Fixed-Income Security: Definition, Types, and Examples
A fixed-income security is a type of investment that provides a fixed return to the investor over a specified period of time. These securities are typically issued by governments, municipalities, corporations, and other entities to raise capital.
There are several types of fixed-income securities, each with its own characteristics and risk profiles. The most common types include:
4. Corporate Bonds: Corporate bonds are issued by corporations to raise capital for various purposes, such as expansion or acquisitions. They offer higher yields compared to government and municipal bonds, but also carry a higher level of risk.
5. Mortgage-Backed Securities: Mortgage-backed securities (MBS) are created by pooling together a group of mortgages and selling them to investors. These securities provide a stream of income based on the principal and interest payments from the underlying mortgages.
6. Asset-Backed Securities: Asset-backed securities (ABS) are created by pooling together various types of assets, such as auto loans, credit card receivables, or student loans. These securities provide a stream of income based on the cash flows generated by the underlying assets.
These are just a few examples of fixed-income securities, and there are many other types available in the market. Investors choose fixed-income securities for their stable income streams and relatively lower risk compared to other types of investments.
What is a Fixed-Income Security?
A fixed-income security is a type of investment that provides a fixed return to the investor over a specific period of time. It is a debt instrument issued by a government, corporation, or other entity to raise capital. Fixed-income securities are considered less risky than stocks because they offer a guaranteed income stream and the return of principal at maturity.
Characteristics of Fixed-Income Securities:
- Fixed Interest Rate: Fixed-income securities have a predetermined interest rate that remains constant throughout the life of the investment. This allows investors to know exactly how much income they will receive.
- Fixed Maturity Date: These securities have a specific maturity date, which is the date when the issuer will repay the principal amount to the investor.
- Regular Income Payments: Investors receive regular interest payments, usually on a monthly, quarterly, or annual basis, depending on the terms of the security.
- Low Risk: Fixed-income securities are generally considered low-risk investments because they provide a predictable income stream and the return of principal at maturity.
Types of Fixed-Income Securities:
There are several types of fixed-income securities, including:
- Bonds: Bonds are debt securities issued by governments, municipalities, and corporations. They have a fixed interest rate and maturity date.
- Treasury Securities: Treasury securities are issued by the government to finance its operations. They include Treasury bills, notes, and bonds.
- Certificates of Deposit (CDs): CDs are time deposits offered by banks and financial institutions. They have a fixed interest rate and maturity date.
- Mortgage-Backed Securities (MBS): MBS are securities backed by a pool of mortgage loans. They provide investors with a share of the interest and principal payments from the underlying mortgages.
These are just a few examples of fixed-income securities, and there are many other types available in the market.
Types of Fixed-Income Securities
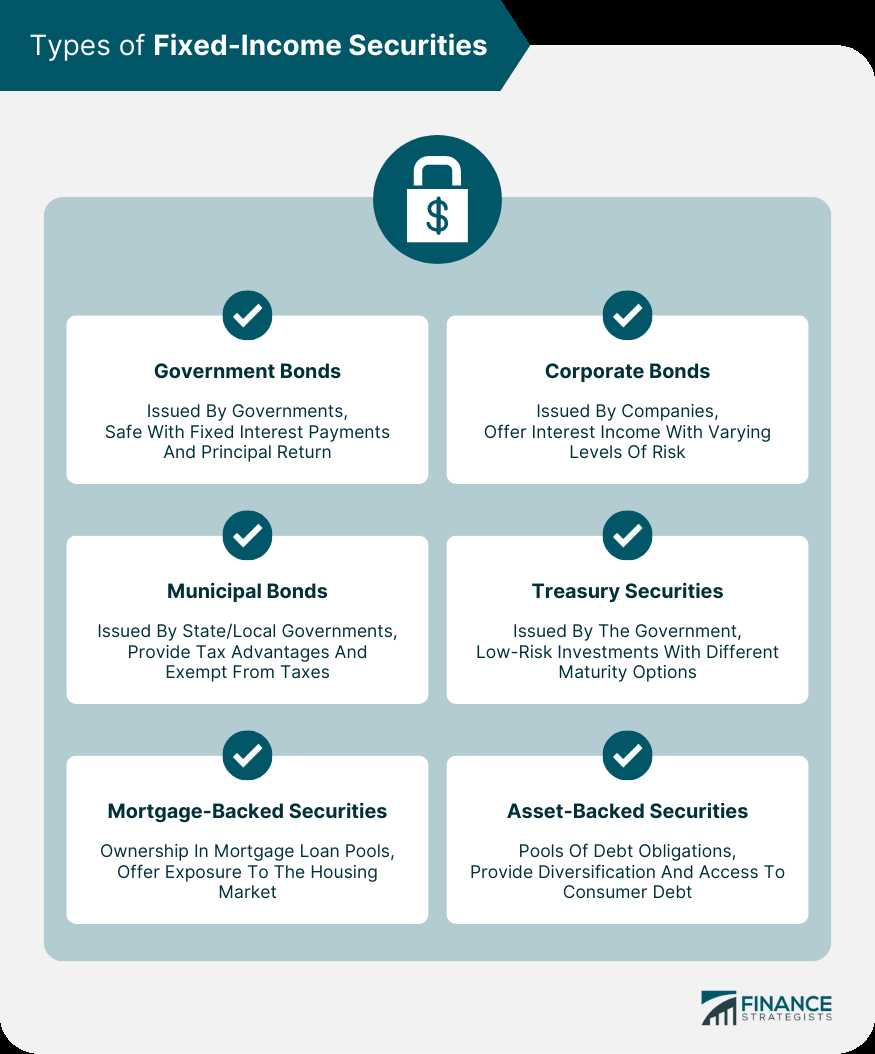
