Funds From Operations (FFO): A Key Measure for Assessing REIT Performance
What is Funds From Operations (FFO)?
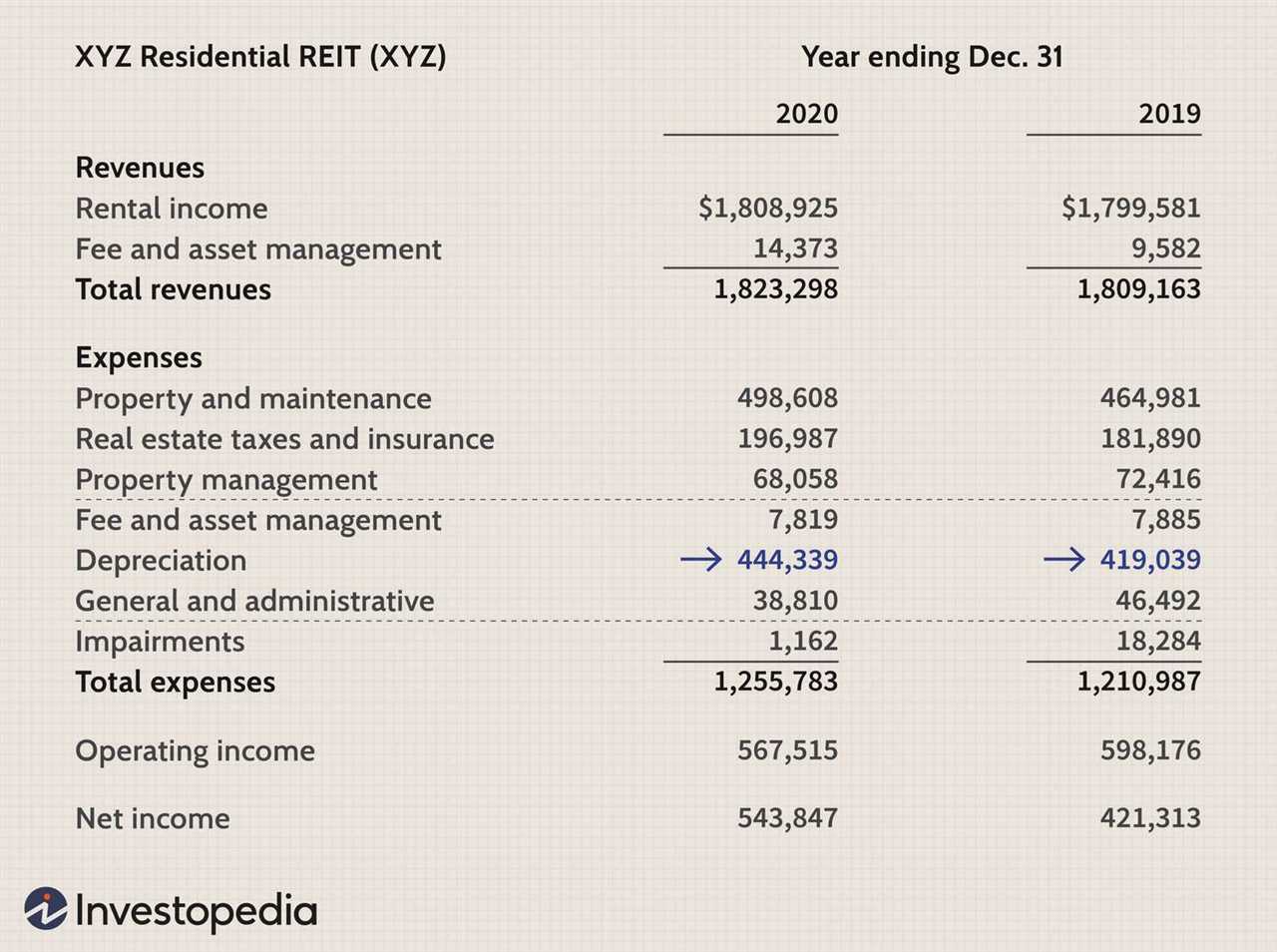
FFO is a measure that represents the cash flow generated by a REIT’s core operations. It is calculated by adding depreciation and amortization expenses, as well as any gains or losses from the sale of properties, to the net income of the REIT. FFO excludes non-cash items such as gains or losses from the sale of investments and non-operating income or expenses.
Why is FFO important for evaluating REIT performance?
