National Insurance Contribution (NIC) Overview

National Insurance Contribution (NIC) is a mandatory contribution that individuals in the United Kingdom make to fund various social security benefits and services. It is a form of tax that is deducted from an individual’s earnings and is used to fund the National Health Service (NHS), state pensions, and other welfare programs.
NIC is calculated based on an individual’s earnings and is paid by both employees and employers. The amount of NIC paid depends on the individual’s earnings and their NIC category.
There are different types of NIC, including Class 1, Class 2, and Class 4 contributions. Class 1 contributions are paid by employees and employers, while Class 2 and Class 4 contributions are paid by self-employed individuals.
Calculating NIC can be complex, as it involves considering various factors such as earnings thresholds, rates, and allowances. The amount of NIC paid is typically a percentage of an individual’s earnings, up to a certain limit.
Changes to NIC rates and thresholds are made periodically by the government, and it is important for individuals to stay updated on these changes to ensure they are paying the correct amount.
Overall, NIC plays a crucial role in funding important social security benefits and services in the UK. It is important for individuals to understand their NIC obligations and ensure they are paying the correct amount to support these programs.
| Type of NIC | Contributor | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Class 1 | Employees and Employers | Contributions are deducted from employees’ earnings and paid by both employees and employers. These contributions fund the state pension, maternity and paternity pay, and other benefits. |
| Class 2 | Self-employed individuals | Contributions are paid by self-employed individuals to qualify for the state pension and other benefits. The amount is a fixed weekly rate. |
| Class 4 | Self-employed individuals | Contributions are based on the profits of self-employed individuals. These contributions fund the state pension and other benefits. |
National Insurance Contribution (NIC) is a mandatory tax that individuals in the United Kingdom pay to fund various state benefits, including the National Health Service (NHS), state pensions, and unemployment benefits. It is a social security system that ensures financial protection for individuals and their families in times of need.
The NIC system is based on the principle of social insurance, where individuals contribute a portion of their earnings to a collective fund that is then used to provide benefits to those who are eligible. The amount of NIC that an individual pays is determined by their earnings and their employment status.
There are different classes of NIC, each with its own set of rules and rates. Class 1 NIC is paid by employees, while Class 2 and Class 4 NIC are paid by self-employed individuals. The rates and thresholds for NIC are set by the government and are subject to change each year.
Calculating NIC can be complex, as it involves considering various factors such as earnings, employment status, and thresholds. Employers deduct NIC from employees’ wages and pay it to HM Revenue and Customs (HMRC) on their behalf. Self-employed individuals are responsible for calculating and paying their own NIC.
Changes to NIC can occur as a result of government policies and budget decisions. It is important for individuals to stay updated on any changes to ensure compliance and to understand how it may affect their finances.
Importance of National Insurance Contribution (NIC)
The National Insurance Contribution (NIC) is a crucial aspect of the UK’s social security system. It plays a vital role in providing financial support to individuals and families in times of need, such as retirement, unemployment, and healthcare expenses.
One of the key reasons why NIC is important is that it helps fund the National Health Service (NHS), which provides healthcare services to all UK residents. Without the contributions from NIC, the NHS would struggle to provide quality healthcare to the population.
NIC also contributes to the state pension system, ensuring that individuals have a source of income during their retirement years. By making regular contributions, individuals build up their entitlement to a state pension, which provides financial security in old age.
Furthermore, NIC helps support the welfare system, providing benefits to those who are unable to work due to disability, illness, or unemployment. These benefits help individuals and families meet their basic needs and maintain a decent standard of living.
Another important aspect of NIC is that it helps maintain the fairness and sustainability of the social security system. By requiring individuals and employers to make contributions based on their earnings, it ensures that the burden of funding social security is distributed fairly across society.
In addition, NIC also helps protect individuals and families from financial hardship in the event of unexpected circumstances, such as accidents, sickness, or bereavement. It provides a safety net that helps individuals cope with the financial impact of these situations.
In summary, the National Insurance Contribution (NIC) is of great importance as it funds essential services such as healthcare, supports the state pension system, provides welfare benefits, ensures fairness in funding social security, and offers financial protection in times of need. It is a crucial component of the UK’s social security system, providing financial security and support to individuals and families throughout their lives.
Types of National Insurance Contributions (NIC)
1. Class 1 NIC
Class 1 NIC is the most common type of contribution and is paid by employees and employers. Employees’ contributions are deducted from their wages, while employers’ contributions are paid on top of the employees’ wages. Class 1 NICs are used to fund a range of benefits, including the State Pension, Jobseeker’s Allowance, and Maternity Allowance.
2. Class 2 NIC
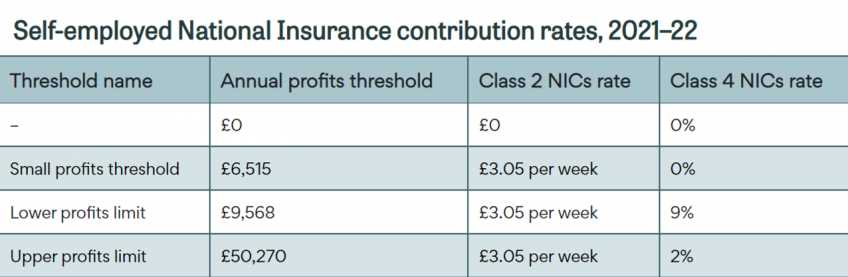
Class 2 NIC is paid by self-employed individuals who have profits above a certain threshold. It is a flat weekly rate and is used to contribute towards the State Pension and other benefits. However, it is important to note that Class 2 NICs will be abolished from April 2023, and self-employed individuals will instead pay Class 3 NICs.
3. Class 3 NIC
4. Class 4 NIC
Class 4 NIC is paid by self-employed individuals on their profits above a certain threshold. It is calculated as a percentage of their profits and is used to fund the State Pension and other benefits. The rate of Class 4 NICs varies depending on the level of profits.
It is important for individuals and employers to understand the different types of National Insurance Contributions (NIC) and how they are calculated. This knowledge can help ensure that the correct contributions are made and that individuals are able to access the benefits and services they are entitled to.
Calculating National Insurance Contributions (NIC)

