Distributed Ledger Technology: A Comprehensive Guide to DLT and Its Functioning
One of the key components of DLT is blockchain technology. A blockchain is a type of distributed ledger that organizes data into blocks, which are then linked together using cryptographic hashes. This ensures that the data is tamper-proof and cannot be altered without the consensus of the network.
DLT offers numerous benefits and applications across various industries. One of the main advantages is increased transparency and trust. Since the ledger is shared among multiple participants, there is no single point of failure or control. This makes DLT particularly useful in industries such as finance, supply chain management, and healthcare.
In finance, DLT can streamline processes such as cross-border payments, securities trading, and identity verification. It can reduce costs, increase efficiency, and eliminate the need for intermediaries. In supply chain management, DLT can provide end-to-end visibility and traceability, ensuring the authenticity and quality of products. In healthcare, DLT can securely store and share patient records, improving data interoperability and privacy.
Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) is a decentralized system that allows multiple participants to maintain a shared and synchronized database without the need for a central authority. It is a transparent and secure way of recording and verifying transactions, making it suitable for various industries such as finance, supply chain management, healthcare, and more.
DLT operates on the principle of consensus, where all participants in the network agree on the validity of transactions before they are added to the ledger. This consensus mechanism ensures that the data stored on the ledger is accurate and tamper-proof.
Types of Distributed Ledger Technology
There are different types of DLT, with the most well-known being blockchain. Blockchain is a distributed ledger that uses cryptographic techniques to secure transactions and maintain data integrity. It is characterized by its decentralized nature and immutability, making it highly resistant to fraud and hacking.
Another type of DLT is directed acyclic graph (DAG), which is a more scalable and efficient alternative to blockchain. DAG structures transactions in a graph-like manner, allowing for parallel processing and faster transaction confirmation. This makes DAG suitable for applications that require high throughput and low latency.
Key Features of Distributed Ledger Technology
DLT offers several key features that make it attractive for various use cases:
- Decentralization: DLT eliminates the need for a central authority, reducing the risk of single points of failure and increasing resilience.
- Transparency: All participants in the network have access to the same information, ensuring transparency and accountability.
- Security: DLT uses cryptographic techniques to secure transactions and prevent unauthorized access or tampering.
- Efficiency: DLT eliminates the need for intermediaries and streamlines processes, resulting in faster and more cost-effective transactions.
- Traceability: DLT provides a complete audit trail of transactions, making it easier to track and verify the origin and authenticity of assets.
Benefits and Applications of DLT
Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) offers numerous benefits and has a wide range of applications across various industries. Here are some of the key benefits and applications of DLT:
1. Transparency and Immutability
DLT provides a transparent and immutable record of transactions. Each transaction is recorded on multiple nodes in the network, making it difficult to alter or tamper with the data. This transparency and immutability make DLT ideal for applications where trust and security are crucial.
2. Enhanced Security
DLT uses cryptographic algorithms to secure data and transactions. The decentralized nature of DLT ensures that there is no single point of failure, making it more resistant to hacking and cyber attacks. This enhanced security makes DLT suitable for applications that deal with sensitive information, such as financial transactions and identity management.
3. Efficiency and Cost Savings
DLT eliminates the need for intermediaries and manual reconciliation processes, reducing the time and cost associated with traditional systems. By automating processes and streamlining workflows, DLT can significantly improve efficiency and cost savings in various industries, including supply chain management, healthcare, and finance.
4. Improved Traceability and Accountability
DLT enables the tracking and tracing of assets and transactions in a transparent and auditable manner. This improves traceability and accountability, making it easier to detect and prevent fraud, counterfeit goods, and other illicit activities. Industries such as logistics, pharmaceuticals, and intellectual property rights can benefit from the enhanced traceability provided by DLT.
5. Decentralization and Peer-to-Peer Networks
DLT operates on a decentralized network, where multiple nodes participate in the validation and verification of transactions. This eliminates the need for a central authority and enables peer-to-peer interactions. Decentralization and peer-to-peer networks offer increased resilience, censorship resistance, and democratization of access to services, making DLT suitable for applications such as decentralized finance (DeFi) and decentralized governance.
6. Smart Contracts and Automation
DLT platforms often support smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with predefined rules and conditions. Smart contracts enable automation of business processes, reducing the need for manual intervention and improving efficiency. Industries such as insurance, real estate, and supply chain management can benefit from the automation capabilities provided by DLT.
How DLT Works: Key Components and Processes
Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) is a decentralized system that enables multiple parties to maintain and update a shared database without the need for a central authority. This technology has gained significant attention due to its potential to revolutionize various industries, including finance, supply chain management, and healthcare.
Key Components of DLT
DLT consists of several key components that work together to ensure the integrity and security of the shared database:
- Nodes: Nodes are individual computers or devices that participate in the DLT network. Each node maintains a copy of the shared database and contributes to the consensus process.
- Blockchain: The blockchain is a distributed ledger that stores all the transactions or data in a series of blocks. Each block contains a unique identifier, a timestamp, and a reference to the previous block, creating a chain of blocks.
