What is a Contract for Differences (CFD)?
A Contract for Differences (CFD) is a financial derivative that allows traders to speculate on the price movements of various financial instruments, such as stocks, indices, currencies, and commodities, without owning the underlying asset. It is a popular trading instrument that offers the potential for profit from both rising and falling markets.
When trading CFDs, the trader enters into an agreement with a broker to exchange the difference in the price of the underlying asset between the opening and closing of the contract. If the trader predicts that the price will rise, they can open a long (buy) position, and if they predict that the price will fall, they can open a short (sell) position.
Definition and Explanation
A CFD is essentially a contract between the trader and the broker, where they agree to settle the difference in the price of the underlying asset in cash. This means that the trader does not own the asset, but rather speculates on its price movements.
CFDs are traded on margin, which means that traders only need to deposit a small percentage of the total trade value to open a position. This allows traders to have greater exposure to the market with a smaller initial investment. However, it also amplifies both potential profits and losses.
CFDs are typically traded over-the-counter (OTC), which means that they are not traded on a centralized exchange. Instead, traders can access CFD markets through online trading platforms provided by brokers.
How are CFDs Used?
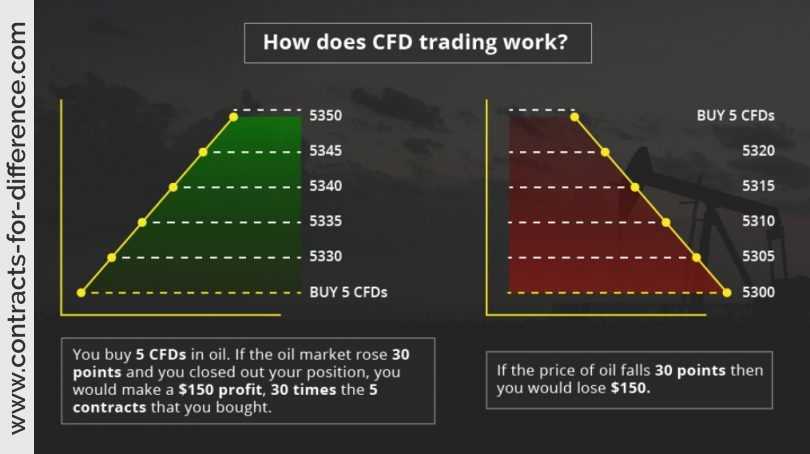
CFDs are used by traders for various purposes, including investing, trading, hedging, and risk management.
Investing and Trading: Traders can use CFDs to speculate on the price movements of various financial instruments, such as stocks, indices, currencies, and commodities. They can take advantage of both rising and falling markets by opening long or short positions.
Hedging and Risk Management: CFDs can be used as a hedging tool to offset potential losses in an existing investment portfolio. Traders can open a position in the opposite direction to their existing holdings, which can help mitigate the impact of adverse market movements.
Examples of CFDs
Some examples of popular CFDs include:
– Stock CFDs: Traders can speculate on the price movements of individual stocks without owning the underlying shares.
Overall, CFDs offer traders a flexible and accessible way to participate in various financial markets and potentially profit from price movements, without the need to own the underlying assets.
Definition and Explanation
A Contract for Differences (CFD) is a financial derivative that allows traders to speculate on the price movements of various underlying assets, such as stocks, indices, commodities, and currencies, without actually owning the underlying asset. It is an agreement between the trader and the broker to exchange the difference in the value of the asset from the time the contract is opened to the time it is closed.
CFDs are popular among traders because they offer several advantages. Firstly, they provide the opportunity to profit from both rising and falling markets. Traders can go long (buy) if they believe the price of the underlying asset will increase, or go short (sell) if they believe the price will decrease. This flexibility allows traders to take advantage of market trends and potentially earn profits in any market condition.
Secondly, CFDs offer leverage, which means traders can control a larger position in the market with a smaller amount of capital. This allows traders to amplify their potential profits, but it also increases the risk of losses. It is important for traders to carefully manage their risk and use appropriate risk management strategies when trading CFDs.
Another key feature of CFDs is the ability to trade on margin. This means that traders only need to deposit a fraction of the total value of the position they want to open. The broker provides the rest of the funds, allowing traders to access larger positions than they would be able to with their own capital. However, trading on margin also increases the potential losses, so it is important for traders to understand the risks involved and set appropriate stop-loss orders.
