct the interest on home equity debt if the loan was used to buy, build, or improve your home.
3. Itemizing Deductions
In order to claim the mortgage interest deduction, you must itemize your deductions on your tax return. This means you will need to keep track of all your deductible expenses, such as mortgage interest, property taxes, and other qualifying expenses. If your total itemized deductions are not higher than the standard deduction, it may not be beneficial for you to claim the mortgage interest deduction.
4. Second Homes and Rental Properties
5. Alternative Minimum Tax
Overall, while the mortgage interest deduction can provide significant tax savings for homeowners, it is important to understand and consider the limitations and restrictions that come with it. Consulting a tax professional can help ensure that you maximize your tax benefits and comply with all applicable tax laws.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
