What are Stock Appreciation Rights (SARs)?
Stock Appreciation Rights (SARs) are a type of equity compensation plan that companies use to reward their employees. SARs give employees the opportunity to benefit from the increase in the company’s stock price over a certain period of time.
Unlike stock options, which give employees the right to purchase company stock at a predetermined price, SARs do not require employees to make any upfront payment. Instead, SARs provide employees with a cash payment equal to the appreciation in the company’s stock price.
When an employee is granted SARs, they are given a specific number of units or shares. The value of these units or shares is tied to the company’s stock price. If the stock price increases during the vesting period, the employee can exercise their SARs and receive a cash payment equal to the increase in value.
One of the key features of SARs is that employees do not need to own the underlying stock to benefit from the increase in value. This makes SARs a popular choice for companies that want to provide their employees with a financial incentive without diluting the ownership of existing shareholders.
SARs can be a valuable tool for companies to attract and retain top talent. They offer employees the opportunity to share in the company’s success and align their interests with those of the shareholders. Additionally, SARs can provide employees with a significant financial reward if the company’s stock price performs well.
Overall, Stock Appreciation Rights are a flexible and effective way for companies to reward and motivate their employees. They provide employees with a direct financial incentive to contribute to the company’s growth and success.
Definition and Basics
Stock Appreciation Rights (SARs) are a type of employee compensation plan that allows employees to benefit from the increase in the value of a company’s stock over a certain period of time. SARs are typically granted to key employees as a way to incentivize and reward their performance and loyalty to the company.
SARs are similar to stock options in that they give employees the right to receive a cash payment or stock equivalent based on the increase in the company’s stock price. However, unlike stock options, SARs do not require employees to purchase the company’s stock at a predetermined price. Instead, employees are granted SARs for free and can exercise them at a later date when the stock price has appreciated.
When an employee exercises their SARs, they receive the difference between the market price of the company’s stock at the time of exercise and the grant price of the SARs. This cash payment or stock equivalent is considered taxable income to the employee.
SARs are typically subject to vesting periods, meaning that employees must remain with the company for a certain period of time before they can exercise their SARs. This helps to incentivize employee retention and loyalty.
Overall, SARs are a valuable tool for companies to attract and retain top talent by providing employees with a direct financial stake in the company’s success. They align the interests of employees with those of shareholders and can be a powerful motivator for employees to work towards increasing the company’s stock price.
How SARs Work
Stock Appreciation Rights (SARs) are a type of employee compensation that allows employees to benefit from the increase in the value of a company’s stock over time. SARs are typically granted to employees as part of their compensation package and are designed to incentivize and reward employees for their contributions to the company’s success.
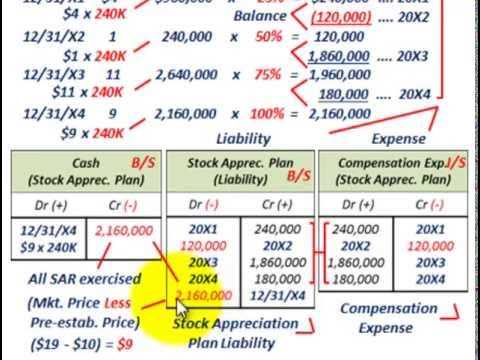
When an employee is granted SARs, they are given the right to receive a cash payment or an equivalent number of shares of stock based on the increase in the company’s stock price. The value of the SARs is tied to the difference between the fair market value of the stock at the time of grant and the fair market value at the time of exercise.
There are two main types of SARs: nonqualified SARs and incentive SARs. Nonqualified SARs are typically offered to all employees, while incentive SARs are usually reserved for key employees and executives.
Exercise and Settlement
Employees can exercise their SARs once they have vested, which means they have met certain conditions, such as completing a certain number of years of service or achieving specific performance goals. Once vested, employees can choose to exercise their SARs by either receiving a cash payment or converting their SARs into shares of stock.
When an employee exercises their SARs, the company will calculate the value of the SARs based on the increase in the stock price and either pay the employee the cash equivalent or issue them the corresponding number of shares. The employee can then choose to hold onto the shares or sell them on the open market.
