Factor Market: Definition, Types, and Examples
There are several types of factor markets, each corresponding to a specific factor of production:
- Labor Market: This market involves the buying and selling of labor services. It includes both skilled and unskilled labor, and individuals offer their skills and time in exchange for wages or salaries. Examples of labor markets include job fairs, online job boards, and recruitment agencies.
- Capital Market: The capital market deals with the buying and selling of capital goods, such as machinery, equipment, and vehicles. Businesses and individuals purchase or lease these assets to enhance their production processes. Examples of capital markets include auctions for used machinery, leasing companies, and financial institutions that provide loans for purchasing capital goods.
- Land Market: The land market involves the buying and selling of land and natural resources. This includes agricultural land, commercial real estate, and mineral rights. Buyers may acquire land for various purposes, such as farming, construction, or resource extraction. Real estate agencies, land auctions, and government agencies involved in land transactions are examples of land markets.
Examples of factor markets in action include a company hiring employees through a job posting on an online platform, a farmer purchasing agricultural machinery from a dealer, and a real estate developer acquiring land for a new construction project.
What is a Factor Market?
A factor market is a marketplace where factors of production, such as labor, capital, and land, are bought and sold. It is a crucial component of the overall economy, as it facilitates the exchange of resources necessary for the production of goods and services.
Types of Factor Markets
There are several types of factor markets, each specializing in the exchange of a specific factor of production:
- Labor Market: The labor market involves the buying and selling of labor services. It includes both skilled and unskilled workers, and the wages are determined by the supply and demand of labor.
- Capital Market: The capital market deals with the buying and selling of capital goods, such as machinery, equipment, and buildings. It allows businesses to acquire the necessary resources to expand their production capacity.
- Land Market: The land market involves the buying and selling of land and other natural resources. It is essential for industries such as agriculture, real estate, and mining.
Examples of Factor Markets
Here are some examples of factor markets:
- In the labor market, individuals sell their skills and expertise to employers in exchange for wages or salaries. This includes professions such as doctors, teachers, and construction workers.
- In the capital market, businesses can obtain funding by selling shares of their company or borrowing money from investors or financial institutions. This allows them to invest in new equipment, technology, or infrastructure.
- In the land market, individuals or businesses can buy or lease land for various purposes, such as agriculture, commercial development, or conservation.
Overall, factor markets play a crucial role in the functioning of the economy by facilitating the exchange of resources necessary for production. They allow individuals and businesses to acquire the factors of production they need and provide opportunities for economic growth and development.
Types of Factor Markets

1. Labor Market: The labor market is where individuals sell their labor services to businesses or organizations in exchange for wages or salaries. It includes both skilled and unskilled workers. Examples of labor markets include job fairs, online job portals, and recruitment agencies.
2. Capital Market: The capital market is where financial capital, such as money, stocks, bonds, and other financial instruments, is bought and sold. It facilitates the transfer of funds between investors and borrowers. Examples of capital markets include stock exchanges, bond markets, and venture capital firms.
3. Land Market: The land market is where land and natural resources are bought and sold. It includes agricultural land, commercial real estate, and natural resource extraction rights. Examples of land markets include real estate agencies, land auctions, and leasing agreements.
Each type of factor market plays a crucial role in the economy. The labor market ensures the availability of a workforce, the capital market provides funding for investment and growth, and the land market allows for the utilization of natural resources and space.
It is important to note that these factor markets are interconnected and influence each other. For example, the availability of skilled labor in the labor market can attract investors in the capital market, leading to economic growth. Similarly, the availability of land resources in the land market can attract businesses and industries, creating job opportunities in the labor market.
Labor Market
The labor market is a crucial component of the factor market, where the supply and demand for labor are determined. It refers to the interaction between employers and employees, where employers seek to hire workers and workers seek employment opportunities.
