Risk Assessment: Definition
Risk assessment is the process of identifying, evaluating, and analyzing potential risks or hazards that may occur in a specific situation or environment. It involves assessing the likelihood and potential impact of these risks, as well as developing strategies to mitigate or manage them.
At its core, risk assessment aims to provide decision-makers with valuable information to make informed choices and prioritize resources effectively. It helps organizations and individuals understand the potential consequences of their actions or inactions, allowing them to take proactive measures to prevent or minimize harm.
There are various types of risks that can be assessed, including financial risks, environmental risks, health and safety risks, cybersecurity risks, and more. Each type of risk requires a specific approach and methodology to assess and manage effectively.
Overall, risk assessment is a crucial tool in risk management, enabling individuals and organizations to identify and understand potential risks, make informed decisions, and implement appropriate measures to protect themselves and their assets.
At its core, risk assessment is about identifying and analyzing potential hazards or uncertainties that could affect the achievement of objectives or the success of a project. It helps in identifying vulnerabilities, assessing the probability of occurrence, and estimating the potential consequences of risks.
The importance of risk assessment lies in its ability to provide a structured and systematic approach to decision-making. It helps in identifying potential risks, evaluating their significance, and developing appropriate strategies to minimize or eliminate them. By conducting a thorough risk assessment, organizations can enhance their ability to anticipate and respond to potential challenges, thereby improving their overall performance and success.
Risk assessment also plays a crucial role in regulatory compliance and risk management. It helps organizations comply with legal and regulatory requirements by identifying potential risks and implementing appropriate controls and safeguards. It also enables organizations to proactively manage risks and reduce the likelihood of costly incidents or disruptions.
Risk Assessment: Methods
Risk assessment is a crucial process in identifying, evaluating, and prioritizing potential risks that may impact an organization or project. There are several methods and approaches that can be used to conduct a risk assessment.
1. Qualitative Risk Assessment
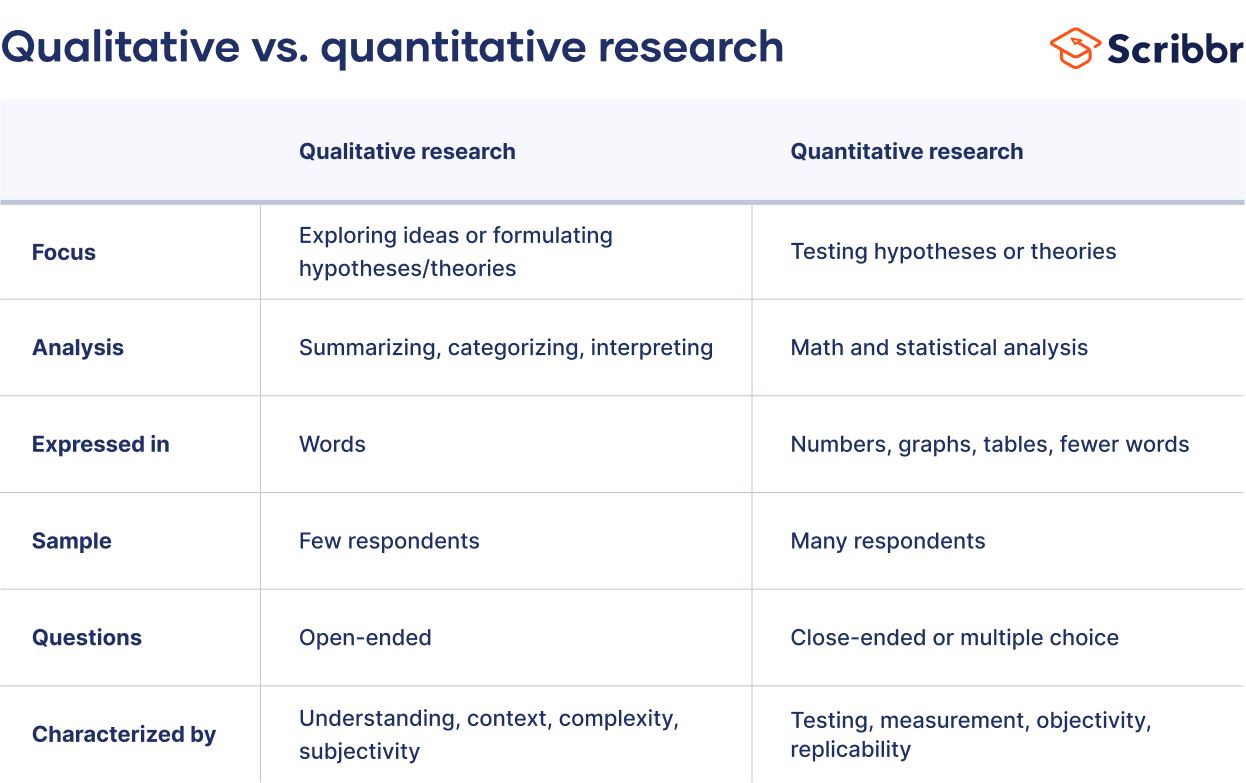
Qualitative risk assessment involves the subjective analysis of risks based on their likelihood and potential impact. This method relies on expert judgment and experience to assess and prioritize risks. It is often used when there is limited data available or when a quick assessment is needed.
