What is Consumer Credit?
Consumer credit refers to the borrowing of funds by individuals to finance their purchases of goods and services. It is a type of loan that allows consumers to make purchases immediately and pay for them over time. Consumer credit is commonly used for buying homes, cars, appliances, electronics, and other high-value items.
Consumer credit can be obtained from various financial institutions such as banks, credit unions, and online lenders. The terms and conditions of consumer credit can vary depending on the lender and the borrower’s creditworthiness. The borrower is required to repay the borrowed amount along with interest and any applicable fees within a specified period.
Consumer credit can be categorized into two types: revolving credit and installment credit. Revolving credit allows consumers to borrow up to a certain credit limit and make payments based on the outstanding balance. Credit cards are a common example of revolving credit. Installment credit, on the other hand, involves borrowing a fixed amount and repaying it in regular installments over a predetermined period. Auto loans and mortgages are examples of installment credit.
Consumer credit can provide several benefits to individuals. It allows them to make purchases that they may not be able to afford upfront. It also provides flexibility in managing their finances by spreading the cost of purchases over time. Additionally, consumer credit can help build a positive credit history, which is important for obtaining future loans and favorable interest rates.
However, consumer credit also has its drawbacks. It can lead to overspending and accumulating debt if not managed responsibly. High interest rates and fees associated with consumer credit can increase the overall cost of purchases. Failure to make timely payments can result in penalties, damage to credit scores, and difficulty in obtaining future credit.
Definition and Explanation
Consumer credit refers to the borrowing of money by individuals or households to finance their purchases of goods and services. It allows consumers to make immediate purchases and pay for them over time, rather than having to save up the full amount before making a purchase. Consumer credit is commonly used for buying big-ticket items such as cars, homes, and appliances, as well as for financing education, healthcare, and other expenses.
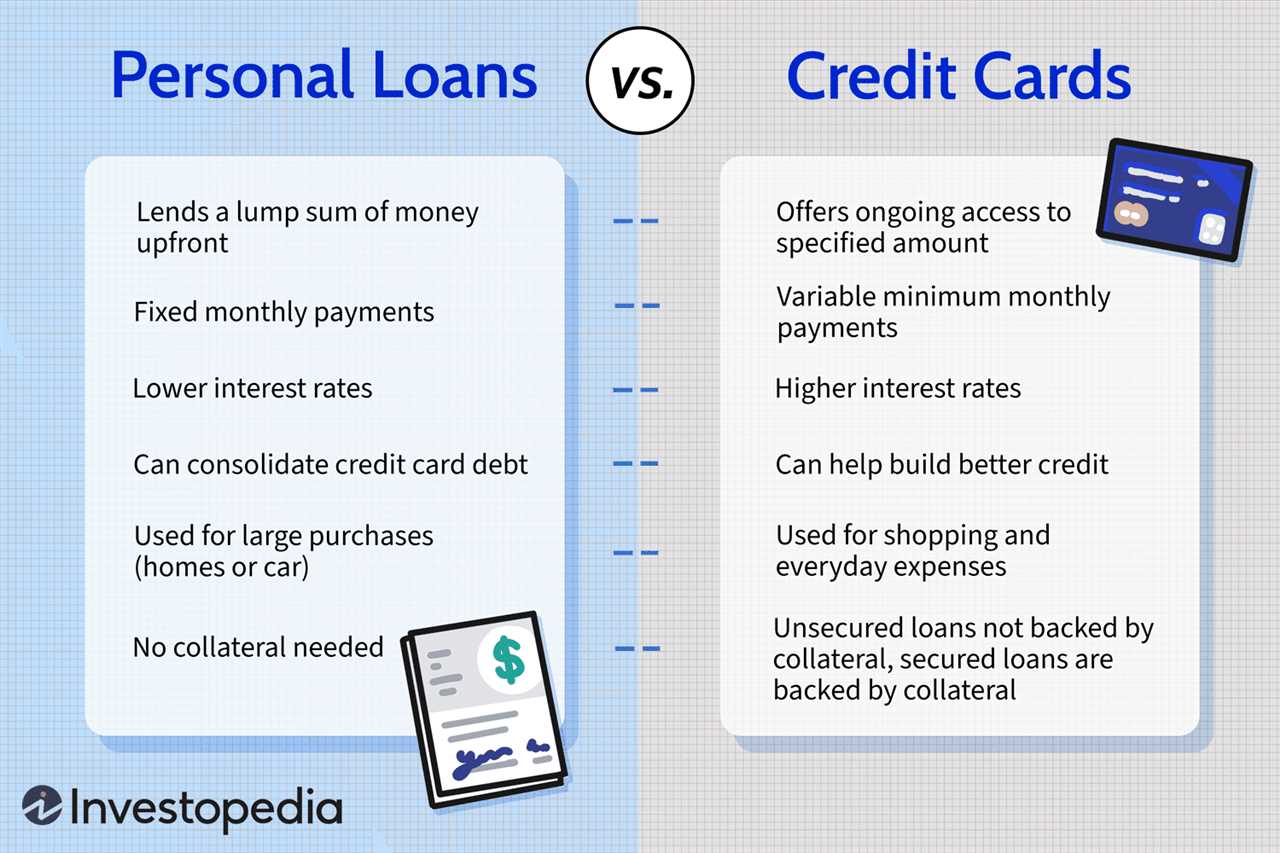
Consumer credit can take various forms, including credit cards, personal loans, mortgages, and lines of credit. These forms of credit provide consumers with access to funds that they can use to make purchases or cover expenses. In return, consumers are required to repay the borrowed amount, usually with interest, over a specified period of time.
