Maturity Definition and Examples
Maturity refers to the date on which a financial instrument, such as a bond or a certificate of deposit (CD), becomes due and is repaid to the investor or the holder of the instrument. It represents the end of the investment period and the point at which the principal amount is returned. Maturity dates are crucial in determining the timing and duration of an investment.
Examples of maturity dates in different financial instruments include:
- A 5-year Treasury bond with a maturity date of December 31, 2025.
- A 1-year certificate of deposit with a maturity date of June 30, 2022.
- A 10-year corporate bond with a maturity date of January 15, 2030.
- A 3-month Treasury bill with a maturity date of September 30, 2021.
Maturity dates are important because they provide investors with a clear timeline for when they can expect to receive their investment back. This allows investors to plan their financial goals and make informed decisions about their investments.
For example, let’s say you purchase a 10-year bond with a maturity date of December 31, 2030. This means that on December 31, 2030, the issuer of the bond will repay you the principal amount you invested, as well as any interest that has accrued over the 10-year period.
Factors to Consider
When considering maturity dates, there are a few factors to keep in mind:
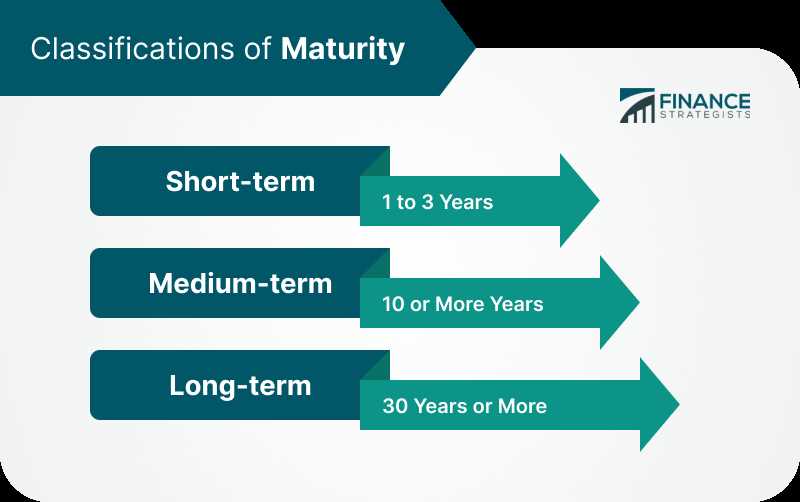
- Investment goals: Your investment goals will play a significant role in determining the maturity date that is right for you. If you have short-term goals, you may opt for investments with shorter maturity dates. If you have long-term goals, you may choose investments with longer maturity dates.
- Interest rates: Interest rates can have an impact on the attractiveness of different maturity dates. Generally, longer maturity dates offer higher interest rates to compensate investors for the longer holding period.
- Liquidity needs: Consider your liquidity needs when choosing investments with specific maturity dates. If you anticipate needing access to your funds before the maturity date, you may want to select investments with shorter maturity dates.
Conclusion
Importance of Maturity Dates in Fixed Income Investments
What is a fixed income investment?

Why are maturity dates important?

Maturity dates are important for several reasons. First, they provide investors with a clear timeline for when they can expect to receive their principal investment back. This allows investors to plan their finances and make informed decisions about their investments.
Furthermore, maturity dates are crucial for investors who may need to access their funds at a specific time. If an investor has a specific financial goal or expense in mind, they can choose a fixed income investment with a maturity date that aligns with their needs.
How do maturity dates affect investment risk?
Examples of Maturity Dates in Different Financial Instruments
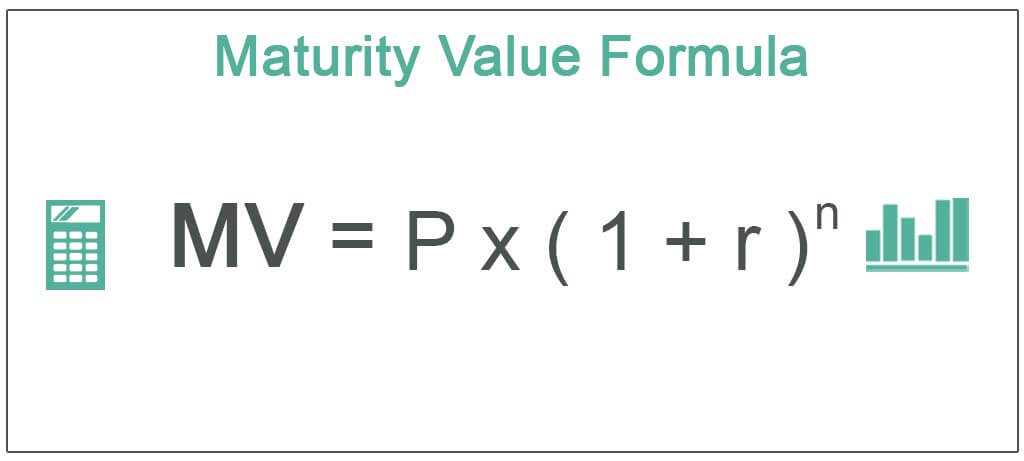
1. Bonds
Bonds are debt instruments issued by governments, municipalities, or corporations to raise capital. They have a fixed maturity date, typically ranging from a few months to several years. For example, a 10-year government bond issued on January 1, 2020, will mature on January 1, 2030. On the maturity date, the bondholder will receive the face value of the bond.
2. Certificates of Deposit (CDs)
CDs are time deposits offered by banks and credit unions. They have a fixed maturity date, which can range from a few months to several years. For instance, a 1-year CD opened on July 1, 2021, will mature on July 1, 2022. Upon maturity, the investor will receive the initial deposit amount plus the accrued interest.
3. Treasury Bills (T-bills)
T-bills are short-term debt instruments issued by the government to finance its operations. They have a maturity date ranging from a few days to one year. For example, a 90-day T-bill issued on September 1, 2021, will mature on November 30, 2021. On the maturity date, the investor will receive the face value of the T-bill.
4. Mortgage Loans
Mortgage loans are long-term loans used to finance the purchase of real estate. They typically have a maturity date of 15, 20, or 30 years. For instance, a 30-year mortgage loan taken out on January 1, 2020, will mature on January 1, 2050. On the maturity date, the borrower will have fully repaid the loan.
5. Options Contracts
Options contracts give the holder the right to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price within a specified period. They have an expiration date, which represents the maturity date of the contract. For example, a call option on a stock expiring on December 31, 2021, will mature on that date. If the option is not exercised by the maturity date, it becomes worthless.
These are just a few examples of maturity dates in different financial instruments. It is essential for investors to be aware of the maturity dates of their investments as it helps them plan their financial goals and manage their cash flows effectively.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