In summary, a Contract for Differences (CFD) is a financial instrument that allows traders to speculate on the price movements of various underlying assets without owning the assets themselves. It offers the opportunity to profit from both rising and falling markets, provides leverage to amplify potential profits, and allows trading on margin to access larger positions. However, it is important for traders to carefully manage their risk and use appropriate risk management strategies when trading CFDs.
How are CFDs Used?
Contract for Differences (CFDs) are widely used in both investing and trading strategies. They offer a flexible and efficient way to gain exposure to various financial markets without actually owning the underlying asset.
One common use of CFDs is for speculative trading. Traders can take advantage of price movements in a wide range of assets, such as stocks, commodities, currencies, and indices, without having to buy or sell the actual asset. This allows traders to potentially profit from both rising and falling markets.
CFDs are also commonly used for hedging purposes. Hedging involves taking positions that offset potential losses in other investments. For example, if an investor holds a portfolio of stocks and is concerned about a market downturn, they can use CFDs to short sell the same stocks and potentially profit from the decline in their value. This can help mitigate losses in the overall portfolio.
Benefits of Using CFDs
There are several benefits to using CFDs in investment and trading strategies:
- Leverage: CFDs allow traders to gain exposure to a larger position than their initial investment. This can amplify potential profits, but it also increases the risk of losses.
- Access to a wide range of markets: CFDs are available on a variety of assets, including stocks, commodities, currencies, and indices. This provides traders with numerous opportunities to diversify their portfolios and take advantage of different market conditions.
- Flexibility: CFDs can be traded on margin, which means traders only need to deposit a fraction of the total value of the position. This allows for greater flexibility and the ability to take larger positions with a smaller amount of capital.
- No ownership of the underlying asset: With CFDs, traders do not actually own the underlying asset. This means they do not have to worry about storage, maintenance, or other costs associated with physical ownership.
- Ability to profit from both rising and falling markets: CFDs allow traders to take both long and short positions, which means they can potentially profit from both upward and downward price movements.
Investing and Trading
With CFDs, investors and traders can take both long and short positions, allowing them to profit from both rising and falling markets. This flexibility makes CFDs an attractive option for those looking to diversify their investment portfolio and take advantage of different market conditions.
CFDs can be traded on a wide range of financial instruments, including stocks, indices, commodities, currencies, and cryptocurrencies. This allows traders to access a diverse range of markets and take advantage of various trading opportunities.
Hedging and Risk Management

One of the key uses of Contract for Differences (CFDs) is for hedging and risk management purposes. Hedging refers to the practice of offsetting potential losses in one investment by taking a position in another investment that is negatively correlated. By using CFDs, investors and traders can effectively hedge their positions and manage their risk exposure.
Similarly, CFDs can be used to hedge against currency risk. For instance, a multinational company that has exposure to foreign currencies can use CFDs to hedge against potential currency fluctuations. By taking positions in currency CFDs, the company can offset the impact of currency movements on its financial results.
Benefits of Hedging with CFDs
There are several benefits to using CFDs for hedging purposes:
- Flexibility: CFDs allow investors and traders to take both long and short positions, providing flexibility in hedging strategies.
- Leverage: CFDs typically offer leverage, which means that investors can control a larger position with a smaller amount of capital. This can enhance the effectiveness of hedging strategies.
- Cost Efficiency: CFDs generally have lower transaction costs compared to traditional financial instruments, making them a cost-effective tool for hedging.
- Accessibility: CFDs are widely available and can be traded on various platforms, making them accessible to a wide range of investors and traders.
