Communism: Key Principles and Characteristics
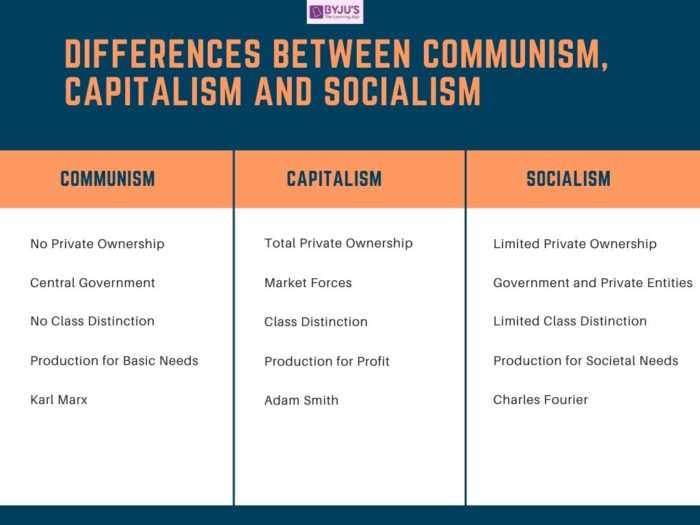
Communism is a socio-economic ideology that aims to create a classless society where the means of production are owned collectively by the community as a whole. It is based on the principles of common ownership and the absence of private property.
One of the key principles of communism is the abolition of social classes. In a communist society, there is no distinction between the working class and the capitalist class. Everyone is considered equal and has equal access to resources and opportunities.
Another characteristic of communism is the central planning of the economy. In a communist system, the government controls and plans all economic activities, including production, distribution, and consumption. This is done with the aim of ensuring that resources are allocated in a fair and equitable manner, and that the needs of all members of society are met.
Communism also advocates for the abolition of private property. In a communist society, all property is owned collectively by the community, and there is no individual ownership of land, factories, or other means of production. This is seen as a way to eliminate exploitation and ensure that wealth is distributed equally among all members of society.
Additionally, communism promotes the idea of a classless society, where there is no hierarchy or inequality. In a communist system, everyone is considered equal and has equal rights and opportunities. This includes equal access to education, healthcare, and other social services.
However, it is important to note that communism has been implemented differently in various countries, and its principles and characteristics have been interpreted and applied in different ways. The Soviet Union, China, and Cuba are examples of countries that have adopted communist systems, but each has had its own unique approach and implementation.
| Key Principles | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Abolition of social classes | Central planning of the economy |
| Abolition of private property | Classless society |
Socialism: Features and Distinctions
Socialism is an economic and political system that aims to create a more equitable society by reducing the gap between the rich and the poor. It is based on the principles of collective ownership and control of the means of production, distribution, and exchange.
Key Features of Socialism
- Collective Ownership: In a socialist system, the means of production, such as factories, land, and resources, are owned and controlled by the community as a whole, rather than by private individuals or corporations. This allows for the equitable distribution of wealth and resources.
- Central Planning: Socialism often involves central planning, where the government or a centralized authority determines the allocation of resources and sets production targets. This ensures that resources are used efficiently and in accordance with the needs of the society.
- Welfare State: Socialism emphasizes the provision of social welfare programs, such as healthcare, education, and housing, to ensure that basic needs are met for all members of society. This helps to reduce inequality and provide equal opportunities for all.
- Worker Control: Socialism seeks to empower workers by giving them control over their workplaces and the decisions that affect their lives. This can be achieved through worker cooperatives or other forms of democratic decision-making within the workplace.
- Redistribution of Wealth: Socialism aims to redistribute wealth and income from the rich to the poor through progressive taxation and social programs. This helps to reduce poverty and create a more equal society.
Distinctions from Capitalism

Socialism differs from capitalism in several key ways:
- In capitalism, the means of production are privately owned, whereas in socialism, they are collectively owned.
- In capitalism, the allocation of resources is determined by the market forces of supply and demand, while in socialism, it is often planned by a centralized authority.
- Capitalism tends to prioritize profit-making and individual accumulation of wealth, while socialism focuses on social welfare and reducing inequality.
- Capitalism relies on competition and the pursuit of self-interest, while socialism emphasizes cooperation and the common good.
Overall, socialism seeks to create a more just and equitable society by reducing economic inequality and ensuring that basic needs are met for all members of society. While there are different interpretations and implementations of socialism, its core principles revolve around collective ownership, central planning, and social welfare.
Capitalism: Main Characteristics and Critiques
Capitalism is an economic system characterized by private ownership of the means of production and the pursuit of profit. It is based on the principles of free market competition, individualism, and limited government intervention. Here are the main characteristics and critiques of capitalism:
- Private Ownership: In capitalism, individuals and businesses have the right to own and control property, including land, factories, and resources. This allows for the accumulation of wealth and the incentive to invest and innovate.
- Free Market: Capitalism operates on the basis of supply and demand, with prices determined by market forces. The market is driven by competition, which encourages efficiency and innovation.
- Profit Motive: The primary goal of capitalism is to generate profit. This drives businesses to maximize their profits by increasing productivity, reducing costs, and expanding their market share.
- Individualism: Capitalism emphasizes individual freedom and self-interest. Individuals are free to pursue their own economic goals and make choices based on their own preferences.
- Limited Government Intervention: Capitalism advocates for minimal government interference in the economy. The role of the government is primarily to enforce property rights, maintain law and order, and provide a legal framework for economic transactions.
While capitalism has been successful in promoting economic growth and innovation, it has also faced criticism and challenges. Some of the critiques of capitalism include:
- Inequality: Capitalism can lead to income and wealth inequality, as those who own capital have more opportunities to accumulate wealth than those who do not.
- Exploitation: Critics argue that capitalism can exploit workers by paying low wages and providing poor working conditions in order to maximize profits.
- Environmental Impact: Capitalism’s focus on profit can lead to the exploitation of natural resources and environmental degradation.
- Market Failures: Capitalism is susceptible to market failures, such as monopolies, externalities, and information asymmetry, which can lead to inefficient allocation of resources and economic instability.
- Social Disconnection: Critics argue that capitalism can foster a sense of social disconnection and alienation, as individuals prioritize their own economic interests over collective well-being.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