Definition
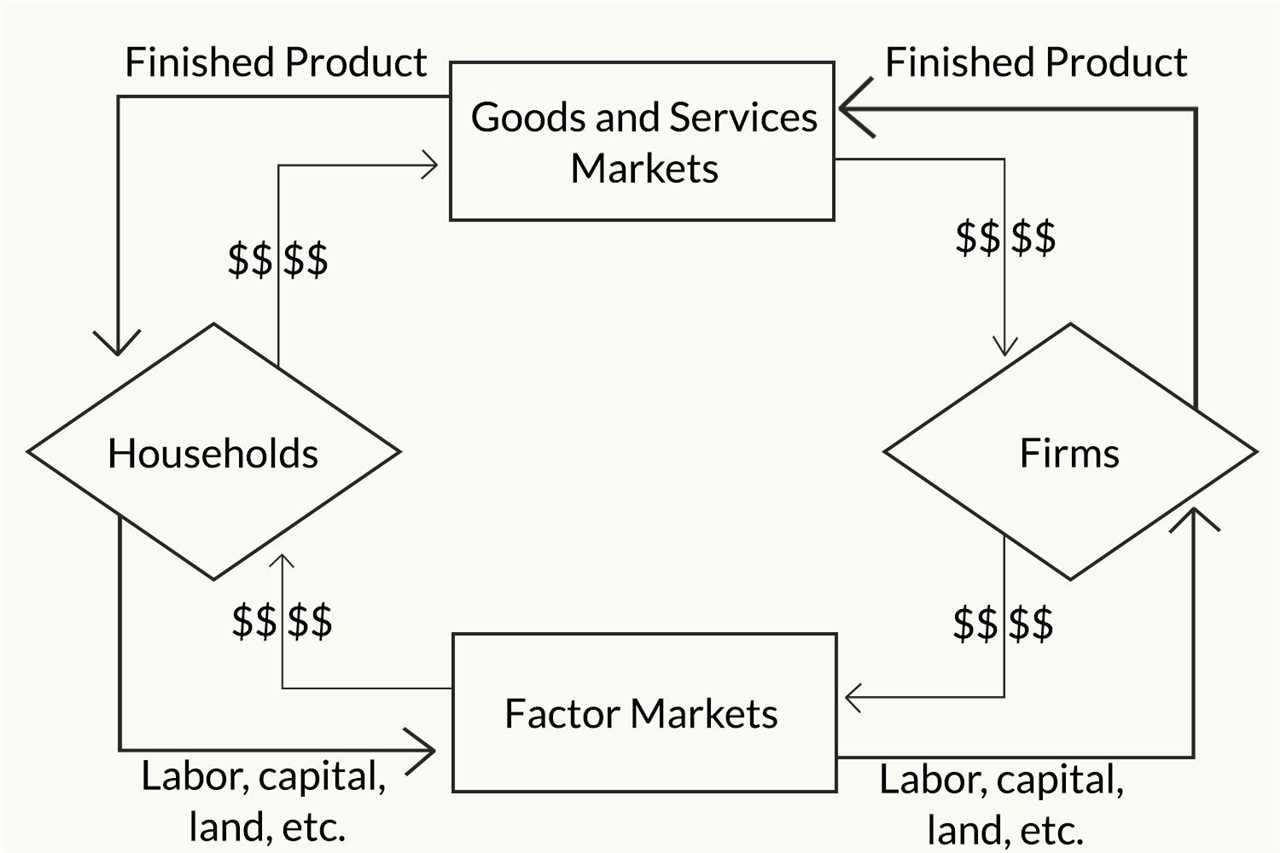
Types
There are various types of labor markets based on different characteristics:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Local Labor Market | Refers to the labor market within a specific geographic area, such as a city or region. |
| National Labor Market | Encompasses the entire labor market of a country, including all regions and industries. |
| International Labor Market | Includes the movement of labor across national borders, where individuals seek employment opportunities in foreign countries. |
| Skilled Labor Market | Focuses on jobs that require specialized skills or knowledge, such as doctors, engineers, or IT professionals. |
| Unskilled Labor Market | Refers to jobs that do not require specific skills or qualifications, such as manual labor or basic service jobs. |
Factors Affecting the Labor Market
The labor market is influenced by various factors, including:
- Economic conditions: The overall state of the economy, such as economic growth, inflation, and unemployment rates, can impact the demand for labor.
- Technological advancements: The adoption of new technologies can lead to changes in the demand for certain types of labor, as some jobs become obsolete while others require new skills.
- Education and training: The level of education and training of the workforce can affect their employability and the types of jobs they can access.
- Government policies: Labor market regulations, minimum wage laws, and labor unions can influence the dynamics of the labor market.
Examples
Examples of the labor market in action include job fairs, recruitment agencies, online job portals, and networking events. Employers advertise job vacancies, screen applicants, and conduct interviews to select suitable candidates. Job seekers submit resumes, attend interviews, and negotiate employment terms.
Capital Market
The capital market is a type of factor market that deals with the buying and selling of financial assets, such as stocks, bonds, and derivatives. It is a market where businesses and governments can raise long-term funds to finance their operations and investments.
In the capital market, individuals and institutions trade financial instruments, which represent ownership or debt obligations. These instruments are bought and sold through various platforms, such as stock exchanges, over-the-counter markets, and electronic trading systems.