- Consensus Mechanism: Consensus mechanisms are protocols or algorithms that enable nodes to agree on the validity of transactions and reach a consensus on the state of the shared database. Examples of consensus mechanisms include Proof of Work (PoW), Proof of Stake (PoS), and Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT).
- Smart Contracts: Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into the code. They automatically execute transactions and enforce the agreed-upon rules without the need for intermediaries.
Processes in DLT
DLT involves several processes that ensure the smooth operation of the network:
- Data Validation: When a new transaction is submitted to the network, nodes validate the transaction’s integrity and authenticity before adding it to the shared database. This process helps prevent fraud and ensures the accuracy of the data.
- Consensus Formation: Nodes in the network participate in the consensus mechanism to agree on the validity and order of transactions. This process ensures that all nodes have a consistent view of the shared database.
- Block Creation: Once a consensus is reached, the validated transactions are grouped into blocks and added to the blockchain. Each block is linked to the previous block, forming an immutable and transparent chain of transactions.
- Transaction Execution: Smart contracts automatically execute transactions based on predefined conditions. They eliminate the need for intermediaries, reduce costs, and increase efficiency.
- Data Replication: Each node in the network maintains a copy of the shared database, ensuring redundancy and fault tolerance. If one node fails, the network can still function properly.
Challenges and Future of Distributed Ledger Technology
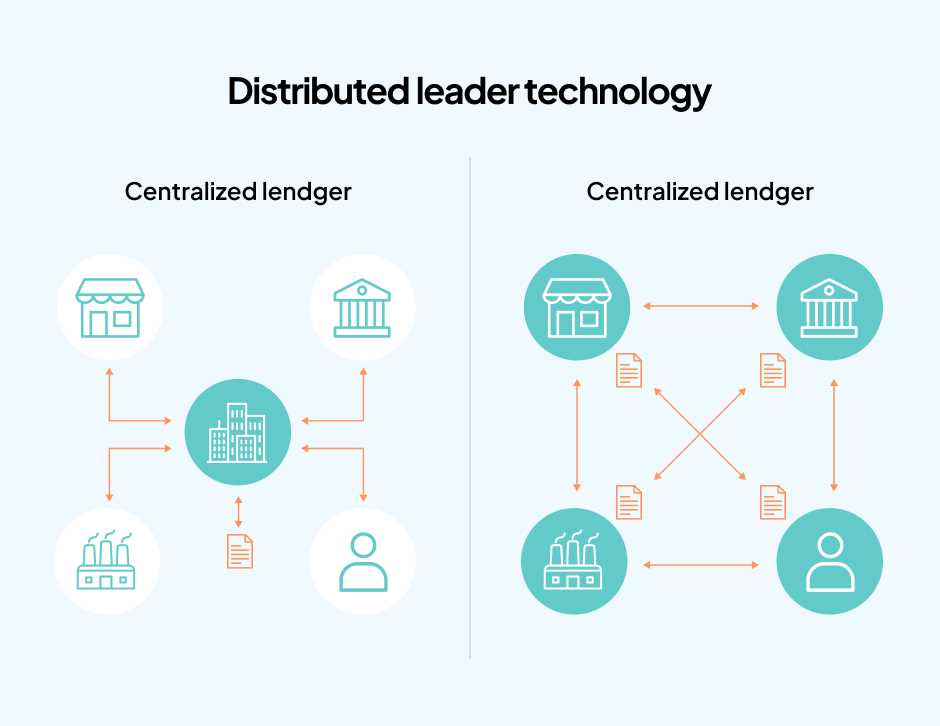
Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) has gained significant attention in recent years due to its potential to revolutionize various industries. However, like any emerging technology, DLT also faces several challenges that need to be addressed for its widespread adoption and success. Additionally, the future of DLT holds immense possibilities and opportunities for further development and innovation.
Challenges
Another challenge is interoperability. There are multiple DLT platforms available, each with its own protocols and standards. This lack of interoperability makes it difficult for different DLT networks to communicate and share data seamlessly. Efforts are underway to establish interoperability standards and frameworks to enable cross-chain communication and data exchange.
Security and privacy are also major concerns in the adoption of DLT. While DLT provides transparency and immutability, it also poses challenges in terms of protecting sensitive information and ensuring data privacy. As DLT evolves, there is a need for robust security measures and privacy-enhancing technologies to address these concerns and build trust among users.
Future of DLT
DLT can also revolutionize supply chain management by providing a transparent and secure platform for tracking and verifying the movement of goods. This can help eliminate fraud, counterfeiting, and improve efficiency in supply chain operations.
Furthermore, DLT can play a crucial role in healthcare by enabling secure and interoperable sharing of patient data. This can improve the accuracy and efficiency of medical diagnoses, facilitate medical research, and enhance patient care outcomes.
As DLT continues to evolve, it is expected to become more user-friendly and accessible to a wider audience. This will drive further adoption and integration of DLT into various industries and everyday life.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
