Call: Definitions in Finance
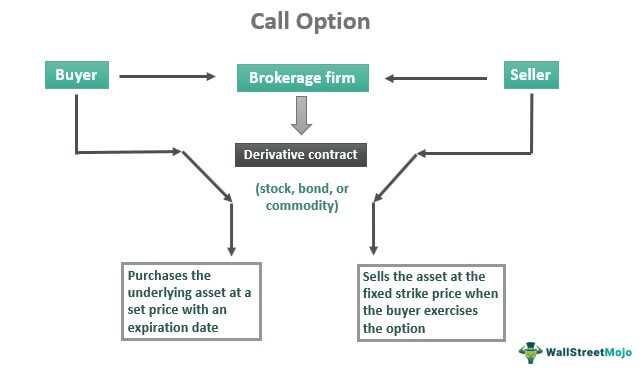
In finance, a call is a financial instrument that gives the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy an underlying asset at a specified price within a specific period of time. This underlying asset can be a stock, bond, commodity, or any other financial instrument.
Call options are commonly used in financial markets to speculate on the price movement of an underlying asset. If an investor believes that the price of a stock will rise, they can purchase a call option to profit from the potential price increase.
Exploring Call Auctions
Call auctions are commonly used in stock exchanges to determine the opening and closing prices of securities. They provide a transparent and efficient way of matching buyers and sellers, especially when there is a large number of orders to be processed.
During a call auction, the orders are matched based on a set of predetermined rules, such as price priority or time priority. Once the clearing price is determined, all the trades are executed at that price, ensuring that all participants receive the same price for their transactions.
Developing a Call Strategy
When trading call options, it is important to develop a strategy that aligns with your investment goals and risk tolerance. Some common call strategies include buying call options to speculate on price increases, selling covered call options to generate income from existing holdings, and using call spreads to limit potential losses.
Before implementing a call strategy, it is crucial to thoroughly understand the risks and potential rewards associated with call options. It is also recommended to consult with a financial advisor or professional who can provide guidance based on your individual circumstances.
A call option is a financial contract that gives the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy a specific asset, such as stocks, at a predetermined price within a specified period of time. The seller of the call option is obligated to sell the asset if the buyer chooses to exercise the option.
Call options are commonly used in the stock market as a way for investors to speculate on the price movement of a particular stock. If an investor believes that the price of a stock will increase, they can purchase a call option to potentially profit from the price appreciation.
How Call Options Work
When an investor purchases a call option, they pay a premium to the seller. This premium is the price of the option and is determined by various factors, including the current price of the underlying asset, the strike price (the predetermined price at which the asset can be bought), the time remaining until the option expires, and market volatility.
If the price of the underlying asset increases above the strike price before the option expires, the buyer can exercise the option and buy the asset at the strike price. They can then sell the asset at the current market price, making a profit equal to the difference between the strike price and the market price, minus the premium paid for the option.
Risks and Benefits of Call Options
Call options offer several benefits to investors. They provide the opportunity to profit from the price appreciation of an asset without actually owning the asset. This can be useful for investors who want to speculate on the price movement of a stock without committing a large amount of capital.
However, call options also come with risks. If the price of the underlying asset does not increase as expected, the buyer can lose the entire premium paid for the option. Additionally, call options have a limited lifespan, so if the price of the underlying asset does not increase before the option expires, the buyer loses the opportunity to profit from the price appreciation.
It is important for investors to carefully consider their investment goals and risk tolerance before purchasing call options. They should also thoroughly research the underlying asset and market conditions to make informed decisions.
Exploring Call Auctions
A call auction is a type of trading mechanism used in financial markets where buyers and sellers come together at a specific time to place their orders. Unlike continuous trading, where orders are executed throughout the trading day, call auctions have a fixed time period for order placement and execution.
Call auctions are commonly used in stock exchanges, especially for the opening and closing of trading sessions. They are also used in other financial markets, such as bond markets and commodity markets. The use of call auctions can vary depending on the specific market and its regulations.
One key advantage of call auctions is that they provide a transparent and equal opportunity for all market participants to place their orders. This helps to prevent any unfair advantages that may arise in continuous trading, such as high-frequency trading or front-running.
Another benefit of call auctions is that they can help to reduce transaction costs. By matching all orders at a single price, call auctions eliminate the need for multiple transactions and the associated costs, such as bid-ask spreads and brokerage fees.
However, call auctions also have some limitations. One limitation is that they can be less liquid compared to continuous trading. Since all orders are matched at a single price, there may be a limited number of buyers and sellers willing to participate in the auction, especially for less liquid securities.
Additionally, call auctions can be more susceptible to manipulation or price manipulation attempts. Market participants may try to influence the call price by placing large orders or colluding with other participants. Regulators and market operators need to have proper mechanisms in place to detect and prevent such manipulative activities.
Developing a Call Strategy
1. Define Your Objectives
2. Assess Your Risk Tolerance
3. Research and Analysis

4. Diversify Your Portfolio

Diversification is a key principle of investing, and it applies to call options as well. By diversifying your call options portfolio, you can spread out your risk and increase your chances of making profitable trades. Consider investing in a variety of stocks and industries to minimize the impact of any single stock’s performance on your overall portfolio.
5. Monitor and Adjust
Developing a call strategy requires careful planning, research, and analysis. By defining your objectives, assessing your risk tolerance, conducting thorough research, diversifying your portfolio, and regularly monitoring and adjusting your strategy, you can increase your chances of success in the world of call options trading.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
