What is Internal Audit?
Internal audit refers to the independent and objective evaluation of an organization’s operations, processes, and controls. It is conducted by a team of internal auditors who are responsible for assessing the effectiveness of risk management, governance, and internal control processes within the organization.
Role of Internal Audit
The primary role of internal audit is to provide assurance to the organization’s management and stakeholders that the organization’s operations are being conducted in accordance with established policies, procedures, and applicable laws and regulations. Internal auditors also play a crucial role in identifying areas of improvement and providing recommendations to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of the organization’s operations.
Scope of Internal Audit
The scope of internal audit can vary depending on the organization’s size, industry, and specific requirements. However, it generally includes the following areas:
- Financial processes and controls
- Operational processes and controls
- Compliance with laws and regulations
- Risk management processes
- Information technology systems and controls
Internal auditors use a systematic and disciplined approach to gather evidence, analyze data, and evaluate the effectiveness of controls and processes. They also assess the reliability and integrity of financial and operational information, and ensure that the organization’s assets are safeguarded.
Benefits of Internal Audit
Internal audit provides several benefits to organizations, including:
- Improved governance and risk management
- Enhanced operational efficiency
- Identification of potential fraud and irregularities
- Increased compliance with laws and regulations
- Enhanced decision-making processes
Overall, internal audit plays a crucial role in helping organizations achieve their objectives by providing independent and objective assessments of their operations and controls.
The Importance of Internal Audit
Internal audit plays a crucial role in the success and sustainability of an organization. It provides an independent and objective assessment of the organization’s operations, risk management, and internal controls. The importance of internal audit can be summarized in the following points:
1. Enhancing Internal Controls:
Internal audit helps in identifying weaknesses in internal controls and provides recommendations for improvement. By conducting regular audits, organizations can strengthen their internal controls, minimize the risk of fraud and error, and ensure compliance with laws and regulations.
2. Identifying Risks:
3. Promoting Efficiency and Effectiveness:
Internal audit evaluates the efficiency and effectiveness of the organization’s operations and processes. By identifying inefficiencies and bottlenecks, organizations can streamline their operations, improve productivity, and achieve cost savings.
4. Ensuring Compliance:
Internal audit ensures that the organization complies with laws, regulations, and internal policies. By conducting compliance audits, organizations can identify any non-compliance issues and take corrective actions to avoid legal and reputational risks.
5. Providing Assurance to Stakeholders:
Internal audit provides assurance to stakeholders, including management, board of directors, and external parties, that the organization’s operations are conducted in a transparent and ethical manner. This helps in building trust and confidence among stakeholders.
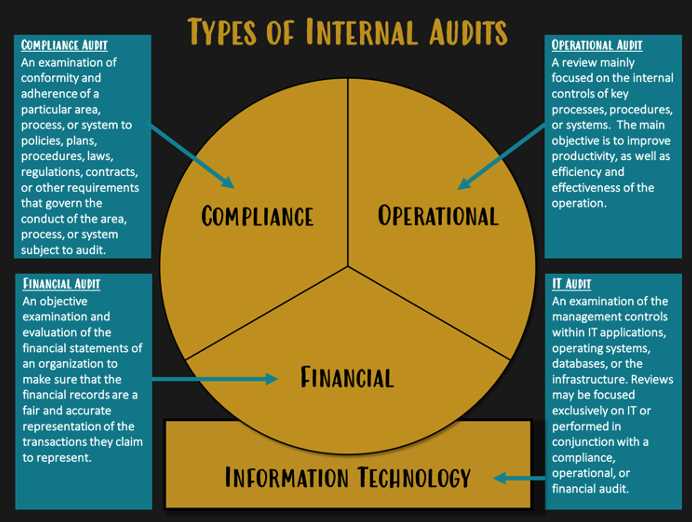
Types of Internal Audit
Internal audit is an essential function within an organization that helps to ensure the effectiveness of internal controls, risk management, and governance processes. There are several types of internal audit that are conducted to address different aspects of an organization’s operations. These types include financial audit, operational audit, and compliance audit.
Financial audit is the most common type of internal audit. It focuses on reviewing an organization’s financial records and statements to ensure accuracy, completeness, and compliance with applicable laws and regulations. Financial audits are typically conducted by certified public accountants (CPAs) who examine financial transactions, internal controls, and financial reporting processes.