Tax Implications
| Benefits of SARs |
|---|
| 1. Aligns employee interests with company performance |
| 2. Provides employees with a financial incentive to work towards the company’s success |
| 3. Allows employees to share in the company’s growth and profitability |
| 4. Can be a valuable tool for attracting and retaining top talent |
Benefits of Stock Appreciation Rights
Stock Appreciation Rights (SARs) offer numerous benefits to both companies and employees. Here are some of the key advantages:
2. Employee Ownership: SARs give employees a sense of ownership in the company. By granting them the right to benefit from the appreciation in the company’s stock price, SARs align the interests of employees with those of the shareholders. This can lead to increased motivation, loyalty, and commitment among employees.
3. Performance-Based Compensation: SARs are typically granted based on an employee’s performance or the company’s performance. This performance-based compensation structure encourages employees to strive for excellence and achieve specific goals, which can ultimately drive the company’s growth and success.
4. Retention and Attraction of Talent: Offering SARs as part of an employee compensation package can help attract and retain top talent. The potential for financial gain through SARs can be a compelling incentive for employees to stay with the company and contribute to its long-term success.
5. Tax Advantages: SARs can offer certain tax advantages for both employees and companies. The specific tax treatment of SARs may vary depending on the jurisdiction and the terms of the plan, but in many cases, SARs are taxed as capital gains rather than ordinary income.
Overall, Stock Appreciation Rights provide a win-win situation for both companies and employees. They offer financial incentives, promote employee ownership, drive performance, attract and retain talent, and may provide tax advantages. Implementing SARs can be a strategic move for companies looking to motivate and reward their employees while aligning their interests with the company’s growth and success.
Financial Incentives

Financial incentives are a key component of stock appreciation rights (SARs) and can provide significant benefits to employees. SARs offer employees the opportunity to share in the financial success of the company by giving them the right to receive the appreciation in the value of the company’s stock.
Another financial incentive of SARs is the ability to defer taxes. When employees exercise their SARs and receive the appreciation in value, they may have the option to defer the taxes on that gain until a later date. This can provide employees with a valuable tax planning strategy, allowing them to potentially reduce their tax liability and maximize their overall financial benefit.
SARs can also provide employees with a sense of financial security. By offering employees the opportunity to participate in the company’s financial success, SARs can create a strong sense of ownership and loyalty. This can lead to increased motivation and productivity, as employees are more likely to be invested in the company’s success.
Key Benefits of Financial Incentives:

- Potential for significant increase in wealth
- Ability to defer taxes
- Creates a sense of financial security
Overall, the financial incentives of stock appreciation rights can be highly attractive to employees. By providing the opportunity for financial gain, tax advantages, and a sense of ownership, SARs can be a valuable tool for companies looking to attract and retain top talent.
Employee Ownership
One of the key benefits of Stock Appreciation Rights (SARs) is that they provide employees with a sense of ownership in the company. When employees are granted SARs, they have the opportunity to participate in the financial success of the company and benefit from its growth.
By giving employees a stake in the company’s performance, SARs can help align their interests with those of the shareholders and management. This can lead to increased motivation, loyalty, and commitment to the company’s success.
Employee ownership through SARs can also create a culture of shared responsibility and accountability. When employees have a financial stake in the company, they are more likely to take ownership of their work and strive for excellence.
Increased Engagement and Retention
Stock Appreciation Rights can be a powerful tool for attracting and retaining top talent. When employees have the opportunity to share in the company’s success, they are more likely to be engaged and committed to their work.
Offering SARs as part of an employee compensation package can also help differentiate a company from its competitors. In a competitive job market, the ability to offer ownership in the company can be a significant advantage in attracting and retaining high-performing employees.
Long-Term Incentives
Stock Appreciation Rights are often used as a long-term incentive to reward and retain key employees. Unlike cash bonuses or other short-term incentives, SARs provide employees with the potential for long-term financial gain.