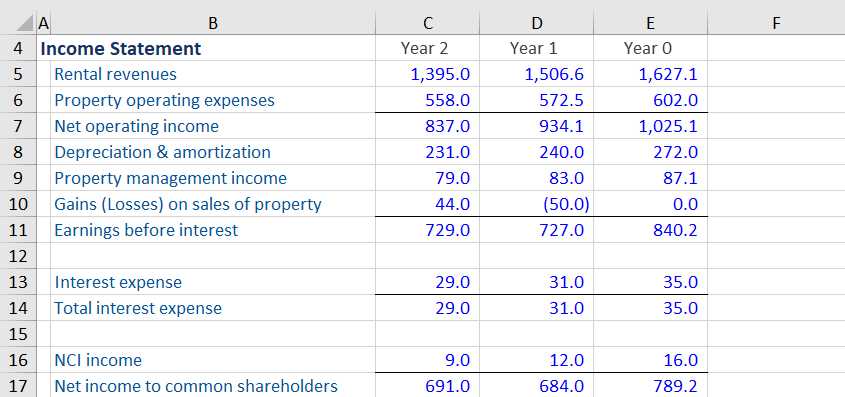
By focusing on FFO, investors can better assess a REIT’s ability to generate sustainable cash flow from its operations. This is particularly important in the real estate industry, where cash flow is a crucial factor in determining the value and profitability of properties.
Furthermore, FFO allows investors to compare the performance of different REITs more effectively. Since FFO is a standardized measure, it provides a consistent basis for evaluating REITs across different property types and geographic locations.
Conclusion
Funds From Operations (FFO) is a key financial metric used to evaluate the performance of Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs). It provides a measure of the cash flow generated by a REIT’s core operations, excluding certain non-cash items and one-time expenses.
Calculation of FFO
FFO is calculated by adding depreciation and amortization expenses, as well as any impairment charges, to the net income of a REIT. It also subtracts any gains from the sale of properties. The formula for calculating FFO is as follows:
This calculation provides a more accurate representation of a REIT’s cash flow because it takes into account the non-cash expenses associated with owning and operating real estate properties. By excluding these non-cash items, FFO provides a clearer picture of the cash generated by a REIT’s core operations.
Importance of FFO
FFO is an important metric for investors and analysts when evaluating the performance of REITs. It allows them to assess the cash flow generated by a REIT’s properties and determine its ability to distribute dividends to shareholders. Since REITs are required to distribute a significant portion of their taxable income to shareholders, FFO is a key indicator of a REIT’s ability to generate consistent and sustainable income.
Additionally, FFO is often used to compare the performance of different REITs within the same sector. By calculating FFO per share, investors can compare the cash flow generated by each share of a REIT’s stock and make informed investment decisions.
Importance of FFO in Evaluating REIT Performance

Unlike net income, which is calculated based on generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) and includes non-cash items such as depreciation and amortization, FFO focuses on the cash flow generated by a REIT’s core operations. This makes it a more accurate measure of the REIT’s ability to generate cash and distribute dividends to its shareholders.
By excluding non-cash items, FFO eliminates the impact of accounting conventions that can distort a REIT’s earnings. For example, depreciation is a non-cash expense that reduces net income but does not affect a REIT’s ability to generate cash. By adding back depreciation to net income, FFO provides a more realistic view of the REIT’s cash flow.
Furthermore, FFO also takes into account certain expenses that are not included in net income, such as gains or losses from the sale of properties and impairments. These items can have a significant impact on a REIT’s financial performance and should be considered when evaluating its overall profitability.
Investors and analysts use FFO as a key measure to assess the sustainability of a REIT’s dividend payments. Since REITs are required to distribute a significant portion of their taxable income to shareholders in the form of dividends, it is crucial to evaluate whether the REIT’s cash flow is sufficient to support these distributions. FFO provides a more accurate measure of the REIT’s cash flow available for distribution compared to net income.
Additionally, FFO is also used to compare the performance of different REITs within the same sector. By looking at the FFO per share, investors can determine which REITs are generating higher cash flows relative to their share price. This can help identify REITs that may be undervalued or overvalued in the market.
| Benefits of FFO in evaluating REIT performance: |
|---|
| 1. Provides a clearer picture of a REIT’s financial health and profitability |
| 2. Eliminates the impact of non-cash items on earnings |
| 3. Takes into account certain expenses not included in net income |
| 4. Assesses the sustainability of dividend payments |
| 5. Allows for comparison of different REITs within the same sector |

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
