Laddering: A Comprehensive Guide with Meaning, Overview, Examples, and FAQ

Laddering is a marketing research technique that involves asking a series of questions to uncover consumers’ preferences and priorities. It is commonly used in product development, brand positioning, and market segmentation.
The laddering process typically involves conducting in-depth interviews or surveys with consumers. The interviewer starts by asking about the product or service attributes, then moves on to the functional consequences (i.e., what the product does), and finally explores the personal values and self-identity that are associated with the product. This line of questioning helps uncover the underlying motivations and emotional connections that drive consumer behavior.
For example, let’s consider a hypothetical scenario where a company is developing a new smartphone. Through laddering interviews, they may discover that consumers value a sleek design (attribute), because it makes them feel stylish and sophisticated (functional consequence), which aligns with their desire to be seen as trendy and modern (personal value). Armed with this insight, the company can then tailor their marketing messages to highlight these emotional benefits and appeal to their target audience.
What is Laddering?
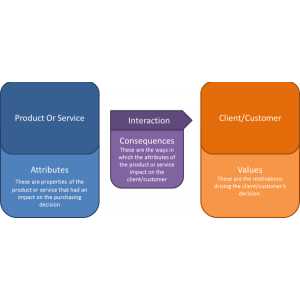
Laddering is a marketing research technique used to understand consumer preferences and decision-making processes. It involves asking individuals to rank a series of items or attributes in order of importance.
How does laddering work?
Laddering typically involves a series of interviews or surveys with consumers. Participants are presented with a list of items or attributes and asked to rank them in order of importance. The researcher then probes deeper, asking participants to explain why they ranked certain items higher or lower.
Through this process, researchers aim to uncover the underlying motivations and values that drive consumer decision-making. For example, a participant may rank a particular attribute, such as “environmentally friendly,” as very important. When asked why, they may explain that they prioritize sustainability and want to make choices that align with their values.
Benefits of laddering
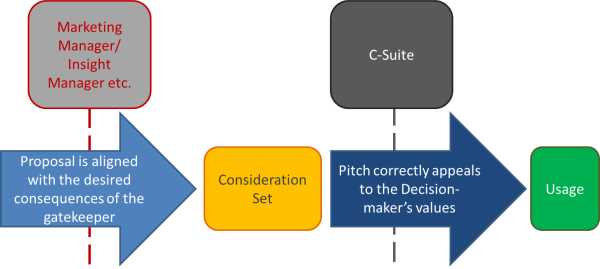
Some benefits of laddering include:
- Identifying key attributes that drive consumer decision-making
- Developing more effective marketing strategies and messaging
- Creating products and services that align with consumer values
Overall, laddering is a powerful tool for marketers to gain deeper insights into consumer behavior and develop strategies that effectively target their audience.
Overview of Laddering
In the world of finance, laddering is a strategy that involves the systematic purchase or sale of financial instruments with different maturity dates. This technique is commonly used in bond investing, but it can also be applied to other types of investments such as certificates of deposit (CDs) or annuities.
The concept behind laddering is to spread out investments or withdrawals over a period of time, rather than investing or withdrawing all at once. By doing so, investors can potentially reduce their exposure to interest rate risk and take advantage of different interest rate environments.
The benefits of laddering are twofold. First, it helps to mitigate interest rate risk. If interest rates rise, the investor will be able to reinvest the maturing bonds at higher rates, thus increasing their overall yield. On the other hand, if interest rates decline, the investor will still have some bonds with higher yields that were purchased when rates were higher.
Second, laddering provides investors with a consistent income stream. As each bond matures, the investor receives the principal back, which can then be reinvested or used for other purposes. This can be particularly useful for individuals who rely on investment income for their living expenses.
Examples of Laddering Techniques
Laddering is a powerful market research technique that allows researchers to uncover deep insights into consumer preferences and decision-making processes. By using a series of probing questions, laddering helps to reveal the underlying motivations and values that drive consumer behavior. Here are some examples of laddering techniques:
Frequently Asked Questions about Laddering
Here are some frequently asked questions about laddering:
1. What is laddering?
Laddering is an investment strategy that involves spreading out investments over a range of different maturity dates. It is commonly used in fixed-income investments, such as bonds or certificates of deposit, where investors purchase multiple securities with staggered maturity dates.
2. How does laddering work?
3. What are the advantages of laddering?
Some advantages of laddering include:
- Reduced interest rate risk: By spreading out investments over different maturity dates, laddering helps to mitigate the impact of interest rate fluctuations.
- Steady income: Laddering provides a regular stream of income as securities mature and are reinvested.
- Flexibility: Laddering allows investors to have access to funds periodically as securities mature, providing liquidity.
4. Are there any disadvantages to laddering?
While laddering can be a useful investment strategy, there are some potential disadvantages to consider:
- Lower potential returns: Laddering may result in lower overall returns compared to investing in longer-term securities with higher yields.
- Increased complexity: Managing a laddered portfolio requires monitoring and reinvesting funds periodically, which can be more complex compared to investing in a single security.
- Market risk: Laddering does not eliminate the risk of market fluctuations, and the value of securities can still be affected by changes in interest rates or economic conditions.
5. What types of investments can be used in laddering?
Laddering can be used with various fixed-income investments, including:
- Bonds: Treasury bonds, corporate bonds, municipal bonds, etc.
- Certificates of Deposit (CDs): Time deposits with fixed interest rates and maturity dates.
- Fixed Annuities: Insurance contracts that provide a guaranteed income stream over a specified period.
6. How do I start laddering?
To start laddering, you can follow these steps:
- Set your investment goals: Determine your investment objectives and time horizon.
- Choose your investment vehicles: Select the type of securities you want to include in your ladder.
- Decide on the ladder structure: Determine the number of rungs in your ladder and the duration of each rung.
- Allocate your funds: Divide your investment capital among the different rungs of your ladder.
- Monitor and adjust: Regularly review and adjust your ladder as securities mature or market conditions change.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