Operational audit, on the other hand, evaluates an organization’s operational processes and procedures to identify areas for improvement and efficiency. This type of audit helps management to assess whether the organization’s resources are being used effectively and whether operational goals and objectives are being achieved. Operational audits may cover areas such as production, sales, procurement, and human resources.
Compliance audit focuses on assessing an organization’s compliance with laws, regulations, and internal policies. It ensures that the organization is following applicable laws and regulations, as well as its own internal policies and procedures. Compliance audits are important for organizations operating in regulated industries, such as healthcare, finance, and manufacturing.
In addition to these types of internal audit, there are also other specialized audits that may be conducted based on the specific needs and risks of an organization. These audits may include IT audit, environmental audit, and quality audit, among others.
Financial Audit
A financial audit is one of the most common types of internal audits conducted by organizations. It focuses on examining the financial records and statements of a company to ensure accuracy, reliability, and compliance with accounting standards and regulations. The main objective of a financial audit is to provide assurance to stakeholders, such as investors, creditors, and management, that the financial information presented by the company is trustworthy and reflects the true financial position of the organization.
Purpose of Financial Audit
The purpose of a financial audit is to assess the financial health and performance of a company. It involves a thorough examination of financial transactions, records, and statements to identify any errors, irregularities, or fraudulent activities. The audit process includes reviewing financial documents, conducting interviews with key personnel, performing analytical procedures, and testing internal controls.
Key Steps in a Financial Audit
A financial audit typically follows a structured process to ensure comprehensive and accurate results. The key steps involved in a financial audit include:
- Testing: This step includes gathering and analyzing financial data, performing substantive tests, and assessing the effectiveness of internal controls.
- Evaluation: The auditor evaluates the findings from the testing phase, identifies any issues or discrepancies, and determines the overall reliability of the financial statements.
- Reporting: The auditor prepares a detailed report summarizing the audit findings, including any identified weaknesses or areas for improvement.
- Follow-up: After the audit report is issued, the auditor may follow up to ensure that any identified issues are addressed and resolved by management.
Benefits of Financial Audit
A financial audit provides several benefits to organizations, including:
- Enhanced credibility: A financial audit enhances the credibility of the company’s financial statements, as it provides assurance to stakeholders that the information presented is accurate and reliable.
- Improved internal controls: Through the audit process, weaknesses in internal controls can be identified and addressed, leading to improved financial management and risk mitigation.
- Compliance with regulations: A financial audit ensures that the company is compliant with accounting standards and regulations, reducing the risk of penalties or legal issues.
- Identification of fraud or errors: The audit process helps in detecting any fraudulent activities or errors in financial records, allowing for timely corrective actions.
- Insights for decision-making: The findings of a financial audit provide valuable insights to management for making informed decisions regarding financial strategies, investments, and resource allocation.
Operational Audit
An operational audit is a type of internal audit that focuses on evaluating the efficiency and effectiveness of an organization’s operations. It involves a comprehensive review of the processes, procedures, and systems in place to ensure that they are aligned with the organization’s goals and objectives.
Objective:
The main objective of an operational audit is to identify areas where the organization can improve its operational efficiency and effectiveness. This includes identifying any inefficiencies, bottlenecks, or gaps in processes that may be hindering the organization’s ability to achieve its goals.
Scope:
The scope of an operational audit can vary depending on the organization and its specific needs. It may focus on a particular department or function within the organization, or it may encompass the entire organization. The audit may also cover a specific time period or be ongoing, depending on the objectives and requirements of the organization.
Process:
The process of conducting an operational audit typically involves several steps. These include:
1. Planning: This involves defining the objectives of the audit, determining the scope and methodology, and identifying the resources and timeline required for the audit.
2. Data Collection: This step involves gathering relevant data and information about the organization’s operations. This may include reviewing documents, conducting interviews with key personnel, and analyzing data and performance metrics.
3. Analysis: Once the data has been collected, it is analyzed to identify any areas of concern or opportunities for improvement. This may involve comparing the organization’s performance against industry benchmarks or best practices.
4. Reporting: The findings of the audit are documented in a report, which includes an analysis of the current state of operations, identified areas for improvement, and recommendations for action. This report is typically presented to management and other stakeholders.
Benefits:
An operational audit can provide several benefits to an organization. These include:
1. Improved Efficiency: By identifying and addressing inefficiencies in processes and systems, an operational audit can help the organization streamline its operations and reduce costs.
