Importance of Revenue Recognition

Revenue recognition is a crucial aspect of accounting that plays a significant role in determining a company’s financial performance. It involves the process of identifying and recording revenue from the sale of goods or services, and it is essential for businesses to accurately recognize revenue to provide transparent and reliable financial statements.
Accurate revenue recognition allows businesses to assess their financial health, make informed decisions, and provide reliable information to investors, creditors, and other stakeholders. It provides a clear picture of a company’s revenue-generating activities, helping stakeholders evaluate its profitability and growth potential.
Proper revenue recognition also ensures compliance with accounting standards and regulations. By following the established guidelines, businesses can avoid legal and regulatory issues, maintain transparency, and build trust with their stakeholders.
Furthermore, revenue recognition impacts various financial metrics and ratios, such as gross profit margin, net profit margin, and return on investment. Accurate revenue recognition enables businesses to analyze these metrics accurately, assess their financial performance, and make informed decisions to improve profitability and efficiency.
Step 4: Allocate the Transaction Price
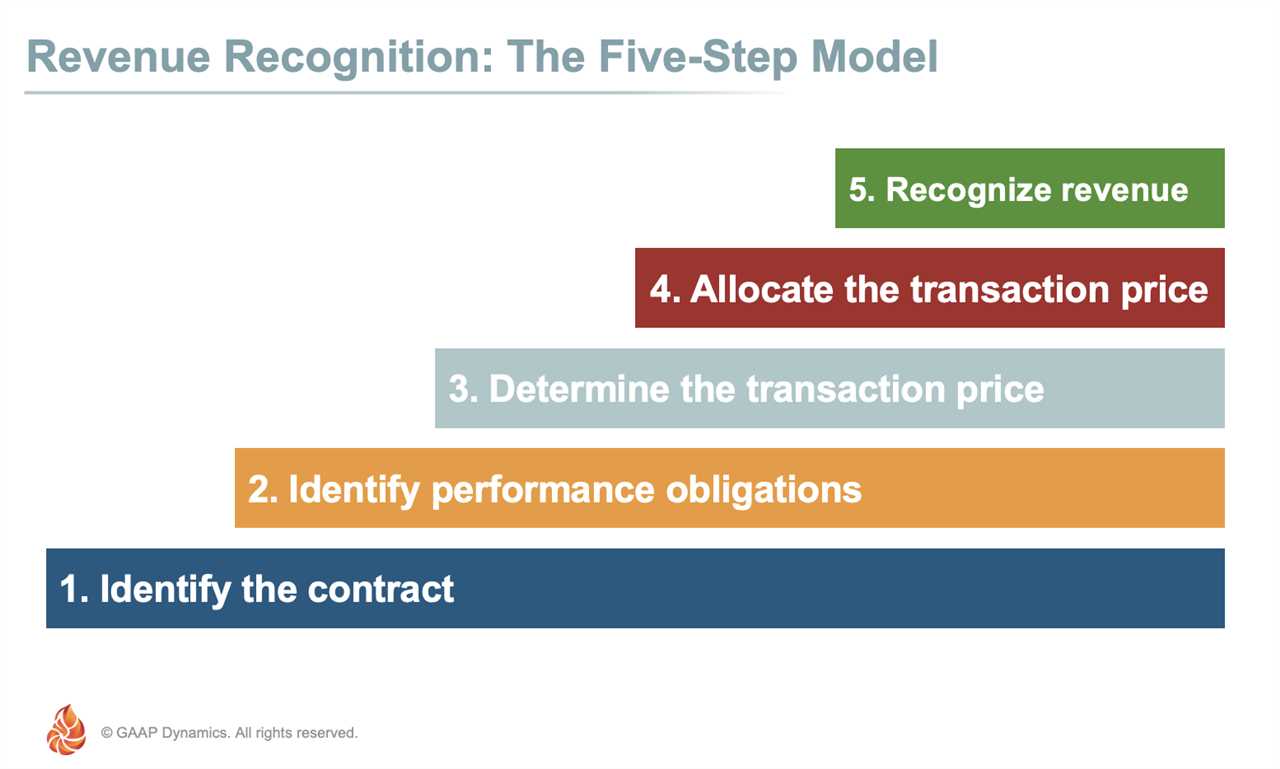
Allocating the transaction price is a crucial step in the revenue recognition process. Once the contract and performance obligations have been identified, it is important to determine how the transaction price should be allocated to each obligation.
Why is allocation important?
Allocation is important because it ensures that revenue is recognized accurately and in accordance with the performance obligations outlined in the contract. It allows for the proper distribution of revenue among the various goods or services provided.
Factors to consider in allocation:
- Stand-alone selling prices: The stand-alone selling prices of the goods or services involved should be considered when allocating the transaction price. This helps determine the relative value of each obligation.
- Variable consideration: If the transaction price includes variable consideration, such as discounts or rebates, it should be allocated appropriately based on the estimated amount that is expected to be earned.
- Constraints: Any constraints or limitations on the revenue recognition should be taken into account when allocating the transaction price. This ensures that revenue is recognized only when it is probable that a significant reversal will not occur in the future.
By carefully considering these factors, businesses can ensure that the transaction price is allocated accurately and in accordance with the contract terms. This helps to provide a clear and transparent picture of the revenue generated from each performance obligation.
Step 5: Recognize Revenue
Once the transaction price has been determined and the performance obligations have been identified and allocated, the next step in revenue recognition is to actually recognize the revenue.
This step involves determining when and how much revenue should be recognized based on the progress of the performance obligations and the satisfaction of any specific criteria outlined in the contract.