Types of Consumer Credit

There are several types of consumer credit that individuals can utilize:
- Credit Cards: Credit cards allow consumers to make purchases up to a certain credit limit. They offer convenience and flexibility, but also come with high-interest rates if the balance is not paid in full each month.
- Personal Loans: Personal loans are unsecured loans that individuals can use for various purposes. They typically have fixed interest rates and fixed repayment terms.
- Mortgages: Mortgages are loans used to finance the purchase of a home. They are secured by the property itself and usually have long repayment terms.
- Lines of Credit: Lines of credit provide consumers with access to a predetermined amount of funds that they can borrow and repay as needed. They are often used for ongoing expenses or emergencies.
Consumer credit plays a significant role in the economy, as it allows individuals to make purchases and stimulate economic growth. However, it is important for consumers to use credit responsibly and understand the terms and conditions of the credit agreements they enter into. Failure to repay consumer credit can lead to financial difficulties, damaged credit scores, and legal consequences.
Pros of Consumer Credit

Consumer credit offers several advantages and benefits for individuals looking to make purchases or access funds for various purposes. Here are some of the pros of consumer credit:
- Convenience: Consumer credit provides a convenient way for individuals to make purchases without having to carry large amounts of cash. With credit cards and other forms of consumer credit, people can easily make transactions online or in-store.
- Flexibility: Consumer credit offers flexibility in terms of payment options. Individuals can choose to pay off their credit balance in full each month or make minimum payments and carry a balance. This flexibility allows consumers to manage their finances according to their needs and preferences.
- Rewards and Perks: Many credit cards and consumer credit programs offer rewards and perks to cardholders. These rewards can include cashback, airline miles, discounts, or points that can be redeemed for various benefits. By using consumer credit, individuals can take advantage of these rewards and maximize their purchasing power.
- Emergency Funds: Consumer credit can serve as a safety net during emergencies. In unexpected situations where immediate funds are needed, having access to consumer credit can provide individuals with the necessary funds to cover expenses until they can arrange alternative sources of funds.
- Building Credit History: Responsible use of consumer credit can help individuals build a positive credit history. By making timely payments and managing their credit wisely, individuals can establish a good credit score, which can be beneficial when applying for loans, mortgages, or other forms of credit in the future.
Overall, consumer credit offers convenience, flexibility, rewards, emergency funds, and the opportunity to build credit history. However, it is important to use consumer credit responsibly and avoid excessive debt that can lead to financial difficulties.
Advantages and Benefits of Consumer Credit
Consumer credit plays a crucial role in the financial services industry, providing individuals with the ability to make purchases and access funds that they may not have otherwise been able to afford. There are several advantages and benefits associated with consumer credit, which make it a popular choice for many consumers.
1. Convenience and Flexibility
One of the main advantages of consumer credit is the convenience and flexibility it offers. With consumer credit, individuals can make purchases and pay for them over time, rather than having to pay the full amount upfront. This allows consumers to spread out the cost of expensive items, making them more affordable and manageable.
2. Access to Funds
Consumer credit provides individuals with access to funds that they may need for various purposes. Whether it’s for emergencies, home improvements, education, or other expenses, consumer credit allows individuals to borrow money and meet their financial needs. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals who do not have significant savings or who need funds quickly.
3. Building Credit History
Consumer credit can also help individuals build their credit history and improve their credit score. By responsibly using and repaying consumer credit, individuals can demonstrate their ability to manage debt and make timely payments. This can have a positive impact on their creditworthiness and make it easier for them to access credit in the future, such as for purchasing a home or a car.
4. Rewards and Incentives
Many consumer credit products offer rewards and incentives to customers, such as cashback, travel points, or discounts. These rewards can provide additional value to consumers, allowing them to earn benefits while using consumer credit for their everyday expenses. By taking advantage of these rewards, consumers can save money or enjoy other perks.
5. Consumer Protection
Consumer credit often comes with built-in protections for consumers. For example, many credit cards offer fraud protection, which can help individuals recover their money if their card is stolen or used fraudulently. Additionally, consumer credit laws and regulations provide safeguards against unfair lending practices and ensure that consumers are treated fairly.
Cons of Consumer Credit
While consumer credit can provide many advantages and benefits, it is important to also consider the potential drawbacks and risks associated with it.
