Profit and Loss Statement: Meaning, Importance, Types, and Examples
Meaning of Profit and Loss Statement
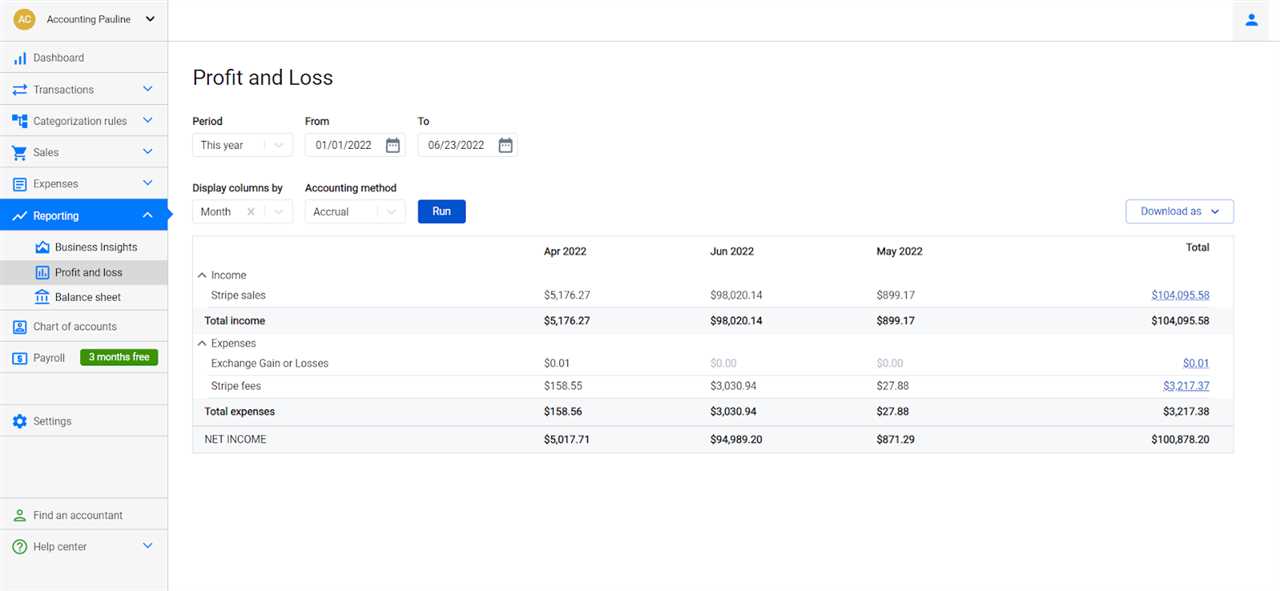
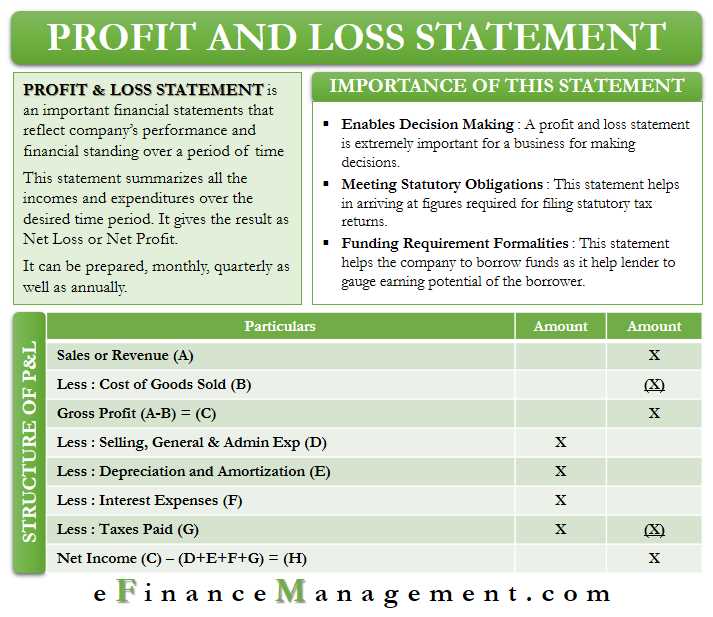
The profit and loss statement shows the net income or net loss of a company by subtracting the total expenses from the total revenues. It reflects the financial results of the company’s operations over a given period, such as a month, quarter, or year.
The statement includes various components, such as:
- Revenue: The total amount of money generated from the sale of goods or services.
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): The direct costs associated with producing or delivering the goods or services sold.
- Gross Profit: The difference between revenue and COGS, representing the profitability before considering other expenses.