There are different methods for recognizing revenue, depending on the nature of the performance obligations and the terms of the contract. Some common methods include:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Over time | Revenue is recognized over the duration of the performance obligations, based on the progress made towards completion. |
| At a point in time | Revenue is recognized at a specific point in time, typically when control of the goods or services is transferred to the customer. |
It is important to carefully assess the terms of the contract and the specific circumstances of the transaction to determine the appropriate method for recognizing revenue.
Additionally, any constraints or contingencies that may impact the recognition of revenue should be taken into consideration. These could include factors such as customer acceptance, return rights, or warranty obligations.
By accurately recognizing revenue, businesses can provide transparent financial reporting and ensure compliance with accounting standards. It also allows stakeholders to make informed decisions based on the company’s financial performance.
Overall, recognizing revenue is a crucial step in the revenue recognition process, as it determines when and how much revenue should be recorded in the financial statements.
Step 6: Determine the Transaction Price
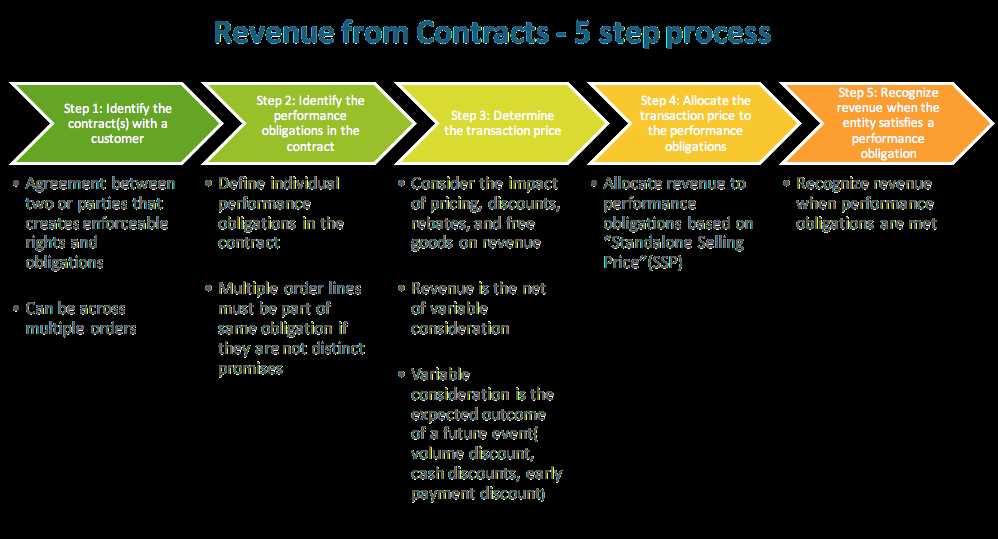
To determine the transaction price, several factors need to be considered:
| 1. Variable Consideration: | Any potential adjustments to the transaction price due to factors such as discounts, rebates, refunds, or performance bonuses should be taken into account. |
| 2. Time Value of Money: | If the contract includes a significant financing component, the transaction price should be adjusted to reflect the time value of money. |
| 3. Non-Cash Consideration: | If the consideration includes non-cash assets, such as goods or services, their fair value should be determined and included in the transaction price. |
| 4. Consideration Payable to the Customer: | If the entity expects to pay consideration to the customer, such as refunds or credits, it should be deducted from the transaction price. |
By carefully considering these factors, entities can accurately determine the transaction price and ensure proper revenue recognition. It is important to document the rationale behind the determination of the transaction price to provide transparency and support for the recognition of revenue.
Overall, determining the transaction price is a critical step in the revenue recognition process, as it sets the foundation for recognizing revenue and ensures that the financial statements reflect the economic substance of the underlying transactions.
Step 7: Allocate the Transaction Price
Allocating the transaction price is a crucial step in revenue recognition. Once the transaction price has been determined in step 3, it needs to be allocated to the performance obligations identified in step 2.
During this step, the company must determine how much of the transaction price should be allocated to each performance obligation based on their relative standalone selling prices. The standalone selling price is the price at which the company would sell the performance obligation on a standalone basis.
It is important to note that if a performance obligation has no standalone selling price, the company needs to estimate it using the best available information. This estimation should be done with caution and in accordance with the relevant accounting standards.
Once the transaction price has been allocated to each performance obligation, the company can move on to the final step of revenue recognition, which is step 8: Recognize Revenue.
Step 5: Recognize Revenue
Recognizing revenue is the final step in the revenue recognition process. Once the performance obligations have been identified, the transaction price has been determined, and the transaction price has been allocated, it is time to recognize revenue.
Revenue is recognized when control of the goods or services is transferred to the customer. This typically occurs when the customer obtains the right to use the goods or services, or when the customer takes legal ownership of the goods.
Benefits of Proper Revenue Recognition
Proper revenue recognition is crucial for businesses for several reasons:
- Accurate financial reporting: Proper revenue recognition ensures that financial statements accurately reflect the company’s performance and financial position.
- Compliance with accounting standards: Following the proper revenue recognition guidelines ensures compliance with accounting standards, reducing the risk of penalties or legal issues.
- Investor confidence: Accurate and transparent revenue recognition enhances investor confidence in the company’s financial statements, making it more attractive to potential investors.
- Effective decision-making: Reliable revenue recognition allows management to make informed decisions based on accurate financial information.
- Comparison with industry peers: Proper revenue recognition allows for meaningful comparisons with industry peers, facilitating benchmarking and performance evaluation.
Conclusion
Recognizing revenue is the final step in the revenue recognition process and is crucial for accurate financial reporting, compliance with accounting standards, investor confidence, effective decision-making, and comparison with industry peers. By following the proper guidelines and methods for revenue recognition, businesses can ensure the reliability and transparency of their financial statements.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