There are two main types of participants in the capital market: borrowers and lenders. Borrowers, such as corporations and governments, issue financial instruments to raise capital for their projects or to refinance existing debt. Lenders, on the other hand, provide the capital by purchasing these instruments.
The capital market plays a crucial role in the economy by facilitating the flow of funds between borrowers and lenders. It allows businesses to access the necessary capital to expand their operations, invest in new technologies, and create jobs. It also provides individuals and institutions with investment opportunities to grow their wealth.
Within the capital market, there are different types of financial instruments that can be traded:
- Stocks: These represent ownership in a company and give shareholders the right to vote on corporate matters and receive dividends.
- Bonds: These are debt securities issued by governments, municipalities, and corporations to raise funds. Bondholders receive periodic interest payments and the principal amount upon maturity.
- Derivatives: These are financial contracts whose value is derived from an underlying asset, such as stocks, bonds, commodities, or currencies. Examples include options, futures, and swaps.
- Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs): These are investment funds that trade on stock exchanges and represent a diversified portfolio of assets, such as stocks, bonds, or commodities.
The capital market is regulated by financial authorities to ensure fair and transparent trading practices. These regulations aim to protect investors, maintain market integrity, and prevent fraud and manipulation.
Overall, the capital market is a vital component of the global financial system, enabling the efficient allocation of capital and fostering economic growth.
Land Market
The land market operates based on the principles of supply and demand. The price of land is determined by factors such as location, fertility, accessibility, and potential for development. Land in prime locations or with high agricultural productivity tends to have a higher price compared to land in remote or less fertile areas.
In the land market, buyers and sellers negotiate the terms of the transaction, including the price, duration of the lease, or any restrictions on land use. Real estate agents or brokers often facilitate these transactions by connecting buyers and sellers and providing information about available land and its characteristics.
The land market plays a crucial role in the economy as it enables the efficient allocation of land resources. It allows individuals and businesses to acquire land for productive purposes, such as farming or building infrastructure, which contributes to economic growth and development.
Additionally, the land market can have social and environmental implications. The availability and affordability of land can impact housing prices, urban development patterns, and access to natural resources. Governments often intervene in the land market through zoning regulations, land use planning, and taxation to ensure sustainable and equitable land use.
Examples of transactions in the land market include the sale of farmland to a farmer, the leasing of land for a shopping mall development, or the purchase of land for a public park. These transactions involve the transfer of land ownership or usage rights in exchange for monetary compensation.
| Advantages of the Land Market | Disadvantages of the Land Market |
|---|---|
| – Facilitates efficient allocation of land resources | – Can lead to land speculation and price volatility |
| – Enables individuals and businesses to acquire land for productive purposes | – May contribute to inequality in land ownership |
| – Allows for economic growth and development | – Can result in environmental degradation if not regulated |
| – Provides opportunities for investment and financial returns | – May lead to displacement of local communities |
Examples of Factor Markets
In economics, a factor market refers to the marketplace where factors of production, such as labor, capital, and land, are bought and sold. These factors are essential for the production of goods and services. Here are some examples of factor markets:
1. Labor Market: The labor market is a factor market where individuals sell their labor services to businesses or organizations in exchange for wages or salaries. This includes both skilled and unskilled workers, such as doctors, teachers, construction workers, and office employees.
2. Capital Market: The capital market is a factor market where individuals and businesses buy and sell capital goods, such as machinery, equipment, and buildings. This market allows businesses to acquire the necessary tools and resources to produce goods and services efficiently.
3. Land Market: The land market is a factor market where individuals and businesses buy and sell land or natural resources. This includes agricultural land, commercial properties, and mineral rights. The land market plays a crucial role in determining the allocation and use of land resources.
4. Financial Market: The financial market is a factor market where individuals and businesses buy and sell financial assets, such as stocks, bonds, and derivatives. While not directly related to the factors of production, the financial market indirectly affects factor markets by providing the necessary funds for investment in labor, capital, and land.
5. Technology Market: The technology market is a factor market where individuals and businesses buy and sell technological innovations, patents, and licenses. This market allows businesses to access new technologies and improve their production processes, leading to increased productivity and competitiveness.
6. Entrepreneurship Market: The entrepreneurship market is a factor market where individuals with innovative ideas and skills sell their services as entrepreneurs. These individuals take risks and organize the other factors of production to create new businesses and drive economic growth.
These are just a few examples of factor markets. Each factor market plays a crucial role in the overall functioning of the economy by facilitating the efficient allocation of resources and promoting economic growth.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
