In-House: Definition, Meaning in Business, Risks, and Advantages
In-house refers to the practice of conducting business activities or operations within an organization rather than outsourcing them to external parties. It involves utilizing the company’s own resources, such as employees, equipment, and facilities, to perform tasks and functions that would otherwise be delegated to third-party service providers.
Definition
Meaning in Business
In-house operations are commonly found in various areas of business, including but not limited to IT, marketing, human resources, accounting, and legal departments. By keeping these functions in-house, companies can tailor their strategies and processes to their specific needs, maintain confidentiality and security of sensitive information, and have better oversight and control over the quality and timeliness of work.
Risks and Advantages
There are both risks and advantages associated with in-house operations. One of the main risks is the potential increase in costs, as companies need to invest in hiring and training employees, acquiring equipment and technology, and maintaining facilities. Additionally, in-house operations may limit access to specialized expertise and resources available in the external market.
Furthermore, in-house operations can offer greater flexibility and responsiveness to changing business needs. Companies can quickly adapt and make adjustments to their processes and strategies without relying on external providers. This can be particularly beneficial in industries where agility and innovation are crucial for success.
What is In-House?
In-house refers to the practice of conducting business activities or operations within an organization rather than outsourcing them to external parties. It involves utilizing the resources and expertise available within the company to handle various tasks and functions.
When a company chooses to keep certain functions in-house, it means that it has dedicated teams or departments that are responsible for carrying out those specific activities. These can include functions such as accounting, marketing, human resources, IT, legal, and more.
However, in-house operations also come with their own set of challenges. Companies need to invest in infrastructure, technology, and training to support their in-house teams. They need to stay updated with the latest industry trends and regulations to ensure compliance. Additionally, maintaining in-house teams can be more expensive than outsourcing, especially for specialized functions that require highly skilled professionals.
Despite the challenges, many companies choose to keep certain functions in-house because of the advantages it offers. In-house teams provide greater control, flexibility, and customization compared to outsourcing. They can adapt quickly to changing business needs and priorities. In-house operations also allow companies to build and retain internal expertise, which can be a valuable asset in the long run.
The Meaning of In-House in Business
In-house refers to the practice of conducting business activities or operations within an organization, rather than outsourcing them to external parties. It involves utilizing the company’s own resources, such as employees, equipment, and facilities, to perform tasks and functions that would otherwise be contracted out to third-party service providers.
When a company chooses to keep certain functions in-house, it means that it wants to maintain control and have direct oversight over those activities. This can include various departments and functions, such as marketing, accounting, human resources, IT, and customer service. By keeping these functions in-house, companies can ensure that they align with their overall business objectives and maintain a consistent level of quality and service.
Advantages of In-House
- Control: One of the main advantages of in-house operations is the level of control it provides. Companies have full control over the processes, resources, and outcomes, allowing them to make decisions and implement changes more efficiently.
- Cost savings: In some cases, keeping certain functions in-house can be more cost-effective than outsourcing. By utilizing existing resources and expertise, companies can avoid the additional costs associated with hiring external service providers.
- Confidentiality and security: By keeping sensitive information and data in-house, companies can ensure a higher level of confidentiality and security. This is particularly important for industries that deal with sensitive customer information or proprietary data.
- Flexibility and customization: In-house operations allow companies to have more flexibility and customization options. They can tailor their processes and services to meet specific requirements and adapt quickly to changes in the market or customer demands.
Risks of In-House
- Increased costs: While in-house operations can be cost-effective in some cases, they can also lead to increased costs. Companies need to invest in resources, infrastructure, and training to support in-house functions, which can be a significant financial burden.
- Limited expertise: Outsourcing certain functions allows companies to tap into specialized expertise and knowledge that may not be available in-house. By keeping everything in-house, companies may miss out on the benefits of external expertise and innovation.
- Operational challenges: Managing in-house operations can present various operational challenges, such as recruiting and retaining skilled employees, ensuring efficient workflows, and dealing with potential bottlenecks or capacity constraints.
- Reduced scalability: In-house operations may limit a company’s ability to scale rapidly or adjust its capacity based on fluctuating demand. This can be a disadvantage in industries with seasonal or unpredictable market conditions.
Risks and Advantages of In-House
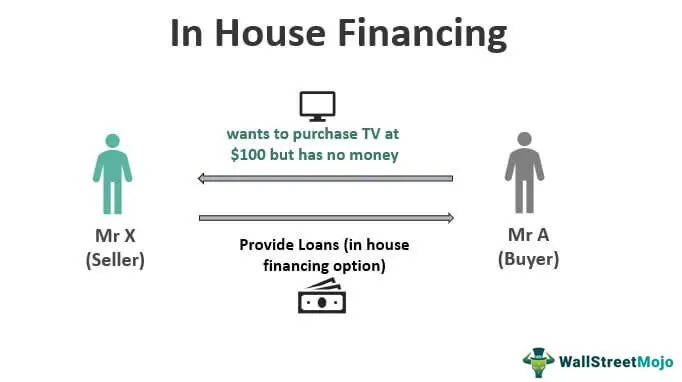
Risks of In-House
One of the main risks of keeping tasks in-house is the potential for increased costs. When a business chooses to handle tasks internally, they are responsible for all associated expenses, including salaries, benefits, and overhead costs. This can be particularly burdensome for small businesses with limited resources.
Another risk of in-house operations is the lack of specialized expertise. Business owners and employees may not have the necessary skills or knowledge to effectively handle certain tasks, leading to subpar results. This can have a negative impact on the overall success of the business.
In-house operations also carry the risk of limited scalability. As a business grows, it may become increasingly difficult to handle all tasks internally. This can lead to bottlenecks, delays, and decreased efficiency. Additionally, if key employees leave the company, there may be a gap in knowledge and expertise that is difficult to fill.
Advantages of In-House
Despite the risks, there are also advantages to keeping tasks in-house. One of the main advantages is increased control and oversight. When a business handles tasks internally, they have direct control over the quality and timeline of the work. This can be particularly important for businesses that prioritize quality control or have strict deadlines.
In-house operations also allow for greater flexibility and customization. Business owners can tailor processes and workflows to fit their specific needs, rather than relying on external providers who may have a one-size-fits-all approach. This can lead to increased efficiency and better alignment with overall business goals.
Another advantage of in-house operations is the potential for increased employee engagement and loyalty. When employees are directly involved in the tasks and processes of the business, they may feel a greater sense of ownership and pride in their work. This can lead to higher levels of motivation and productivity.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
