What is a Depository?
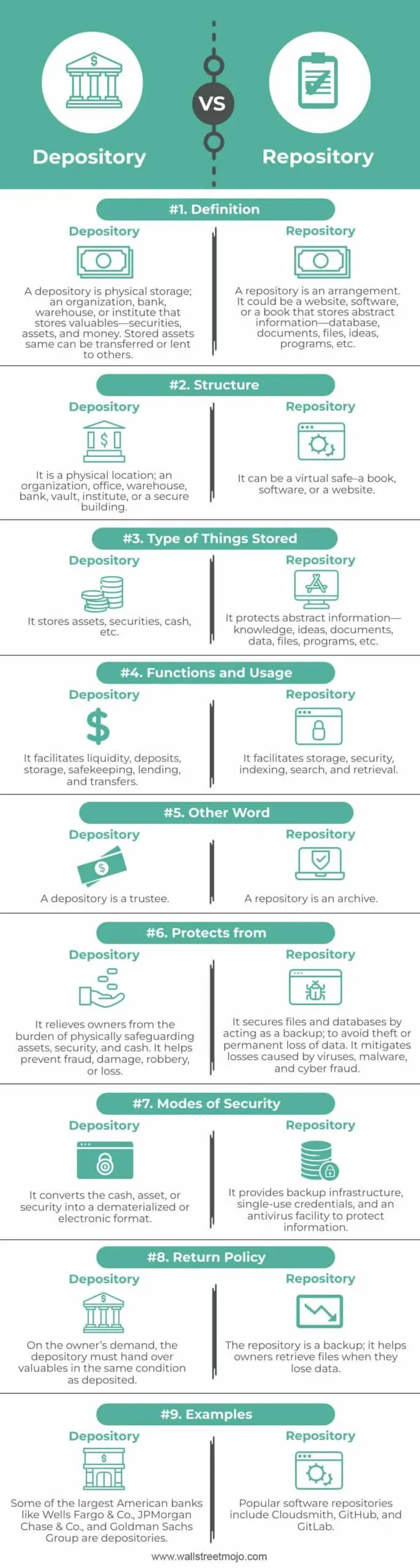
A depository is a financial institution that holds and safeguards various types of assets on behalf of its clients. These assets can include stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and other securities. Depositories play a crucial role in the functioning of financial markets by providing a secure and efficient system for the custody and transfer of these assets.
Depositories act as intermediaries between investors and issuers of securities. When investors purchase securities, they are typically held in electronic form in a depository account. This eliminates the need for physical certificates and simplifies the process of buying, selling, and transferring securities.
Depositories also provide additional services such as settlement, clearing, and record-keeping. They ensure that transactions are executed smoothly and that ownership of securities is accurately recorded. This helps to maintain the integrity and transparency of financial markets.
There are different types of depositories, including central depositories and custodian banks. Central depositories are typically operated by a central securities depository (CSD) and are responsible for the safekeeping and settlement of securities at a national level. Custodian banks, on the other hand, are commercial banks that offer depository services to institutional clients such as asset managers and pension funds.
Examples of depositories include the Depository Trust Company (DTC) in the United States, Euroclear in Europe, and the Central Depository Services Limited (CDSL) in India. These depositories play a vital role in the global financial system by facilitating the efficient and secure movement of securities.
Definition and Meaning
A depository is a financial institution or organization that holds and safeguards various types of assets on behalf of individuals, businesses, or other entities. It acts as a custodian and provides a secure storage facility for these assets, ensuring their safety and integrity.
The primary function of a depository is to facilitate the safekeeping, transfer, and settlement of securities such as stocks, bonds, and mutual funds. It plays a crucial role in the functioning of financial markets by providing a centralized location for the holding and trading of these assets.
Custodial depositories, on the other hand, are privately owned institutions that offer custody services to individuals, businesses, and institutional investors. They hold a wide range of assets, including securities, cash, precious metals, and other valuable items, on behalf of their clients.
Functions of a Depository