2. Enhanced Effectiveness: The audit can also help the organization improve the effectiveness of its operations by identifying areas where it can better align its processes and systems with its goals and objectives.
3. Risk Mitigation: An operational audit can help identify and mitigate risks that may be present in the organization’s operations. This can help prevent potential losses or negative impacts on the organization.
4. Compliance: The audit can also ensure that the organization is complying with relevant laws, regulations, and internal policies and procedures.
Conclusion:
An operational audit is a valuable tool for organizations to assess and improve their operational efficiency and effectiveness. By identifying areas for improvement and providing recommendations for action, the audit can help organizations achieve their goals and objectives more effectively.
The Importance of Compliance Audit
A compliance audit is a crucial component of internal audit, as it focuses on ensuring that an organization is adhering to relevant laws, regulations, and internal policies. This type of audit evaluates the effectiveness of an organization’s internal controls and processes to identify any non-compliance issues.
Why is Compliance Audit Important?
Compliance audits play a vital role in maintaining the integrity and reputation of an organization. Here are some key reasons why compliance audits are important:
- Legal Compliance: Compliance audits help organizations ensure that they are meeting all legal requirements imposed by government authorities. By identifying and addressing any non-compliance issues, organizations can avoid legal penalties and potential damage to their reputation.
- Risk Management: Compliance audits help organizations identify and mitigate potential risks associated with non-compliance. By assessing the effectiveness of internal controls and processes, organizations can proactively address any vulnerabilities and minimize the likelihood of non-compliance incidents.
- Internal Policy Adherence: Compliance audits also evaluate an organization’s adherence to its own internal policies and procedures. This ensures that employees are following established guidelines and protocols, promoting consistency and accountability within the organization.
- Financial Integrity: Compliance audits help organizations maintain financial integrity by ensuring accurate financial reporting and preventing fraudulent activities. By evaluating financial controls and processes, organizations can identify any weaknesses or irregularities and take appropriate corrective actions.
- Stakeholder Confidence: Compliance audits provide assurance to stakeholders, including shareholders, customers, and business partners, that an organization is operating in a compliant and ethical manner. This enhances trust and confidence in the organization, which can lead to improved relationships and business opportunities.
The 5 Cs of Internal Audit
Internal audit is a crucial function within organizations, providing independent and objective assurance on the effectiveness of risk management, control, and governance processes. To ensure the success of internal audit, it is important to understand the five Cs that are essential for its effectiveness.
1. Competence
The first C of internal audit is competence. Internal auditors should possess the necessary knowledge, skills, and experience to perform their duties effectively. They should be well-versed in auditing techniques, risk assessment, and relevant industry regulations. Ongoing professional development is also important to keep up with the evolving business environment.
2. Confidentiality
Confidentiality is another crucial aspect of internal audit. Internal auditors have access to sensitive and confidential information about the organization. It is essential that they maintain the highest level of confidentiality and handle the information with utmost care. Breaching confidentiality can have serious consequences for the organization and its stakeholders.
3. Independence
Independence is a fundamental principle of internal audit. Internal auditors should be free from any conflicts of interest that may compromise their objectivity and impartiality. They should have the authority and freedom to carry out their work without interference from management or other parties. This ensures that their findings and recommendations are unbiased and reliable.
4. Objectivity
Objectivity is closely related to independence. Internal auditors should approach their work with an unbiased and impartial mindset. They should gather and evaluate evidence objectively, without being influenced by personal biases or external pressures. This ensures that their findings and recommendations are based on facts and provide an accurate assessment of the organization’s risks and controls.
5. Communication

Effective communication is essential for the success of internal audit. Internal auditors should be able to clearly communicate their findings, recommendations, and observations to management and other stakeholders. They should use clear and concise language, avoiding technical jargon, to ensure that the information is easily understood. Good communication skills help in building trust and credibility with stakeholders and facilitate the implementation of audit recommendations.
| Internal Audit | Competence | Confidentiality | Independence | Objectivity | Communication |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Having the necessary knowledge, skills, and experience | Maintaining the highest level of confidentiality | Being free from conflicts of interest | Approaching work with an unbiased and impartial mindset | Effectively communicating findings and recommendations |
| Importance | Ensures effective performance of audit duties | Protects sensitive and confidential information | Ensures objectivity and impartiality | Provides accurate assessment of risks and controls | Builds trust and facilitates implementation of recommendations |

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
