What is a Portfolio Manager?
A portfolio manager is a financial professional who is responsible for managing a portfolio of investments on behalf of clients or an organization. They play a crucial role in the investment process by making decisions on what securities to buy, sell, or hold in order to achieve the client’s investment objectives.
Portfolio managers are typically employed by asset management firms, banks, or other financial institutions. They work closely with clients to understand their investment goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon. Based on this information, they develop an investment strategy and construct a portfolio that aligns with the client’s objectives.
Portfolio managers are skilled in analyzing financial markets, conducting research on individual securities, and monitoring the performance of investments. They use various tools and techniques to assess the risk and return potential of different assets, and make informed investment decisions accordingly.
Types of portfolio managers can vary depending on the type of investments they manage. Some portfolio managers specialize in equities, while others focus on fixed income securities, real estate, or alternative investments. They may also specialize in managing portfolios for specific types of clients, such as high-net-worth individuals, pension funds, or endowments.
The duties of a portfolio manager include conducting market research, analyzing financial statements, monitoring portfolio performance, and communicating with clients. They are responsible for staying up-to-date with market trends, economic conditions, and regulatory changes that may impact the portfolio. Additionally, they may collaborate with other professionals, such as research analysts and traders, to execute investment strategies.
In summary, a portfolio manager is a financial professional who manages investment portfolios on behalf of clients or organizations. They play a crucial role in the investment process by developing strategies, making investment decisions, and monitoring portfolio performance to help clients achieve their financial goals.
Definition, Types, and Duties

A portfolio manager is a financial professional who is responsible for managing investment portfolios on behalf of individuals, institutions, or organizations. They are experts in analyzing market trends, assessing risk, and making investment decisions to maximize returns for their clients.
Types of Portfolio Managers

There are various types of portfolio managers, each specializing in different areas of investment:
1. Equity Portfolio Managers: These managers focus on investing in stocks and other equity securities. They conduct extensive research and analysis to identify undervalued stocks and make informed investment decisions.
2. Fixed Income Portfolio Managers: These managers specialize in investing in fixed income securities such as bonds and treasury bills. They analyze interest rates, credit ratings, and market conditions to make investment decisions that generate stable income for their clients.
3. Alternative Investment Portfolio Managers: These managers invest in alternative assets such as real estate, private equity, hedge funds, and commodities. They have expertise in evaluating the potential risks and returns associated with these non-traditional investments.
Duties of a Portfolio Manager
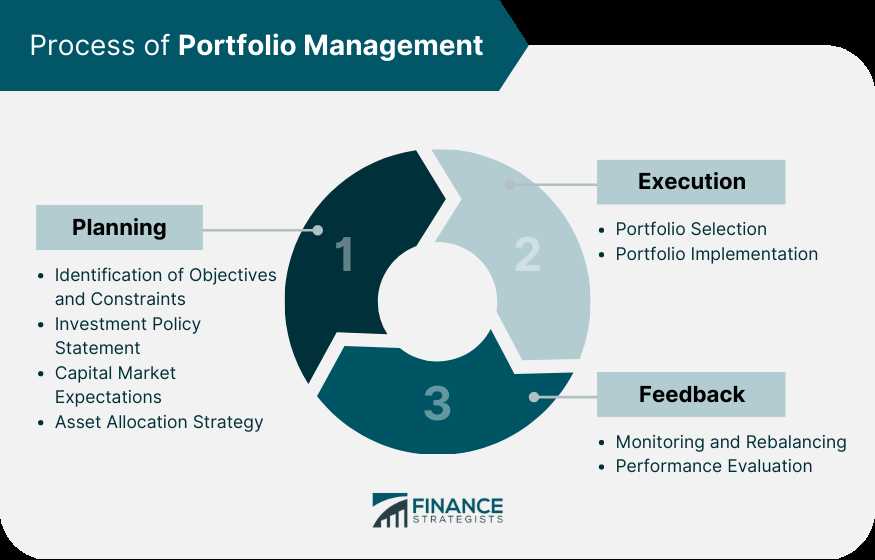
The duties of a portfolio manager may vary depending on the type of portfolio they manage and the specific goals of their clients. However, some common duties include:
1. Investment Research: Portfolio managers conduct thorough research and analysis of various investment opportunities to identify potential investments that align with their clients’ objectives.
2. Asset Allocation: They determine the optimal allocation of assets within a portfolio to achieve a balance between risk and return. This involves diversifying investments across different asset classes and sectors.
3. Risk Management: Portfolio managers assess and manage the risks associated with investments. They develop strategies to mitigate risks and protect the portfolio from market fluctuations.
4. Performance Monitoring: They continuously monitor the performance of the portfolio and make necessary adjustments to ensure it remains aligned with the clients’ goals. They track market trends, economic indicators, and company financials to make informed investment decisions.
5. Client Communication: Portfolio managers regularly communicate with their clients to provide updates on the portfolio’s performance and discuss any changes in investment strategies. They address client concerns and provide guidance on investment decisions.
6. Compliance: Portfolio managers adhere to legal and regulatory requirements in managing client portfolios. They ensure compliance with investment guidelines, disclosure requirements, and ethical standards.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