A depository performs several important functions in the financial system:
- Safekeeping: The primary function of a depository is to ensure the safekeeping of assets entrusted to its care. It maintains secure storage facilities and employs robust security measures to protect these assets from theft, damage, or loss.
- Settlement: Depositories facilitate the settlement of securities transactions by providing a platform for the transfer of ownership and the exchange of funds. They ensure that the buyer receives the securities and the seller receives the payment in a timely and efficient manner.
- Record-keeping: Depositories maintain detailed records of the assets held on behalf of their clients. These records include information about the ownership, quantity, and other relevant details of the securities or other assets.
- Corporate actions: Depositories play a crucial role in managing corporate actions such as dividend payments, stock splits, and mergers. They ensure that these actions are executed accurately and efficiently, and that the rights and interests of the shareholders are protected.
- Information dissemination: Depositories provide timely and accurate information about the assets held in their custody. This information is essential for investors, regulators, and other market participants to make informed decisions and monitor the overall health of the financial markets.
Conclusion
Depositories are essential institutions in the financial system that provide a secure and efficient infrastructure for the holding and trading of assets. They play a crucial role in ensuring the integrity and stability of financial markets, and their services are vital for investors, businesses, and other entities involved in the buying and selling of securities.
Types of Depositories
Depositories can be classified into different types based on the nature of the assets they hold and the services they provide. Here are some of the common types of depositories:
- Commercial Banks: Commercial banks are the most common type of depository institutions. They accept deposits from individuals and businesses and provide various banking services such as checking accounts, savings accounts, and loans.
- Savings Banks: Savings banks are financial institutions that primarily focus on accepting deposits and providing savings accounts. They often offer higher interest rates on savings accounts compared to commercial banks.
- Credit Unions: Credit unions are member-owned financial cooperatives that provide banking services to their members. They operate on a not-for-profit basis and offer competitive interest rates on deposits.
- Building Societies: Building societies are financial institutions that specialize in providing mortgage loans and accepting savings deposits. They are often owned by their members and operate similarly to credit unions.
- Investment Banks: Investment banks are financial institutions that provide a range of services, including underwriting securities, facilitating mergers and acquisitions, and advising on investment strategies. They also accept deposits from institutional clients.
- Brokerage Firms: Brokerage firms are financial intermediaries that facilitate the buying and selling of securities on behalf of their clients. While they primarily focus on investment services, some brokerage firms also offer deposit accounts.
Examples of Depositories
A depository is a financial institution that holds and safeguards securities on behalf of investors. There are several types of depositories, each serving a specific purpose in the financial market. Here are some examples of depositories:
1. Central Depository
2. Commercial Bank
Commercial banks can also act as depositories by offering custodial services for securities. They provide a secure environment for investors to hold their securities and offer services such as safekeeping, settlement, and asset servicing. Examples of commercial banks acting as depositories include JPMorgan Chase and Bank of America.
3. Clearing House

A clearing house is a financial institution that acts as an intermediary between buyers and sellers in the market. It ensures the smooth settlement of transactions by facilitating the transfer of securities and funds. Clearing houses often provide depository services to hold securities during the settlement process. Examples of clearing houses with depository services include the National Securities Clearing Corporation (NSCC) in the United States and the Depository Clearing Limited (DCL) in India.
4. Mutual Fund Company

Many mutual fund companies also act as depositories for the securities held in their funds. They hold and safeguard the securities on behalf of the fund investors, ensuring their safekeeping and proper administration. Examples of mutual fund companies acting as depositories include Vanguard and Fidelity.
5. International Central Securities Depository (ICSD)
An ICSD is a depository that specializes in holding and settling international securities. It provides a centralized platform for the safekeeping and transfer of cross-border securities, facilitating global investment and trading. Examples of ICSDs include Clearstream and Euroclear.
These are just a few examples of depositories in the financial market. Each type of depository plays a crucial role in ensuring the safe and efficient functioning of the securities market, providing investors with a secure environment to hold their investments.
Depositories in Banking
In the banking industry, depositories play a crucial role in the safekeeping and management of various financial assets. A depository is an institution that holds and safeguards assets such as stocks, bonds, and other securities on behalf of investors.
Depositories are responsible for maintaining accurate records of ownership and facilitating the transfer of securities between buyers and sellers. They provide a centralized system for the settlement of trades, ensuring that transactions are executed smoothly and efficiently.
Commercial depositories, on the other hand, are privately owned institutions that offer custodial services to individual investors and financial institutions. These depositories may specialize in specific types of assets or cater to a wide range of securities.
Examples of depositories in the banking industry include the Depository Trust Company (DTC) in the United States, Euroclear in Europe, and Clearstream in Luxembourg. These depositories handle trillions of dollars’ worth of securities transactions on a daily basis, providing a vital infrastructure for the global financial markets.
In summary, depositories in banking are essential institutions that facilitate the safekeeping and transfer of securities. They ensure the integrity and efficiency of the financial system, playing a crucial role in the functioning of the global economy.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