By tying the value of SARs to the company’s stock price, employees have a vested interest in the company’s long-term success. This can help align their goals with the company’s strategic objectives and encourage them to stay with the company for an extended period.
| Benefits of Employee Ownership through SARs |
|---|
| 1. Sense of ownership and participation in the company’s success |
| 2. Increased motivation, loyalty, and commitment |
| 3. Shared responsibility and accountability |
| 4. Attracting and retaining top talent |
| 5. Differentiation in a competitive job market |
| 6. Long-term financial gain |
| 7. Alignment of goals with the company’s strategic objectives |
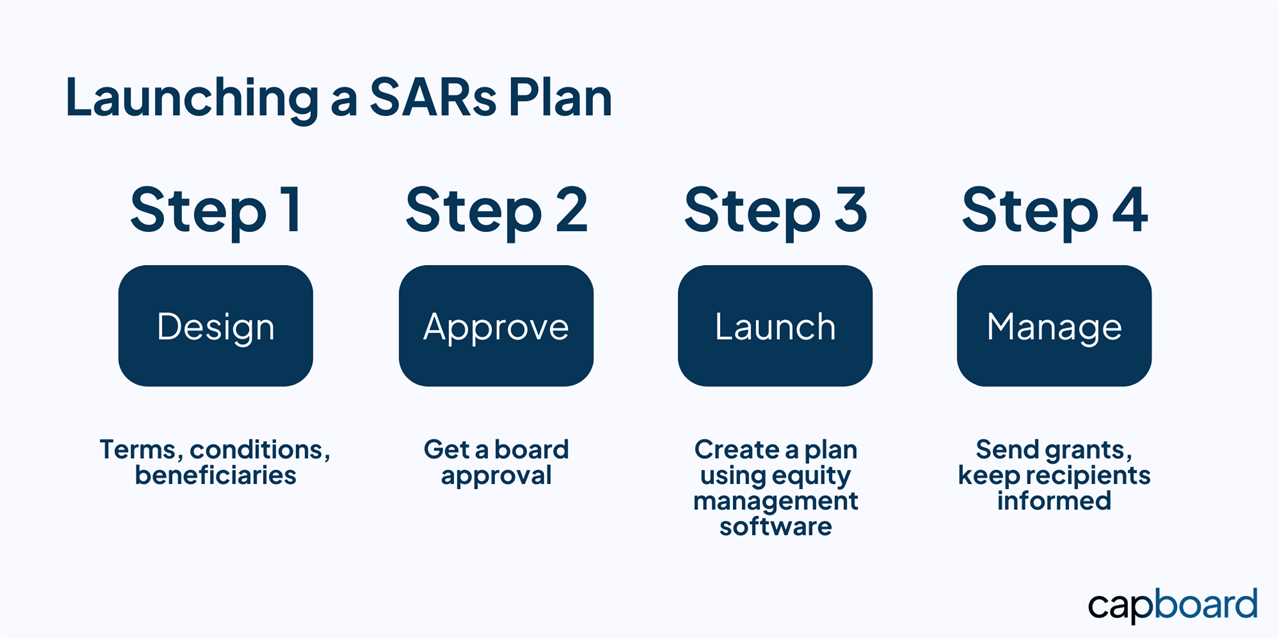
Implementing Stock Appreciation Rights
Implementing Stock Appreciation Rights (SARs) in a company involves several steps to ensure a smooth and effective process. Here are some key considerations:
- Designing the SARs Program: The first step is to design the SARs program, taking into account the company’s goals, objectives, and the needs of its employees. This includes determining the eligibility criteria, the number of SARs to be granted, and the vesting schedule.
- Granting SARs: Once the program is designed and communicated, the company can grant SARs to eligible employees. This involves preparing the necessary documentation, such as SAR agreements, and obtaining the required approvals.
- Tracking and Accounting: Companies need to establish a system to track and account for SARs. This includes maintaining accurate records of SAR grants, exercises, and forfeitures, as well as complying with accounting standards and regulations.
- Valuation and Reporting: Companies must determine the fair value of SARs at the grant date and report this information in their financial statements. This requires the use of appropriate valuation methods and adherence to accounting principles.
- Employee Education and Support: Ongoing education and support for employees is essential to ensure they understand the benefits and mechanics of SARs. This can include providing regular updates, offering training sessions, and offering assistance with exercising SARs.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: Companies should regularly monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of their SARs program. This includes assessing employee satisfaction, tracking the impact on company performance, and making any necessary adjustments or improvements.
By carefully implementing Stock Appreciation Rights, companies can create a valuable incentive for employees and align their interests with the success of the organization.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