One common approach in qualitative risk assessment is the use of risk matrices. A risk matrix is a visual tool that categorizes risks based on their likelihood and impact, usually using a color-coded grid. This allows stakeholders to easily understand and communicate the level of risk associated with different scenarios.
2. Quantitative Risk Assessment
Quantitative risk assessment involves the use of numerical data and statistical analysis to assess risks. This method relies on data-driven models and calculations to estimate the probability of a risk occurring and the potential impact it may have.
There are various techniques used in quantitative risk assessment, such as Monte Carlo simulation, fault tree analysis, and sensitivity analysis. These techniques help in quantifying risks and providing a more accurate assessment of their potential impact.
Quantitative risk assessment is often used when there is sufficient data available and when a more detailed analysis is required. It allows for a more objective and precise evaluation of risks, which can help in making informed decisions and allocating resources effectively.
3. Mixed Methods
In some cases, a combination of qualitative and quantitative methods may be used to conduct a risk assessment. This approach allows for a more comprehensive analysis, taking into account both subjective judgments and objective data.
Exploring Different Approaches and Techniques for Risk Assessment
1. Qualitative Risk Assessment
2. Quantitative Risk Assessment
There are several techniques and tools that can be used within qualitative and quantitative risk assessment:
| Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| Brainstorming | A group discussion technique that helps identify and evaluate potential risks. |
| Checklists | A predefined list of risks that can be reviewed and assessed. |
| Interviews | Conducting interviews with key stakeholders to gather information and assess risks. |
| Probability and Impact Matrix | A matrix that helps assess risks based on their probability and impact. |
| Monte Carlo Simulation | A statistical technique that models and simulates various scenarios to assess risks. |
Risk Assessment: Qualitative Vs. Quantitative
Qualitative Risk Assessment
Qualitative risk assessment is a subjective method that focuses on the likelihood and impact of risks without assigning specific numerical values. Instead of using precise measurements, this approach relies on expert judgment and experience to evaluate risks based on their qualitative characteristics.
However, qualitative risk assessment has some limitations. The lack of numerical values makes it difficult to compare and prioritize risks objectively. It can also be subjective and prone to biases, as different experts may have different interpretations of risk likelihood and impact. Furthermore, qualitative risk assessment may not provide the level of detail required for certain decision-making processes.
Quantitative Risk Assessment
Quantitative risk assessment, on the other hand, is an objective method that uses numerical values to assess risks. It involves the collection and analysis of data to quantify the likelihood and impact of risks, allowing for more precise calculations and comparisons.
One of the main advantages of quantitative risk assessment is its ability to provide a more accurate and objective assessment of risks. The use of numerical values enables organizations to prioritize risks based on their potential impact and allocate resources accordingly. It also allows for more rigorous analysis and modeling, making it suitable for complex and data-driven decision-making processes.
However, quantitative risk assessment also has its limitations. It requires a significant amount of data and expertise to perform accurate calculations, which may not be feasible for all organizations. Additionally, the reliance on numerical values can lead to a false sense of precision and may overlook qualitative aspects of risks that cannot be easily quantified.
Choosing the Right Approach
Deciding between qualitative and quantitative risk assessment depends on various factors, including the organization’s resources, objectives, and the nature of the risks being assessed. In some cases, a combination of both approaches may be appropriate, leveraging the strengths of each method.
Ultimately, the choice between qualitative and quantitative risk assessment should be based on the specific needs and context of the organization. It is important to consider the limitations and benefits of each approach and tailor the risk assessment process accordingly to ensure effective risk management.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
