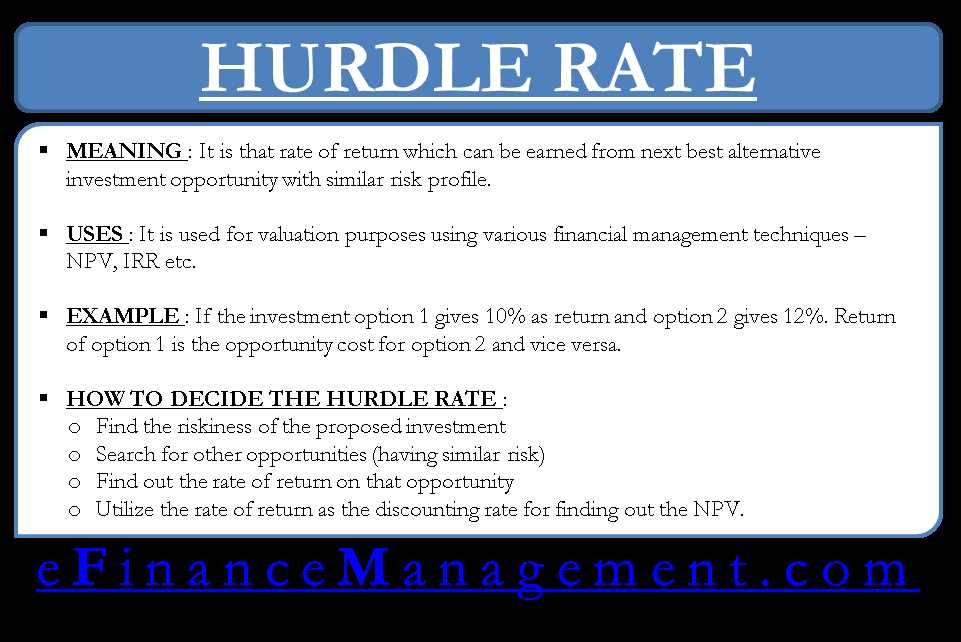
Hurdle Rate: What It Is and Why It Matters
The hurdle rate is a critical concept in finance and investment. It is the minimum rate of return that a project or investment must achieve in order to be considered viable or worthwhile. In other words, it is the benchmark or threshold that determines whether an investment is profitable or not.
Businesses and investors use the hurdle rate to evaluate the potential risks and rewards of different investment opportunities. By comparing the expected return of an investment to the hurdle rate, they can determine whether the investment is likely to generate enough profit to justify the associated risks.
For businesses, the hurdle rate is particularly important when evaluating new projects or expansion opportunities. It helps them assess the financial feasibility of these initiatives and make informed decisions about resource allocation. By comparing the expected cash flows of a project to the hurdle rate, businesses can determine whether the project will generate enough value to cover its costs and generate a return.
Similarly, investors use the hurdle rate to assess the potential return on investment of different assets or securities. It helps them evaluate the risk-reward tradeoff and make investment decisions that align with their financial goals and risk tolerance. By comparing the expected returns of various investment options to the hurdle rate, investors can identify opportunities that offer the most favorable risk-adjusted returns.
The hurdle rate is a critical concept in finance and investment. It is the minimum rate of return that an investment or project must achieve in order to be considered viable or worthwhile. In other words, it is the benchmark or threshold that an investment needs to meet or exceed in order to be considered successful.
The hurdle rate can vary depending on the industry, company, and specific project. It is often higher for riskier investments or projects that require a significant amount of capital. For example, a technology startup may have a higher hurdle rate compared to a stable, established company.
How Businesses Utilize the Hurdle Rate
Businesses utilize the hurdle rate in several ways:
1. Evaluating investment opportunities
One of the primary uses of the hurdle rate is to evaluate potential investment opportunities. When a business is considering investing in a new project or venture, it will compare the expected rate of return of the investment to the hurdle rate. If the expected rate of return is higher than the hurdle rate, the investment is considered viable and may be pursued. On the other hand, if the expected rate of return is lower than the hurdle rate, the investment is deemed unattractive and may be rejected.
2. Setting performance targets
The hurdle rate also serves as a benchmark for setting performance targets within a business. By setting the hurdle rate at a certain level, businesses can establish a minimum level of performance that projects or investments must meet in order to be considered successful. This helps businesses prioritize and allocate resources to projects that have the potential to generate returns above the hurdle rate.
3. Assessing risk
Investors and the Hurdle Rate
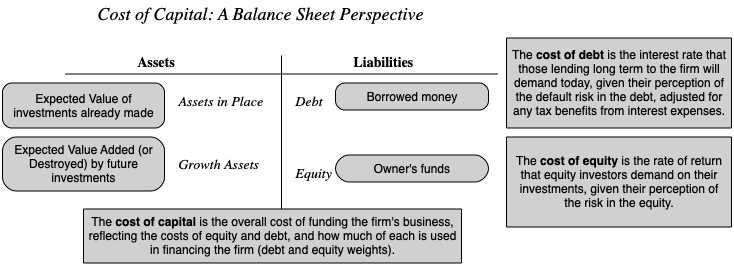
Investors play a crucial role in determining the hurdle rate for a business. The hurdle rate represents the minimum rate of return that investors expect to receive on their investment. It serves as a benchmark for evaluating the attractiveness of an investment opportunity.
When considering whether to invest in a particular business or project, investors compare the expected rate of return with the hurdle rate. If the expected rate of return is higher than the hurdle rate, the investment is considered attractive and may be pursued. On the other hand, if the expected rate of return is lower than the hurdle rate, the investment is deemed unattractive and may be rejected.
The hurdle rate is influenced by various factors, including the level of risk associated with the investment. Higher-risk investments typically require a higher hurdle rate to compensate investors for taking on additional risk. Conversely, lower-risk investments may have a lower hurdle rate.
Investors also consider the time value of money when determining the hurdle rate. The time value of money recognizes that a dollar received in the future is worth less than a dollar received today. Therefore, investors expect a higher rate of return to account for the delay in receiving their investment.
The hurdle rate can vary among different investors based on their individual risk tolerance and investment objectives. Some investors may have a higher hurdle rate due to a preference for higher-risk investments, while others may have a lower hurdle rate if they prioritize stability and lower risk.
Investors utilize the hurdle rate to make informed investment decisions. By comparing the expected rate of return with the hurdle rate, investors can assess the risk and potential reward of an investment opportunity. This analysis helps investors allocate their capital efficiently and maximize their returns.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