- Operating Expenses: The costs incurred to run the day-to-day operations of the business, such as rent, salaries, and utilities.
- Operating Income: The difference between gross profit and operating expenses, indicating the profitability from core operations.
- Other Income and Expenses: Any additional income or expenses not directly related to the core operations of the business.
- Net Income or Net Loss: The final result after considering all revenues, costs, and expenses, indicating the overall profitability or loss of the business.
Importance of Profit and Loss Statement
The profit and loss statement is essential for several reasons:
- Financial Performance Evaluation: It helps assess the financial performance of a business and determine its profitability. By comparing the statement over different periods, stakeholders can identify trends and make informed decisions.
- Budgeting and Forecasting: The statement provides valuable information for creating budgets and forecasting future financial outcomes. It helps businesses set realistic financial goals and track their progress.
- Investor and Creditor Analysis: Investors and creditors rely on the profit and loss statement to evaluate the financial health of a business before making investment or lending decisions.
- Tax Reporting: The statement serves as a basis for calculating income taxes owed to the government. It provides a comprehensive overview of the business’s revenues, expenses, and net income.
Overall, the profit and loss statement is a crucial financial tool that provides insights into a company’s profitability and financial performance. It helps stakeholders make informed decisions, plan for the future, and assess the overall health of the business.
Importance of the Profit and Loss Statement
The profit and loss statement is important for several reasons. Firstly, it helps businesses track their revenue and expenses, allowing them to identify areas of strength and weakness in their operations. By analyzing the statement, businesses can make informed decisions to improve profitability and efficiency.
Secondly, the profit and loss statement is crucial for external stakeholders, such as investors, lenders, and potential business partners. These stakeholders use the statement to evaluate the financial health and performance of a company before making investment or lending decisions. A positive net income indicates that a company is generating profits, which can attract investors and lenders.
Thirdly, the profit and loss statement provides valuable information for tax purposes. Businesses use the statement to calculate their taxable income and determine the amount of taxes they owe. Accurate and detailed financial records are essential for complying with tax regulations and avoiding penalties.
Components of the Profit and Loss Statement

The profit and loss statement consists of several components that provide a comprehensive view of a company’s financial performance. These components include:
1. Revenue: This section includes the total amount of money generated from the sale of goods or services. It is important to break down revenue by product or service category to identify the most profitable areas of the business.
2. Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): COGS represents the direct costs associated with producing or delivering the goods or services sold. This includes raw materials, labor, and any other costs directly attributed to production.
3. Gross Profit: Gross profit is calculated by subtracting the COGS from the revenue. It represents the profit generated before deducting operating expenses.
4. Operating Expenses: Operating expenses include all costs incurred in running the day-to-day operations of the business, such as rent, salaries, utilities, and marketing expenses.
5. Operating Income: Operating income is calculated by subtracting the operating expenses from the gross profit. It represents the profit generated from the core operations of the business.
6. Other Income and Expenses: This section includes any additional income or expenses that are not directly related to the core operations of the business, such as interest income or expenses.
7. Net Income or Loss: Net income or loss is calculated by subtracting the other income and expenses from the operating income. It represents the final profit or loss generated by the business during the specified period.
By analyzing these components, businesses can gain insights into their financial performance, identify areas for improvement, and make informed decisions to drive growth and profitability.
Importance of the Profit and Loss Statement
1. Assessing Financial Performance:
The profit and loss statement helps businesses assess their financial performance by showing the revenue generated and the expenses incurred during a specific period. It allows businesses to evaluate their profitability and identify areas where they can improve their financial performance.
2. Decision Making:
The profit and loss statement is an essential tool for making informed business decisions. It provides valuable insights into the company’s financial health and helps management make strategic decisions regarding pricing, cost control, and investment opportunities. By analyzing the statement, businesses can identify trends, patterns, and areas of concern that need attention.
3. Investor Confidence:
Investors and stakeholders rely on the profit and loss statement to assess the financial stability and profitability of a company. It provides them with the necessary information to make investment decisions and evaluate the company’s ability to generate returns. A well-prepared profit and loss statement can instill confidence in investors and attract potential investors.
4. Compliance and Reporting:
The profit and loss statement is a requirement for compliance and reporting purposes. It is necessary for tax filings, financial audits, and regulatory reporting. By maintaining accurate and up-to-date profit and loss statements, businesses can ensure compliance with legal and financial reporting requirements.
5. Benchmarking and Comparison:
The profit and loss statement allows businesses to benchmark their financial performance against industry standards and competitors. By comparing their revenue, expenses, and net income with similar businesses, companies can identify areas where they are lagging or excelling. This information can be used to set goals, make improvements, and stay competitive in the market.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
