Lessor: Definition, Types, Vs Landlord and Lessee
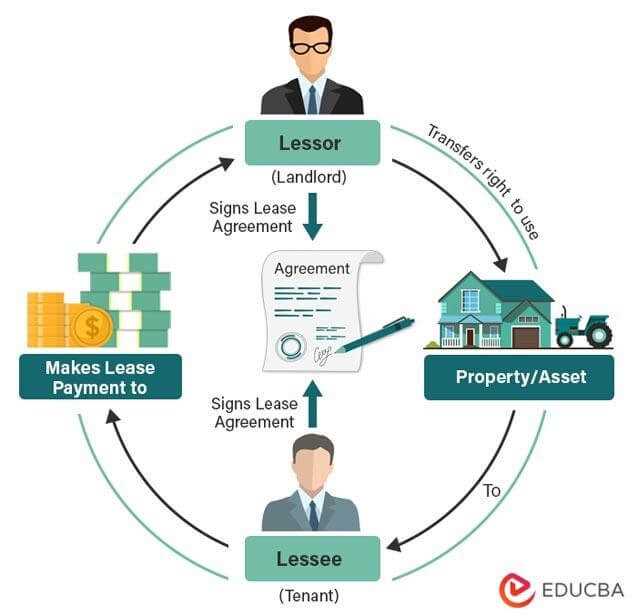
The main difference between a lessor and a landlord is the type of property being leased. A lessor typically refers to someone who leases out personal property, such as vehicles, equipment, or furniture. On the other hand, a landlord usually refers to someone who leases out real property, such as houses, apartments, or commercial buildings.
In addition to the distinction between personal and real property, there are also different types of lessors. Some common types of lessors include:
| Type of Lessor | Description |
|---|---|
| Individual Lessors | Individuals who own and lease out their personal property. |
| Corporate Lessors | Companies or corporations that own and lease out property as part of their business operations. |
| Financial Institutions | Banks or other financial institutions that provide leasing services for various types of property. |
| Government Agencies | Government entities that lease out property for public use or to generate revenue. |
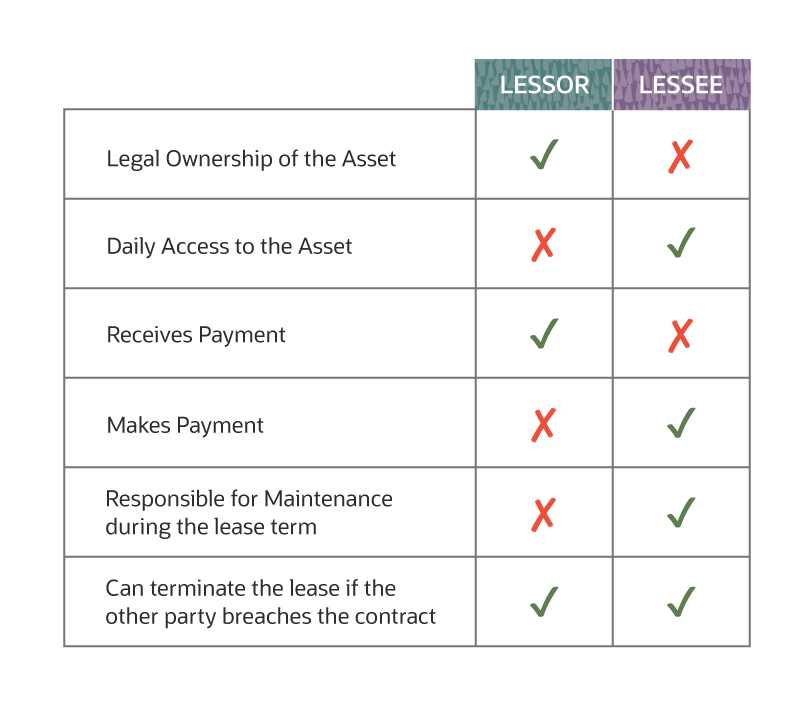
It is important to understand the difference between a lessor and a lessee. While the lessor is the owner of the property, the lessee is the party who rents or leases the property from the lessor. The lessee is responsible for making regular payments to the lessor in exchange for the use of the property.
What is a Lessor?
When entering into a lease agreement, the lessor grants the lessee the right to use the property for a specified period of time. This can range from a few months to several years, depending on the terms of the lease. The lessor retains ownership of the property throughout the duration of the lease.
One of the key responsibilities of a lessor is to provide the lessee with a habitable and safe living or working environment. This includes ensuring that the property is in good condition, making any necessary repairs, and complying with all relevant building codes and regulations.
In addition to maintaining the property, the lessor is also responsible for collecting rent from the lessee. This typically involves setting the rental price, establishing payment terms, and enforcing any late payment penalties or eviction procedures if necessary.
Types of Lessors
1. Individual Lessors
An individual lessor is a person who owns a property and leases it to another party. This can be an individual who owns a single residential property and rents it out to tenants, or it can be an individual who owns multiple properties and operates as a landlord. Individual lessors are responsible for maintaining the property, collecting rent, and addressing any issues that may arise during the lease term.
2. Corporate Lessors
Corporate lessors are companies or organizations that own and lease properties. These can be real estate investment trusts (REITs), property management companies, or corporations that specialize in leasing commercial spaces. Corporate lessors often have a portfolio of properties and may offer additional services such as property management, maintenance, and lease negotiations.
3. Government Lessors
Government lessors include federal, state, and local government entities that own and lease properties. This can include government-owned buildings, office spaces, or land that is leased to private businesses or individuals. Government lessors often have specific regulations and requirements that must be followed by lessees.
4. Financial Institutions
5. Manufacturer Lessors
Manufacturer lessors are companies that produce and lease equipment or machinery. This can include construction equipment, medical devices, or industrial machinery. Manufacturer lessors often have specialized knowledge about the equipment they lease and may offer maintenance and repair services as part of the lease agreement.
Lessor vs Landlord and Lessee
Definition
A landlord, on the other hand, is a more general term that refers to the owner of a property who rents it out. The landlord can be the lessor, but not all lessors are landlords. A landlord can also refer to someone who rents out multiple properties.
The lessee is the individual or entity that rents the property from the lessor. They are responsible for paying rent and adhering to the terms of the lease agreement.
Responsibilities
The landlord, as a broader term, may have additional responsibilities depending on the jurisdiction and the specific rental property. They may be responsible for providing certain amenities, such as utilities or parking spaces, and handling any disputes or issues that arise during the tenancy.
The lessee’s main responsibility is to pay rent on time and take care of the property. They must also comply with the terms of the lease agreement, such as not subleasing the property without permission or not causing damage beyond normal wear and tear.
Key Differences

The main difference between a lessor and a landlord is the level of involvement in the rental property. A lessor can be an individual or entity that owns the property solely for the purpose of leasing it, while a landlord may own multiple properties and have a more extensive rental portfolio.
Another difference is the legal relationship between the parties. The lessor-lessee relationship is established through a lease agreement, which outlines the terms and conditions of the rental. The landlord-tenant relationship, on the other hand, is governed by landlord-tenant laws and regulations, which vary by jurisdiction.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