Examples of CFDs
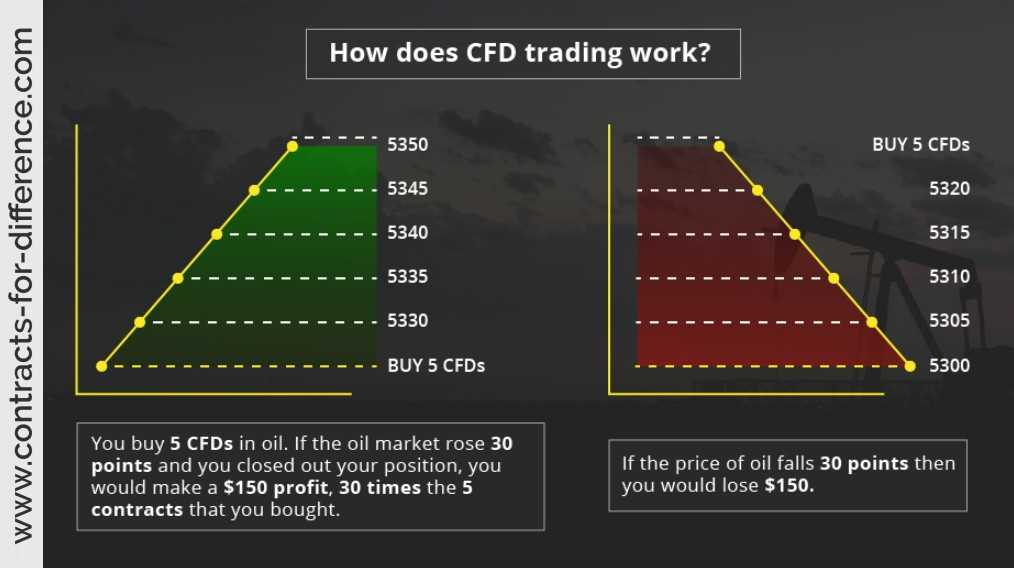
Contract for Differences (CFDs) can be used to trade a wide range of financial instruments. Here are some examples of CFDs:
1. Stocks: With CFDs, you can trade shares of various companies without actually owning the underlying stock. This allows you to speculate on the price movement of the stock without the need to physically buy or sell it.
3. Commodities: CFDs can be used to trade commodities like gold, oil, or natural gas. This allows you to speculate on the price movement of these commodities without the need to physically buy or store them.
4. Forex: CFDs can be used to trade currency pairs in the foreign exchange market. This allows you to speculate on the exchange rate between two currencies without the need to physically exchange them.
5. Cryptocurrencies: CFDs can also be used to trade cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum. This allows you to speculate on the price movement of cryptocurrencies without the need to physically own or store them.
Overall, CFDs provide a flexible and convenient way to trade a wide range of financial instruments, allowing you to take advantage of price movements in various markets without the need for ownership or physical delivery.
Stocks and Indices
One of the most popular uses of Contract for Differences (CFDs) is for trading stocks and indices. CFDs allow traders to speculate on the price movements of individual stocks or entire stock market indices without actually owning the underlying assets. This provides traders with the opportunity to profit from both rising and falling markets.
Trading Stocks
When trading stocks using CFDs, traders can take both long and short positions. If a trader believes that the price of a particular stock will increase, they can open a long position and profit from the price appreciation. On the other hand, if a trader believes that the price of a stock will decrease, they can open a short position and profit from the price decline.
CFD trading allows traders to access a wide range of stocks from various markets around the world. This provides traders with the opportunity to diversify their portfolios and take advantage of different market conditions. Additionally, CFDs offer leverage, which means that traders can trade larger positions with a smaller amount of capital, potentially magnifying their profits.
Trading Indices
In addition to trading individual stocks, CFDs can also be used to trade stock market indices. Stock market indices represent the overall performance of a group of stocks from a particular market or sector. Popular indices include the S&P 500, Dow Jones Industrial Average, and FTSE 100.
Trading indices using CFDs allows traders to speculate on the overall direction of the stock market without having to buy or sell individual stocks. Traders can take advantage of both bullish and bearish market conditions by opening long or short positions on indices.
CFD trading on indices provides traders with exposure to a diversified portfolio of stocks, reducing the risk associated with trading individual stocks. It also allows traders to trade the performance of entire markets or sectors, rather than relying on the performance of a single stock.
| Advantages of Trading Stocks and Indices with CFDs |
|---|
| 1. Access to a wide range of stocks and indices from global markets |
| 2. Ability to profit from both rising and falling markets |
| 3. Leverage, which allows traders to trade larger positions with less capital |
| 4. Diversification by trading a portfolio of stocks or entire market indices |
| 5. Reduced risk compared to trading individual stocks |
Overall, trading stocks and indices with CFDs provides traders with flexibility, diversification, and the opportunity to profit from various market conditions. However, it is important to note that CFD trading carries risks, and traders should carefully consider their risk tolerance and trading strategies before engaging in CFD trading.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
