Liquid Market: Definition, Benefits in Trading, and Examples
A liquid market refers to a financial market where there is a high volume of trading activity and a large number of buyers and sellers. In a liquid market, it is easy to buy or sell an asset without significantly impacting its price. This is because there are enough participants in the market willing to buy or sell at any given time.
There are several benefits of trading in a liquid market:
- Price Stability: In a liquid market, the prices of assets tend to be more stable. This is because there is a constant flow of buyers and sellers, which prevents large price fluctuations. Traders can enter and exit positions without worrying about drastic price changes.
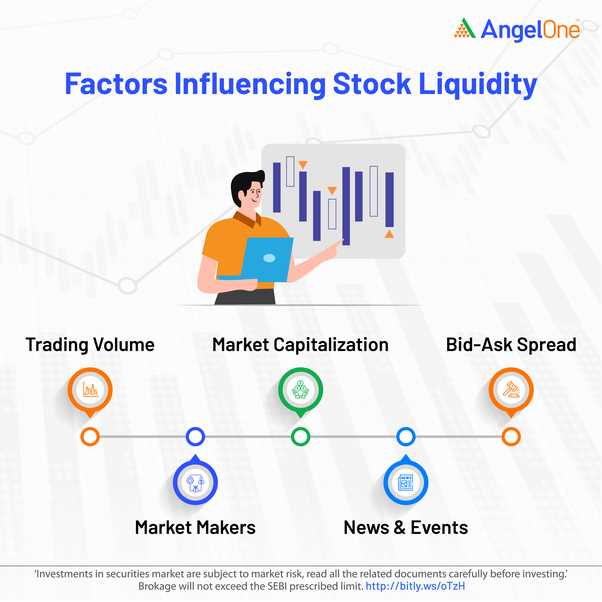
- Tight Bid-Ask Spreads: Bid-ask spreads refer to the difference between the highest price a buyer is willing to pay and the lowest price a seller is willing to accept. In a liquid market, bid-ask spreads are usually narrow, which means traders can buy and sell assets at competitive prices.
- Quick Execution: In a liquid market, orders can be executed quickly. There is a high level of market activity, which ensures that trades are filled promptly. Traders do not have to wait for long periods to buy or sell assets.
- Lower Transaction Costs: Trading in a liquid market often results in lower transaction costs. This is because there is a high level of competition among market participants, including brokers and market makers. As a result, traders can find better pricing and lower fees.
- Access to More Opportunities: In a liquid market, there are more trading opportunities available. Traders can choose from a wide range of assets and easily enter or exit positions. This allows for greater flexibility and the ability to take advantage of market movements.
Examples of liquid markets include major stock exchanges like the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and the NASDAQ. These exchanges have a large number of listed companies and attract a significant amount of trading activity. Other examples include the forex market, where currencies are traded, and the futures market, where contracts for commodities and financial instruments are bought and sold.
What is a Liquid Market?
A liquid market refers to a financial market where there is a high level of trading activity and a large number of participants buying and selling assets. In a liquid market, assets can be easily bought or sold without causing significant price changes. This is because there is a sufficient volume of buyers and sellers, allowing for quick and efficient transactions.
One of the key characteristics of a liquid market is the presence of high trading volumes. This means that there is a large number of transactions occurring on a regular basis. The higher the trading volume, the more liquid the market is considered to be. This is important for traders and investors as it ensures that they can enter and exit positions easily without impacting the market price.
Another important aspect of a liquid market is the tight bid-ask spread. The bid-ask spread refers to the difference between the highest price that a buyer is willing to pay (bid) and the lowest price that a seller is willing to accept (ask). In a liquid market, the bid-ask spread is usually small, indicating that there is a high level of competition among buyers and sellers. This allows traders to execute trades at prices close to the prevailing market price.
Furthermore, a liquid market provides transparency and price discovery. With a large number of participants actively trading, the market price of assets is constantly being updated and reflects the most up-to-date information. This allows traders to make informed decisions based on the current market conditions.
Overall, a liquid market is highly desirable for traders and investors as it offers several benefits. It provides easy entry and exit into positions, tight bid-ask spreads, and transparent price discovery. These factors contribute to increased efficiency and reduced transaction costs, making it easier for market participants to execute trades and manage their portfolios.
Benefits of Trading in a Liquid Market
Trading in a liquid market offers several advantages for investors and traders. Here are some of the key benefits:
1. Ease of buying and selling:
In a liquid market, there is a high level of trading activity, which means that there are always buyers and sellers available. This makes it easy for investors to buy and sell their assets quickly and at a fair price. It also reduces the risk of not being able to find a buyer or seller when needed.
2. Narrow bid-ask spreads:
In a liquid market, the bid-ask spread is usually narrow. The bid-ask spread is the difference between the highest price a buyer is willing to pay (bid) and the lowest price a seller is willing to accept (ask). A narrow bid-ask spread means that there is less cost associated with buying and selling assets, which can increase profitability for traders.
3. Price stability:
In a liquid market, large trading volumes help to stabilize prices. When there are many buyers and sellers, it is less likely that a single large transaction will significantly impact the price of an asset. This reduces the risk of sudden price fluctuations and provides a more stable trading environment.
4. Lower transaction costs:
Due to the high level of trading activity and competition in a liquid market, transaction costs such as brokerage fees and commissions tend to be lower. This can result in cost savings for investors and traders, especially for those who engage in frequent trading.
5. Access to a wide range of assets:
Liquid markets typically offer a wide range of assets for trading, including stocks, bonds, commodities, and currencies. This provides investors with the opportunity to diversify their portfolios and take advantage of different investment opportunities.
6. Efficient price discovery:
In a liquid market, prices are determined based on the forces of supply and demand. The high level of trading activity ensures that prices reflect the most up-to-date information and market conditions. This allows investors to make informed decisions and reduces the risk of overpaying or selling at a disadvantageous price.
Examples of Liquid Markets
There are several examples of liquid markets that exist in the financial world. These markets are characterized by high trading volumes, tight bid-ask spreads, and low transaction costs. Here are some examples:
| Market | Description |
|---|---|
| Foreign Exchange (Forex) Market | The forex market is the largest and most liquid market in the world, with daily trading volumes exceeding $5 trillion. It operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, and involves the buying and selling of currencies. |
| Stock Market | |
| Bond Market | The bond market is a liquid market where investors can buy and sell bonds issued by governments, municipalities, and corporations. It provides a means for these entities to raise capital, and investors can trade bonds to manage their portfolios. |
| Commodity Market | The commodity market is where commodities, such as gold, oil, and agricultural products, are traded. These markets have high liquidity due to the constant demand for these essential goods. Futures contracts are often used to trade commodities. |
| Derivatives Market | The derivatives market is a financial market where derivative instruments, such as options and futures contracts, are traded. These instruments derive their value from an underlying asset, such as stocks or commodities. The derivatives market provides liquidity and allows investors to hedge their risks. |
These are just a few examples of liquid markets, but there are many more in the financial world. The liquidity of these markets allows investors to enter and exit positions easily, ensuring that there is always a buyer or seller available. This liquidity also helps to reduce volatility and spreads, making trading more efficient and cost-effective.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