For employees, NIC is deducted automatically from their salary by their employer. The amount deducted is based on the employee’s earnings and the applicable NIC class. The employer then contributes an additional amount on behalf of the employee.
Self-employed individuals are responsible for calculating and paying their own NIC. The amount is determined based on their profits and the applicable NIC class. It is important for self-employed individuals to keep accurate records of their income and expenses to ensure the correct calculation of NIC.
To calculate NIC, you need to know the relevant thresholds and rates for the specific NIC class. These can be found on the official government website or obtained from a qualified accountant or tax advisor. Once you have the necessary information, you can use it to determine the amount of NIC you owe.
Here is an example of how NIC can be calculated:
| NIC Class | Earnings | Rate | Amount |
|---|---|---|---|
| Class 1 | £30,000 | 12% | £3,600 |
| Class 2 | £40,000 | 3% | £1,200 |
| Class 4 | £50,000 | 9% | £4,500 |
It is important to note that NIC rates and thresholds may change over time, so it is crucial to stay updated with the latest information from the government or seek professional advice.
Changes to National Insurance Contributions (NIC)
As with any government policy, National Insurance Contributions (NIC) are subject to change. It is important for individuals and businesses to stay informed about these changes to ensure compliance and to plan their finances accordingly.
Reasons for Changes
Changes to NIC can occur for a variety of reasons, including:
- Government policy changes
- Economic factors
- Social and demographic changes
- Changes in employment patterns
Impact on Individuals
Changes to NIC can have a direct impact on individuals’ finances. They may result in changes to the amount of NIC individuals are required to pay, which can affect their take-home pay. It is important for individuals to understand these changes and how they may affect their financial situation.
Impact on Businesses
Changes to NIC can also have implications for businesses. They may result in increased costs for employers, which can affect their ability to hire new employees or provide competitive wages. It is important for businesses to understand these changes and plan accordingly to ensure they can meet their financial obligations.
Staying Informed

To stay informed about changes to NIC, individuals and businesses can:
- Regularly check the government’s official websites and publications for updates
- Subscribe to newsletters or email updates from relevant government departments
- Consult with a financial advisor or accountant who can provide guidance on the latest changes
- Attend seminars or workshops on NIC and related topics
By staying informed, individuals and businesses can ensure they are aware of any changes to NIC and can take appropriate action to comply with the new regulations.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