1. High interest rates: One of the main disadvantages of consumer credit is the high interest rates that are often charged. This can result in borrowers paying significantly more for their purchases over time, especially if they only make minimum payments.
2. Debt accumulation: Consumer credit can easily lead to debt accumulation if not managed properly. It is easy for individuals to overspend and rely too heavily on credit, which can quickly spiral into a cycle of debt that is difficult to escape.
3. Impact on credit score: Late or missed payments on consumer credit accounts can have a negative impact on an individual’s credit score. This can make it more difficult to obtain future credit or loans, and may result in higher interest rates or less favorable terms.
4. Temptation to overspend: Having access to consumer credit can tempt individuals to overspend and make impulsive purchases. This can lead to financial instability and difficulty in meeting other financial obligations.
5. Hidden fees and charges: Some consumer credit agreements may include hidden fees and charges that borrowers may not be aware of. These additional costs can add up over time and increase the overall cost of borrowing.
6. Risk of identity theft: When using consumer credit, individuals may be at risk of identity theft or fraud. Personal and financial information can be compromised, leading to unauthorized transactions and potential financial loss.
7. Limited financial flexibility: Consumer credit can limit an individual’s financial flexibility, as a portion of their income may need to be allocated towards debt repayment. This can restrict their ability to save, invest, or respond to unexpected financial emergencies.
8. Potential for predatory lending: In some cases, consumers may be targeted by predatory lenders who offer high-interest loans with unfavorable terms. This can result in individuals becoming trapped in a cycle of debt and facing financial hardship.
Overall, while consumer credit can provide immediate purchasing power and convenience, it is important for individuals to carefully consider the potential risks and drawbacks before taking on debt. Responsible borrowing and diligent financial management are key to avoiding the negative consequences of consumer credit.
Cons of Consumer Credit: Disadvantages and Risks
- Accumulating Debt: One of the biggest risks of consumer credit is the potential to accumulate debt. If individuals are not careful with their spending habits and fail to make timely payments, they can easily find themselves in a cycle of debt that becomes difficult to escape.
- High Interest Rates: Consumer credit often comes with high interest rates, especially for individuals with lower credit scores. This means that the cost of borrowing money can be significantly higher, resulting in larger overall payments and potentially increasing the financial burden on the borrower.
- Hidden Fees and Charges: Some consumer credit agreements may include hidden fees and charges that borrowers may not be aware of. These additional costs can add up over time and make the overall cost of borrowing even higher than initially anticipated.
- Impact on Credit Score: Taking on consumer credit can have an impact on an individual’s credit score. If borrowers fail to make payments on time or default on their loans, it can negatively affect their credit history and make it more difficult to obtain credit in the future.
- Overspending: Consumer credit can sometimes lead individuals to overspend and live beyond their means. The availability of credit can create a false sense of affordability, causing individuals to make purchases they cannot actually afford and potentially leading to financial instability.
- Debt Collection and Legal Consequences: If borrowers consistently fail to make payments on their consumer credit obligations, they may face debt collection efforts and even legal consequences. This can further damage their financial situation and lead to additional stress and hardship.
While consumer credit can be a useful tool when used responsibly, individuals must be aware of the potential risks and disadvantages to make informed decisions about their financial well-being.
Consumer Credit in Financial Services
Consumer credit plays a vital role in the financial services industry. It refers to the provision of credit to individuals for personal, family, or household purposes. This type of credit allows consumers to make purchases or access funds that they may not have immediately available.
Consumer credit in financial services offers several benefits to both consumers and businesses. Firstly, it provides individuals with the ability to make large purchases, such as buying a house or a car, without having to save up the full amount. This allows consumers to enjoy the benefits of these purchases immediately, rather than having to wait for years to accumulate enough savings.
Secondly, consumer credit provides individuals with a safety net in times of financial emergencies. It allows them to access funds quickly and easily, which can be crucial in situations such as unexpected medical expenses or home repairs.
Furthermore, consumer credit can help individuals build their credit history and improve their credit score. By responsibly managing their credit, consumers can demonstrate their ability to repay loans and establish a positive credit history. This can be beneficial when applying for future loans or credit cards, as lenders often consider an individual’s credit history and score when making lending decisions.
However, consumer credit also comes with certain risks and disadvantages. One of the main drawbacks is the potential for individuals to accumulate excessive debt. If consumers are not careful with their borrowing habits, they may find themselves in a cycle of debt, struggling to make repayments and facing high interest charges.
Additionally, consumer credit can sometimes lead to impulsive buying behavior. The availability of credit can tempt individuals to make purchases they cannot afford, leading to financial strain in the long run.
Overall, consumer credit is an essential component of the financial services industry, providing individuals with access to funds and the ability to make important purchases. However, it is crucial for consumers to use credit responsibly and understand the potential risks involved. By doing so, they can enjoy the benefits of consumer credit while avoiding the pitfalls of excessive debt.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
