Benefits of Share Buybacks
1. Increased Earnings Per Share (EPS)

One of the primary benefits of share buybacks is the potential to increase a company’s earnings per share (EPS). By reducing the number of outstanding shares, the company effectively spreads its earnings over a smaller base, resulting in a higher EPS. This can be particularly beneficial for companies looking to boost their stock price or attract investors.
2. Enhanced Shareholder Value
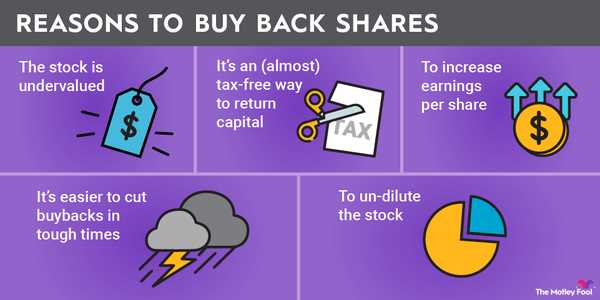
Share buybacks can also contribute to enhancing shareholder value. When a company repurchases its own shares, it signals to the market that it believes its stock is undervalued. This can lead to an increase in demand for the company’s shares, driving up the stock price and benefiting existing shareholders. Additionally, by reducing the number of outstanding shares, share buybacks can increase the ownership percentage of existing shareholders, potentially increasing their overall value.
| Benefits of Share Buybacks |
|---|
| Increased Earnings Per Share (EPS) |
| Enhanced Shareholder Value |
Overall, share buybacks can be a strategic tool for companies to allocate their capital efficiently and create value for their shareholders. However, it is important to note that share buybacks should be implemented judiciously, taking into consideration the company’s financial health and long-term growth prospects.
Motivations for Share Repurchases
1. Enhancing Shareholder Value
One of the main motivations for share repurchases is to enhance shareholder value. By reducing the number of outstanding shares, the company can increase its earnings per share (EPS), which is a key metric used by investors to assess a company’s profitability. This can lead to an increase in the company’s stock price, benefiting existing shareholders.
2. Capital Allocation
Companies may also choose to repurchase shares as a way to allocate capital efficiently. If a company has excess cash on its balance sheet, it can use that cash to repurchase shares instead of investing in new projects or acquisitions. This can be a more attractive option if the company believes that its stock is undervalued and that repurchasing shares will generate a higher return for shareholders.
3. Tax Efficiency
Another motivation for share repurchases is tax efficiency. When a company repurchases its own shares, it can return capital to shareholders in a tax-efficient manner. Shareholders can choose to sell their shares back to the company, which may result in capital gains tax treatment, or they can hold onto their shares and potentially benefit from future price appreciation.
4. Signaling Effect
Share repurchases can also have a signaling effect on the market. When a company announces a share repurchase program, it signals to investors that the company believes its stock is undervalued. This can create positive sentiment among investors and potentially attract new investors to the stock.
5. Defensive Measure
In some cases, companies may repurchase shares as a defensive measure. For example, if a company believes that its stock is undervalued and vulnerable to a hostile takeover, it may repurchase shares to increase its ownership and make it more difficult for the acquiring company to gain control.
Overall, share repurchases can be motivated by a combination of factors, including enhancing shareholder value, capital allocation, tax efficiency, signaling effect, and defensive measures. It is important for investors to understand these motivations and evaluate them in the context of the company’s overall financial strategy.
Impact of Buybacks on Shareholders
Share buybacks can have a significant impact on shareholders, both in the short term and the long term. Here are some key ways in which buybacks can affect shareholders:
1. Increased Earnings per Share (EPS)
When a company repurchases its own shares, the number of outstanding shares decreases. As a result, the company’s earnings are divided among a smaller number of shares, leading to an increase in earnings per share (EPS). This can be beneficial for shareholders as it indicates a higher profitability per share.
2. Potential for Capital Appreciation
Share buybacks can also lead to an increase in the stock price. When a company repurchases its own shares, it reduces the supply of shares in the market, which can create a demand-supply imbalance and drive up the stock price. This can result in capital appreciation for shareholders who hold onto their shares.
3. Enhanced Return on Investment
4. Increased Ownership Percentage
When a company repurchases its own shares, the ownership percentage of existing shareholders increases. This can be advantageous for shareholders as it consolidates their ownership and gives them a larger stake in the company’s future earnings and decision-making processes.
5. Potential Tax Benefits
In some jurisdictions, share buybacks can have tax advantages for shareholders. For example, in certain countries, capital gains tax rates may be lower for shareholders who sell their shares back to the company through a buyback program. This can result in potential tax savings for shareholders.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