Fixed-income securities are a type of investment that provide a fixed return to the investor over a specified period of time. These securities are typically issued by governments, corporations, and other entities to raise capital. There are several types of fixed-income securities, each with its own characteristics and risk profile. Here are some of the most common types:
- Treasury Bonds: These are long-term debt securities issued by the government. They have a maturity period of 10 years or more and are considered to be one of the safest investments.
- Corporate Bonds: These are debt securities issued by corporations to raise capital. They have a fixed interest rate and maturity period, and their risk level depends on the creditworthiness of the issuing company.
- Municipal Bonds: These are debt securities issued by state and local governments to finance public projects. They are exempt from federal taxes and can provide a tax-free income to investors.
- Government Agency Bonds: These are debt securities issued by government-sponsored agencies, such as Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac. They have a lower risk compared to corporate bonds and offer a slightly higher yield than Treasury bonds.
- Certificates of Deposit (CDs): These are time deposits offered by banks and other financial institutions. They have a fixed interest rate and maturity period, and the investor receives the principal and interest at the end of the term.
- Asset-backed Securities: These are securities backed by a pool of assets, such as mortgages or car loans. They offer a fixed income stream and are typically rated by credit rating agencies.
- Preferred Stocks: These are equity securities that have characteristics of both stocks and bonds. They offer a fixed dividend payment and have a higher claim on assets compared to common stocks.
These are just a few examples of the types of fixed-income securities available in the market. Each type has its own advantages and risks, and investors should carefully consider their investment goals and risk tolerance before investing in any particular security.
Examples of Fixed-Income Securities

2. Corporate Bonds: These are debt securities issued by corporations to raise capital for various purposes, such as expanding operations or funding new projects. Corporate bonds have different interest rates and maturity dates, depending on the creditworthiness of the issuing company. They offer higher yields compared to government bonds but also carry higher risks.
4. Mortgage-Backed Securities: These are debt securities that represent an ownership interest in a pool of mortgage loans. Mortgage-backed securities provide investors with regular interest payments based on the interest and principal payments made by homeowners. They can be issued by government-sponsored entities like Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac or private financial institutions.
6. Preferred Stocks: While not technically fixed-income securities, preferred stocks have characteristics of both stocks and bonds. Preferred stockholders receive fixed dividend payments, similar to coupon payments, before common stockholders. They have no maturity date but can be redeemed by the issuing company at a predetermined price.
These are just a few examples of the many types of fixed-income securities available in the market. Each type has its own risk and return profile, and investors should carefully consider their investment objectives and risk tolerance before investing in any fixed-income security.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
